Student Reading
... Galaxies have been divided into three basic shapes: elliptical, spiral, and irregular. Elliptical galaxies appear smooth and featureless. They can be baseball-shaped to football-shaped. Spiral galaxies are pinwheel-shaped disks with two or more “arms” winding out from a central bulge. These arms var ...
... Galaxies have been divided into three basic shapes: elliptical, spiral, and irregular. Elliptical galaxies appear smooth and featureless. They can be baseball-shaped to football-shaped. Spiral galaxies are pinwheel-shaped disks with two or more “arms” winding out from a central bulge. These arms var ...
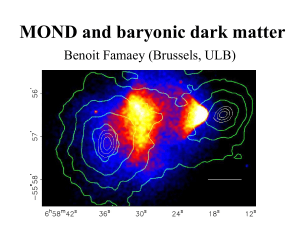
MOND as an alternative to dark matter: the Bullet
... of the vector field (zero in static systems) Acts as as a source term => plays the role of dark matter! • Matter power spectrum ok without DM (Dodelson & Liguori 2006), but IN THE PRESENT MODEL needs DM in the form of e.g. 2eV neutrinos to fit the angular power spectrum of the CMB, in order not to c ...
... of the vector field (zero in static systems) Acts as as a source term => plays the role of dark matter! • Matter power spectrum ok without DM (Dodelson & Liguori 2006), but IN THE PRESENT MODEL needs DM in the form of e.g. 2eV neutrinos to fit the angular power spectrum of the CMB, in order not to c ...
Formation of Globular Clusters: In and Out of Dwarf Galaxies
... progenitor galaxies at intermediate redshifts • Model explains observed sizes, masses, ages, metallicities • Dynamical evolution explains the present mass function and may be important for metallicity bimodality • Red clusters in the Galaxy are due to massive late gas-rich mergers • Blue clusters ar ...
... progenitor galaxies at intermediate redshifts • Model explains observed sizes, masses, ages, metallicities • Dynamical evolution explains the present mass function and may be important for metallicity bimodality • Red clusters in the Galaxy are due to massive late gas-rich mergers • Blue clusters ar ...
Expansion of the Universe
... us. The velocity of the moving body is measured using the Doppler Effect or spectral line shift. The distance is more difficult to measure. It is measured by its apparent angular size or brightness of objects. Using observable evidence Hubble Law tells us that our Universe is expanding. We observe g ...
... us. The velocity of the moving body is measured using the Doppler Effect or spectral line shift. The distance is more difficult to measure. It is measured by its apparent angular size or brightness of objects. Using observable evidence Hubble Law tells us that our Universe is expanding. We observe g ...
The Extragalactic Distance Database: Color–Magnitude Diagrams
... footprint of the observations used in our analysis is highlighted in yellow. The red boxes represent the footprint of another ACS observation of the galaxy. Footprints of observations other than those used for the production of the galaxy’s CMD often appear in these images, but those that are used a ...
... footprint of the observations used in our analysis is highlighted in yellow. The red boxes represent the footprint of another ACS observation of the galaxy. Footprints of observations other than those used for the production of the galaxy’s CMD often appear in these images, but those that are used a ...
Small Wonders: Andromeda
... perhaps it's best known for being one of the keystones in resolving the Island Universe debate (are there many galaxies or just one?) , and determining interstellar distances by the use of Cepheid variables. At the turn of the century, astronomers questions if the spiral nebula like M31 were ...
... perhaps it's best known for being one of the keystones in resolving the Island Universe debate (are there many galaxies or just one?) , and determining interstellar distances by the use of Cepheid variables. At the turn of the century, astronomers questions if the spiral nebula like M31 were ...
Galaxy Formation, Reionization, the First Stars and Quasars
... • Photodissociation of H2 in accreting gas reduces cooling rate • Ly-alpha pressure can reverse infall in polar regions at 20-30 Msun • Expansion of HII regions can reduce accretion rate at 50-100 Msun • Photoevaporation-driven mass loss from the disk stops accretion and fixes the mass of the st ...
... • Photodissociation of H2 in accreting gas reduces cooling rate • Ly-alpha pressure can reverse infall in polar regions at 20-30 Msun • Expansion of HII regions can reduce accretion rate at 50-100 Msun • Photoevaporation-driven mass loss from the disk stops accretion and fixes the mass of the st ...
Determination of spiral orbits with constant tangential velocity
... The green line shows the expected speed according to Newton, which decreases towards the outside, and the gray-dashed line the decrease very close to the center. Near to the center, the measured velocity agrees really well with the calculation. However, for greater distances from the center a surpri ...
... The green line shows the expected speed according to Newton, which decreases towards the outside, and the gray-dashed line the decrease very close to the center. Near to the center, the measured velocity agrees really well with the calculation. However, for greater distances from the center a surpri ...
What kind of stuff
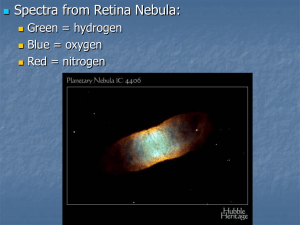
... Spiral galaxies have young stars • Emission lines arise from gas “ionized” by very energetic radiation • Such high energy radiation is NOT produced by cold old stars, implying that very young stars (10 million years old) are present. • They also contain vast amounts of gas and dust ...
... Spiral galaxies have young stars • Emission lines arise from gas “ionized” by very energetic radiation • Such high energy radiation is NOT produced by cold old stars, implying that very young stars (10 million years old) are present. • They also contain vast amounts of gas and dust ...
–1– 2. Milky Way We know a great deal, perhaps more than any
... • Oort (∼ 1927) completed the picture. In this picture the high velocity stars and globular clusters form a different population (so called halo population, or pop II). They do not follow the Galactic rotation, and their spherical distributions are caused by their large random motions. In contrast, ...
... • Oort (∼ 1927) completed the picture. In this picture the high velocity stars and globular clusters form a different population (so called halo population, or pop II). They do not follow the Galactic rotation, and their spherical distributions are caused by their large random motions. In contrast, ...
Messier 87

Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, and generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. One of the most massive galaxies in the local universe, it is notable for its large population of globular clusters—M87 contains about 12,000 compared to the 150-200 orbiting the Milky Way—and its jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends outward at least 1,500 parsecs (4,900 light-years), travelling at relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and is a popular target for both amateur astronomy observations and professional astronomy study.French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, cataloguing it as a nebulous feature while searching for objects that would confuse comet hunters. The second brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, M87 is located about 16.4 million parsecs (53.5 million light-years) from Earth. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive dust lanes. Instead, it has an almost featureless, ellipsoidal shape typical of most giant elliptical galaxies, diminishing in luminosity with distance from the centre. Forming around one sixth of M87's mass, the stars in this galaxy have a nearly spherically symmetric distribution, their density decreasing with increasing distance from the core. At the core is a supermassive black hole, which forms the primary component of an active galactic nucleus. This object is a strong source of multiwavelength radiation, particularly radio waves. M87's galactic envelope extends out to a radius of about 150 kiloparsecs (490,000 light-years), where it has been truncated—possibly by an encounter with another galaxy. Between the stars is a diffuse interstellar medium of gas that has been chemically enriched by elements emitted from evolved stars.