Measuring the mass of galaxies Luminous matter in a
... Measuring the mass of galaxies Luminous matter in a galaxy: • stars (of different masses) • gas (mostly hydrogen) Can detect these directly using optical and radio telescopes - get an estimate of how much mass they contain BUT… also non-luminous matter which we can’t see directly. Example that we kn ...
... Measuring the mass of galaxies Luminous matter in a galaxy: • stars (of different masses) • gas (mostly hydrogen) Can detect these directly using optical and radio telescopes - get an estimate of how much mass they contain BUT… also non-luminous matter which we can’t see directly. Example that we kn ...
PROBLEM SET #9 SOLUTIONS AST142 1. Quasar luminosity
... is accreting at the Eddington rate, and show that these two findings are consistent with one another. ...
... is accreting at the Eddington rate, and show that these two findings are consistent with one another. ...
Nucleosynthesis and Energy Production in Stars: Bethe`s Crowning
... solar energy were generated due to the burning of carbon, then all of it would burn up in only about fifteen hundred years. This follows from the following considerations: burning or oxidation is a chemical process that leads to the release of energy by rearrangement of chernical bonds. The burning ...
... solar energy were generated due to the burning of carbon, then all of it would burn up in only about fifteen hundred years. This follows from the following considerations: burning or oxidation is a chemical process that leads to the release of energy by rearrangement of chernical bonds. The burning ...
Intro to Spectroscopy
... in the red part of the spectrum when an electron moves from Level 3 to Level 2. This allows us to see light produced at a particular temperature in the photosphere (surface) of the Sun. ...
... in the red part of the spectrum when an electron moves from Level 3 to Level 2. This allows us to see light produced at a particular temperature in the photosphere (surface) of the Sun. ...
Word - El Camino College
... While this is fantastic, it still leaves us semi-evolved apes dissatisfied: we want to see something! Those detections come about as plots of sine waves and wiggly lines. I wanna see a planet! Heehee. Now I can. This is so cool! OK, I got distracted there. Back to the story. There has been somethin ...
... While this is fantastic, it still leaves us semi-evolved apes dissatisfied: we want to see something! Those detections come about as plots of sine waves and wiggly lines. I wanna see a planet! Heehee. Now I can. This is so cool! OK, I got distracted there. Back to the story. There has been somethin ...
Fingerprints in Sunlight - VCI
... in the red part of the spectrum when an electron moves from Level 3 to Level 2. This allows us to see light produced at a particular temperature in the photosphere (surface) of the Sun. ...
... in the red part of the spectrum when an electron moves from Level 3 to Level 2. This allows us to see light produced at a particular temperature in the photosphere (surface) of the Sun. ...
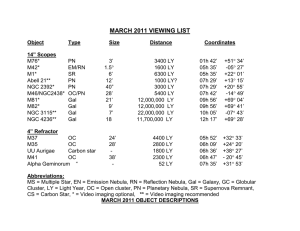
March
... M76 in the constellation Perseus (PURR-see-us) is commonly known as the Butterfly or the Little Dumbbell Nebula. It is a standard planetary nebula with a 16th magnitude central star. The unusual appearance is due to the angle of the nebular ring that is expanding outward from the white dwarf at abo ...
... M76 in the constellation Perseus (PURR-see-us) is commonly known as the Butterfly or the Little Dumbbell Nebula. It is a standard planetary nebula with a 16th magnitude central star. The unusual appearance is due to the angle of the nebular ring that is expanding outward from the white dwarf at abo ...
May 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer than these three but they are phases every 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes, 3 seconds. too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It is 2,160 miles in diameter and averages 239,000 miles from Earth. A New Moon is not visible in the ...
... Starting from New Moon, the Moon cycles through are several stars closer than these three but they are phases every 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes, 3 seconds. too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It is 2,160 miles in diameter and averages 239,000 miles from Earth. A New Moon is not visible in the ...
Origin of the Elements
... the helium begins fusing into carbon (C) at its core, but hydrogen continues to form helium in a thin ...
... the helium begins fusing into carbon (C) at its core, but hydrogen continues to form helium in a thin ...
arXiv:0712.2297v1 [astro
... confirm the intrinsic RV jitter of red giants with the maximum of its distribution at about 20 m s−1 . Furthermore, the RV scatter increases with B-V, easily reaching 100 m s−1 for stars later than K5. Clearly, more observations are needed to understand the nature of the scatter, part of which may b ...
... confirm the intrinsic RV jitter of red giants with the maximum of its distribution at about 20 m s−1 . Furthermore, the RV scatter increases with B-V, easily reaching 100 m s−1 for stars later than K5. Clearly, more observations are needed to understand the nature of the scatter, part of which may b ...
11.3 Measuring Distances in Space
... The distance to a far away object can be determined by measuring two angles and the distance between those two angles. A line (called a baseline) is laid out and angle measurements are taken at the baseline endpoints to the distant object. Geometry and Trigonometry are then used to determine the per ...
... The distance to a far away object can be determined by measuring two angles and the distance between those two angles. A line (called a baseline) is laid out and angle measurements are taken at the baseline endpoints to the distant object. Geometry and Trigonometry are then used to determine the per ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... ordinary matter, is composed of hot gas between galaxies, and in some places that gas has been seen in X-rays. A new technique has been used to observe more of that hot gas. Chandra and XMM-Newton (orbiting X-ray observatories) have been used to observe some distant (2 billion light-years) quasars a ...
... ordinary matter, is composed of hot gas between galaxies, and in some places that gas has been seen in X-rays. A new technique has been used to observe more of that hot gas. Chandra and XMM-Newton (orbiting X-ray observatories) have been used to observe some distant (2 billion light-years) quasars a ...
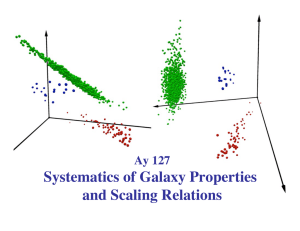
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... completely different family of objects from normal ellipticals they are not just small E’s ...
... completely different family of objects from normal ellipticals they are not just small E’s ...
Observational Constraints The Nebular Hypothesis
... 1. Small dust grains grow into larger—but still relatively small—asteroid-like bodies called planetesimals. 2. Planetesimals repeated crash into each other, resulting in increasingly large planetesimals. Some of these objects grow large enough to be called protoplanets. 3. As the protoplanets grow t ...
... 1. Small dust grains grow into larger—but still relatively small—asteroid-like bodies called planetesimals. 2. Planetesimals repeated crash into each other, resulting in increasingly large planetesimals. Some of these objects grow large enough to be called protoplanets. 3. As the protoplanets grow t ...
The SUN
... The temperature of the sun is 15,600,000 k and 9,900 f on the surface The element helium was named after the sun. The sun is about 70% hydrogen and 28% helium, the other 2% is metals. Solar winds travel through the solar system at 450 km/sec. The Northern Lights are caused by the sun’s flares. The s ...
... The temperature of the sun is 15,600,000 k and 9,900 f on the surface The element helium was named after the sun. The sun is about 70% hydrogen and 28% helium, the other 2% is metals. Solar winds travel through the solar system at 450 km/sec. The Northern Lights are caused by the sun’s flares. The s ...
Constellations, Star Names, and Magnitudes
... The stars appear to circle around the North Celestial Pole (near Polaris) once in 24 hours. Stars within the angle of the observer's latitude away from the North Celestial Pole never rise or set. They are always above the horizon (circumpolar stars). ...
... The stars appear to circle around the North Celestial Pole (near Polaris) once in 24 hours. Stars within the angle of the observer's latitude away from the North Celestial Pole never rise or set. They are always above the horizon (circumpolar stars). ...
I Cloudy with a Chance of Making a star is no easy thing
... it needs to become dense enough to initiate nuclear fusion but has not done so yet. Astronomers can see how this process begins and how it ends, but what comes in the middle is inherently hard to observe, because much of the radiation comes out at far-infrared and submillimeter wavelengths where the ...
... it needs to become dense enough to initiate nuclear fusion but has not done so yet. Astronomers can see how this process begins and how it ends, but what comes in the middle is inherently hard to observe, because much of the radiation comes out at far-infrared and submillimeter wavelengths where the ...
File
... a long way to us but is an insignificant distance in space. The nearest celestial object to earth, the moon, is approximately 400, 000 km away (more than 10 times the earth’s circumference). The sun, which is by far the closest star to earth, is 150 million km away. As we leave the solar system, dis ...
... a long way to us but is an insignificant distance in space. The nearest celestial object to earth, the moon, is approximately 400, 000 km away (more than 10 times the earth’s circumference). The sun, which is by far the closest star to earth, is 150 million km away. As we leave the solar system, dis ...
Star names and magnitudes
... letter from the Greek alphabet in order of decreasing brightness (eg, Sirius,the brightest star in Canis Majoris, is also known as aCMa). This was devised by Bayer in 1603. If there are more than 24 stars in a constellation, then the remainder are numbered in order of Right Ascension (Flamsteed, 192 ...
... letter from the Greek alphabet in order of decreasing brightness (eg, Sirius,the brightest star in Canis Majoris, is also known as aCMa). This was devised by Bayer in 1603. If there are more than 24 stars in a constellation, then the remainder are numbered in order of Right Ascension (Flamsteed, 192 ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 5 Text
... - Apparent Magnitude (Magnitude) If a star doesn’t have all three of these pieces of information, then ignore it and select a different star. These stars may have distances listed, but in many cases those distances are automatically generated from a catalog that is rather out-of-date and unreliable, ...
... - Apparent Magnitude (Magnitude) If a star doesn’t have all three of these pieces of information, then ignore it and select a different star. These stars may have distances listed, but in many cases those distances are automatically generated from a catalog that is rather out-of-date and unreliable, ...
Nebula Beginnings - University of Dayton
... titanic supernova explosions scatter this material back into space where it is used to create new generations of stars. This is the mechanism by which the gas and dust that formed our solar system became enriched with the elements that sustain life on this planet. Hubble spectroscopic observations w ...
... titanic supernova explosions scatter this material back into space where it is used to create new generations of stars. This is the mechanism by which the gas and dust that formed our solar system became enriched with the elements that sustain life on this planet. Hubble spectroscopic observations w ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.