ASTR 1120-001 Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
... If you measured the velocities of many galaxies, you would find that typically: (a) Galaxies (except very nearby ones) were moving away from you, with the most distant ones moving away the slowest (b) Galaxies are moving toward you, with the most distant ones approaching the most rapidly (c) Galaxie ...
... If you measured the velocities of many galaxies, you would find that typically: (a) Galaxies (except very nearby ones) were moving away from you, with the most distant ones moving away the slowest (b) Galaxies are moving toward you, with the most distant ones approaching the most rapidly (c) Galaxie ...
Dark Matter -24-------------------------------~-----------R-E-S-O-N-A-N-C
... Rotation curves of external galaxies were first observed on a large scale in the late sixties, using spectral lines from stars. A feature common to all galaxies was that their rotation curves rose more or less linearly with r for small values of r, and then remained almost perfectly flat, i,.e. v re ...
... Rotation curves of external galaxies were first observed on a large scale in the late sixties, using spectral lines from stars. A feature common to all galaxies was that their rotation curves rose more or less linearly with r for small values of r, and then remained almost perfectly flat, i,.e. v re ...
EvoluGon of high mass stars Solar-‐type stars end their lives by
... This energy loss can be compensated for by increasing the rate of fusion reac=ons, un=l an Fe core is formed. The only way in which internal energy can be generated in this core is for grav ...
... This energy loss can be compensated for by increasing the rate of fusion reac=ons, un=l an Fe core is formed. The only way in which internal energy can be generated in this core is for grav ...
What`s Brewing in the Teapot - Indiana University Astronomy
... universe. Events that occur within the event horizon can have no influence on our observable universe. • Schwarzschild Radius – A measure of the size of the event horizon of a black hole. ...
... universe. Events that occur within the event horizon can have no influence on our observable universe. • Schwarzschild Radius – A measure of the size of the event horizon of a black hole. ...
galaxies2_3_complete
... Interactions with lower approach velocities may lead to a merger – possibly after an elaborate ‘courtship’ Final appearance of galaxies depends on mass and speed of the perturber, and orientation during interaction. Close passage of two gas-rich spirals can produce a Starburst galaxy: * disk g ...
... Interactions with lower approach velocities may lead to a merger – possibly after an elaborate ‘courtship’ Final appearance of galaxies depends on mass and speed of the perturber, and orientation during interaction. Close passage of two gas-rich spirals can produce a Starburst galaxy: * disk g ...
astrocoursespring2012lec5-1-1
... appear smaller and fainter. When a telescope probes about 5 billion light years into look-back time, it can detect only the brightest galaxies, giant, elliptical galaxies – because spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way are too dim to be seen at that distance ...
... appear smaller and fainter. When a telescope probes about 5 billion light years into look-back time, it can detect only the brightest galaxies, giant, elliptical galaxies – because spiral galaxies similar to the Milky Way are too dim to be seen at that distance ...
Galaxies, Cosmology and the Accelera`ng Universe
... • The central black hole blasts out large amounts of ...
... • The central black hole blasts out large amounts of ...
Galaxies * Island universes
... into a thin disk A Galaxy’s color evolves from bluer, towards redder as stellar population ages, young blue stars die out Galaxy collisions common because they’re usually only 100 or fewer galaxy diameters apart Collisions between galaxies produce irregulars which settle into ellipticals More massiv ...
... into a thin disk A Galaxy’s color evolves from bluer, towards redder as stellar population ages, young blue stars die out Galaxy collisions common because they’re usually only 100 or fewer galaxy diameters apart Collisions between galaxies produce irregulars which settle into ellipticals More massiv ...
Word version - GyVe
... Galaxies can be placed into groups that are distinctly colored. When loading a galaxy position file, all galaxies from that file are loaded into a distinct group. Loading multiple galaxy position files will result in each file getting loading into its own distinct group. To assign galaxies to a diff ...
... Galaxies can be placed into groups that are distinctly colored. When loading a galaxy position file, all galaxies from that file are loaded into a distinct group. Loading multiple galaxy position files will result in each file getting loading into its own distinct group. To assign galaxies to a diff ...
2P24.pdf
... UCM0043-0159 is a Sc+ galaxy where recent star formation is taking place simultaneously in the nucleus and in several bursts placed in the spiral arms. The global burst strength is small (0.5%). Thanks to the IFU spectroscopy, we can perform a stellar populations analysis for every knot. In this way ...
... UCM0043-0159 is a Sc+ galaxy where recent star formation is taking place simultaneously in the nucleus and in several bursts placed in the spiral arms. The global burst strength is small (0.5%). Thanks to the IFU spectroscopy, we can perform a stellar populations analysis for every knot. In this way ...
PH607 – Galaxies
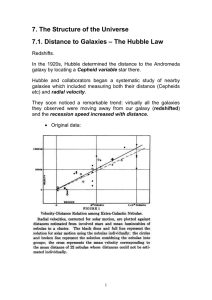
... Hubble and collaborators began a systematic study of nearby galaxies which included measuring both their distance (Cepheids etc) and radial velocity. They soon noticed a remarkable trend: virtually all the galaxies they observed were moving away from our galaxy (redshifted) and the recession speed i ...
... Hubble and collaborators began a systematic study of nearby galaxies which included measuring both their distance (Cepheids etc) and radial velocity. They soon noticed a remarkable trend: virtually all the galaxies they observed were moving away from our galaxy (redshifted) and the recession speed i ...
Messier 87

Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, and generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. One of the most massive galaxies in the local universe, it is notable for its large population of globular clusters—M87 contains about 12,000 compared to the 150-200 orbiting the Milky Way—and its jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends outward at least 1,500 parsecs (4,900 light-years), travelling at relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and is a popular target for both amateur astronomy observations and professional astronomy study.French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, cataloguing it as a nebulous feature while searching for objects that would confuse comet hunters. The second brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, M87 is located about 16.4 million parsecs (53.5 million light-years) from Earth. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive dust lanes. Instead, it has an almost featureless, ellipsoidal shape typical of most giant elliptical galaxies, diminishing in luminosity with distance from the centre. Forming around one sixth of M87's mass, the stars in this galaxy have a nearly spherically symmetric distribution, their density decreasing with increasing distance from the core. At the core is a supermassive black hole, which forms the primary component of an active galactic nucleus. This object is a strong source of multiwavelength radiation, particularly radio waves. M87's galactic envelope extends out to a radius of about 150 kiloparsecs (490,000 light-years), where it has been truncated—possibly by an encounter with another galaxy. Between the stars is a diffuse interstellar medium of gas that has been chemically enriched by elements emitted from evolved stars.