Astronomy Power Point
... in one year….HUGE! • light year is a unit of distance, not time!!!! • 1 light year= ~9.5 million million kilometers ...
... in one year….HUGE! • light year is a unit of distance, not time!!!! • 1 light year= ~9.5 million million kilometers ...
Astronomy Final Study Guide - With Answers!!– Name: **This will be
... The earth’s tides are caused mostly by the gravitational pull from the moon. Wherever the moon is, we will have a high tide. Spring tides happen when the sun, moon, and earth are all lined up in a straight line. During a spring tide, we have very high high tides and very low low tides. There is a hu ...
... The earth’s tides are caused mostly by the gravitational pull from the moon. Wherever the moon is, we will have a high tide. Spring tides happen when the sun, moon, and earth are all lined up in a straight line. During a spring tide, we have very high high tides and very low low tides. There is a hu ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical
... the cross-shaped constellation Cygnus and down to Sagittarius in the south. The Milky Way is packed with riches such as star clusters, nebulae, double stars and variable stars. The disk of the galaxy is a flattened, rotating system which contains our Sun and other intermediate-to-young stars. The Su ...
... the cross-shaped constellation Cygnus and down to Sagittarius in the south. The Milky Way is packed with riches such as star clusters, nebulae, double stars and variable stars. The disk of the galaxy is a flattened, rotating system which contains our Sun and other intermediate-to-young stars. The Su ...
The Sun: center of the Solar System
... million years ago, similar in size to Chicxulub) • Barringer Crater (Arizona; one of the bestpreserved on Earth) • Ries and Steinholm (Germany; same age, probably binary asteroid) ...
... million years ago, similar in size to Chicxulub) • Barringer Crater (Arizona; one of the bestpreserved on Earth) • Ries and Steinholm (Germany; same age, probably binary asteroid) ...
R - Uplift North Hills Prep
... PRACTICE: Two spheres of equal mass and different radii are held a distance d apart. The gravitational field strength is measured on the line joining the two masses at position x which varies. Which graph shows the variation of g with x correctly? ...
... PRACTICE: Two spheres of equal mass and different radii are held a distance d apart. The gravitational field strength is measured on the line joining the two masses at position x which varies. Which graph shows the variation of g with x correctly? ...
ISM and star formation
... Emission Nebulae or H II Regions Regions of gas and dust near stars just formed. The Hydrogen is essentially fully ionized. Temperatures near 10,000 K ...
... Emission Nebulae or H II Regions Regions of gas and dust near stars just formed. The Hydrogen is essentially fully ionized. Temperatures near 10,000 K ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • What: Determine how the height of the sun above the horizon at a specific time is changing as the days pass by measuring the length of the shadow it casts with a gnomon (essentially a stick in the ground). • Time: Once you know how to do it, this only takes a minute per observation. • Commitment: ...
... • What: Determine how the height of the sun above the horizon at a specific time is changing as the days pass by measuring the length of the shadow it casts with a gnomon (essentially a stick in the ground). • Time: Once you know how to do it, this only takes a minute per observation. • Commitment: ...
HW8 - UCSB Physics
... Using this let us first calculate the three requested figures. The given mass of the earth, the sun, and the black hole of NGC 4261 are 5.97 ×1024 kg, 1.99 ×1030 kg (1 M ), and 1.2 ×109 M , respectively. Direct substitution into the equation above gives the values (a),(b),(c) for the earth, the su ...
... Using this let us first calculate the three requested figures. The given mass of the earth, the sun, and the black hole of NGC 4261 are 5.97 ×1024 kg, 1.99 ×1030 kg (1 M ), and 1.2 ×109 M , respectively. Direct substitution into the equation above gives the values (a),(b),(c) for the earth, the su ...
Exercise 7
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
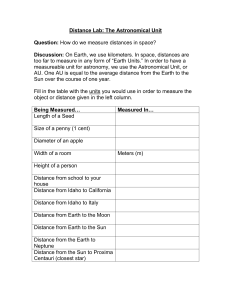
Distance Lab: The Astronomical Unit
... notebook. Use page 104 in the textbook to help you out. 2. Parallax: Look up at the balloon globe hanging above the teachers’ desk. Behind the globe are some pictures of mountains and glaciers that are numbered 1-10. Which number do you see? 3. Move to the other side of the room for a moment, and lo ...
... notebook. Use page 104 in the textbook to help you out. 2. Parallax: Look up at the balloon globe hanging above the teachers’ desk. Behind the globe are some pictures of mountains and glaciers that are numbered 1-10. Which number do you see? 3. Move to the other side of the room for a moment, and lo ...
Stellar Explosions
... observable universe started roughly 13.7 billion years ago from an extremely dense and incredibly hot initial state. ...
... observable universe started roughly 13.7 billion years ago from an extremely dense and incredibly hot initial state. ...
Astronomy review - Petal School District
... other galaxies traveling together called, “The Local Group.” ...
... other galaxies traveling together called, “The Local Group.” ...
Powerpoint file
... lists this as an A5 V star, but it is a g Dor variable which have spectral types F0-F2. Spectra confirm that it is F-type 1SIMBAD ...
... lists this as an A5 V star, but it is a g Dor variable which have spectral types F0-F2. Spectra confirm that it is F-type 1SIMBAD ...
Homework Problem #1: (pdf file)
... brightness at Mauna Kea is listed at the CFHT WWW site as 20.9 mag/arcsec2 . The LRIS pixel scale is 0.22 arcseconds/pixel, the readout noise is 8e- and the inverse gain of the system is 2.0 e-/DN. (a) What is the rate of detected e-/pixel from the sky in the R band? (b) What is the rate of detected ...
... brightness at Mauna Kea is listed at the CFHT WWW site as 20.9 mag/arcsec2 . The LRIS pixel scale is 0.22 arcseconds/pixel, the readout noise is 8e- and the inverse gain of the system is 2.0 e-/DN. (a) What is the rate of detected e-/pixel from the sky in the R band? (b) What is the rate of detected ...
1 HoNoRS227 Examination #3 Name
... Because the star is so close that we should have received radio signals from the planet years ago. C Because the radio signals cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere from outer space. D Because we are able to hear radio waves, this should have been discovered long ago. *E Because massive blue giant ...
... Because the star is so close that we should have received radio signals from the planet years ago. C Because the radio signals cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere from outer space. D Because we are able to hear radio waves, this should have been discovered long ago. *E Because massive blue giant ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • The energy of the electron depends on orbit • When an electron jumps from one orbital to another, it emits (emission line) or absorbs (absorption line) a photon of a certain energy • The frequency of emitted or absorbed photon is related to its energy ...
... • The energy of the electron depends on orbit • When an electron jumps from one orbital to another, it emits (emission line) or absorbs (absorption line) a photon of a certain energy • The frequency of emitted or absorbed photon is related to its energy ...
Star Formation - University of Redlands
... attract more matter. • Planetesimals are the building blocks of the planets. Orion Nebula – Copyright O’Dell and Wong ...
... attract more matter. • Planetesimals are the building blocks of the planets. Orion Nebula – Copyright O’Dell and Wong ...
16SolMW - NMSU Astronomy
... some apparent differences? • Stars come in a wide range of brightnesses – We see stars because they shine (energy from nuclear reactions in their centers, just like the Sun – the Sun is a star!) – The apparent brightness (how bright it appears to us) depends on how bright the star really shines AND ...
... some apparent differences? • Stars come in a wide range of brightnesses – We see stars because they shine (energy from nuclear reactions in their centers, just like the Sun – the Sun is a star!) – The apparent brightness (how bright it appears to us) depends on how bright the star really shines AND ...
Standard 1 Information Sheet
... Comparing the solar spectrum with the spectra of other stars shows that the Sun is a typical star. Analysis of the spectral features of a star provides information on a star’s chemical composition and relative abundance of elements. The most abundant element in the Sun is hydrogen. The Sun’s enormou ...
... Comparing the solar spectrum with the spectra of other stars shows that the Sun is a typical star. Analysis of the spectral features of a star provides information on a star’s chemical composition and relative abundance of elements. The most abundant element in the Sun is hydrogen. The Sun’s enormou ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.