Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry
... releasing it – When fusion requires more energy than it can produce, there is no longer any outward pressure to balance the gravitational force – The core collapses because of its own gravity and then rebounds with a shock wave that violently blow’s the star’s outer layers away from the core – The r ...
... releasing it – When fusion requires more energy than it can produce, there is no longer any outward pressure to balance the gravitational force – The core collapses because of its own gravity and then rebounds with a shock wave that violently blow’s the star’s outer layers away from the core – The r ...
Extra-Solar Planets
... the number of stars in the Milky Way the fraction of stars that have “habitable planets” the number of habitable planets per system the fraction of habitable planets where life evolves the fraction of life-planets that evolve intelligence the fraction of civilizations that communicate the fraction o ...
... the number of stars in the Milky Way the fraction of stars that have “habitable planets” the number of habitable planets per system the fraction of habitable planets where life evolves the fraction of life-planets that evolve intelligence the fraction of civilizations that communicate the fraction o ...
here.
... - A group of gravitationally bound stars formed out of the same cloud, at the same time, and at the same distance from us. - They are ideal laboratories to study stellar evolution, and to probe the Galactic formation and evolutionary ...
... - A group of gravitationally bound stars formed out of the same cloud, at the same time, and at the same distance from us. - They are ideal laboratories to study stellar evolution, and to probe the Galactic formation and evolutionary ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 8
... 14. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit x-rays because ...
... 14. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit x-rays because ...
1_Introduction
... Stars in the solar neighborhood move randomly at speeds of about 40 km/sec relative to the Sun. But… Is it useful to think of stars’ velocity relative to the Sun? ...
... Stars in the solar neighborhood move randomly at speeds of about 40 km/sec relative to the Sun. But… Is it useful to think of stars’ velocity relative to the Sun? ...
Powerpoint for today
... Temperature of background in opposite directions nearly identical. Yet even light hasn't had time to travel from A to B (only A to Earth), so A can know nothing about conditions at B, and vice versa. So why are A and B almost identical? This is “horizon problem”. ...
... Temperature of background in opposite directions nearly identical. Yet even light hasn't had time to travel from A to B (only A to Earth), so A can know nothing about conditions at B, and vice versa. So why are A and B almost identical? This is “horizon problem”. ...
mass of star
... Temperature of background in opposite directions nearly identical. Yet even light hasn't had time to travel from A to B (only A to Earth), so A can know nothing about conditions at B, and vice versa. So why are A and B almost identical? This is “horizon problem”. ...
... Temperature of background in opposite directions nearly identical. Yet even light hasn't had time to travel from A to B (only A to Earth), so A can know nothing about conditions at B, and vice versa. So why are A and B almost identical? This is “horizon problem”. ...
Week 3: Kepler`s Laws, Light and Matter
... emit photons when they come down. Absorption spectrum is produced when we observe a cold gas cloud in front of a hot source of light. In this case, the electrons take away some energy from the light and move up. They may lose this energy by emitting photons in random directions or any other mechanis ...
... emit photons when they come down. Absorption spectrum is produced when we observe a cold gas cloud in front of a hot source of light. In this case, the electrons take away some energy from the light and move up. They may lose this energy by emitting photons in random directions or any other mechanis ...
Physics 1025: Lecture 18 Stellar Magnitudes, Absolute Magnitudes
... To include any magnitude difference found (not just 1 to 5), simply break up the magnitude difference number into smaller numbers in the above table, and multiply each ratio: For example, consider two stars differing in magnitude by 13 magnitudes (e.g. m 1 = 20 and m2 = 7) magnitude diff. Δm = 13 = ...
... To include any magnitude difference found (not just 1 to 5), simply break up the magnitude difference number into smaller numbers in the above table, and multiply each ratio: For example, consider two stars differing in magnitude by 13 magnitudes (e.g. m 1 = 20 and m2 = 7) magnitude diff. Δm = 13 = ...
dm curvas de rotacion
... The orbital velocity of stars can be measured using the Doppler shift. ...
... The orbital velocity of stars can be measured using the Doppler shift. ...
Consider Average Stars
... actually see – is partly an accident of location: nearby stars can look deceptively bright. (The obvious example is the Sun!) But the intrinsic (true) brightness of a star is a good measure of how much energy is being generated, how fast the fuel is being consumed, etc. So it’s something ...
... actually see – is partly an accident of location: nearby stars can look deceptively bright. (The obvious example is the Sun!) But the intrinsic (true) brightness of a star is a good measure of how much energy is being generated, how fast the fuel is being consumed, etc. So it’s something ...
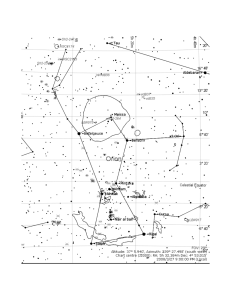
June 2016 night sky chart
... the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brig ...
... the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brig ...
the Sun - University of Redlands
... • Therefore, there are electrons in atoms able to absorb light. • Absorption lines in solar spectrum are from these layers in the atmosphere. ...
... • Therefore, there are electrons in atoms able to absorb light. • Absorption lines in solar spectrum are from these layers in the atmosphere. ...
Sources of Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan
... ―Standard siren‖ – neutron star binaries out to z~1, BH binaries anywhere Precision depends on SNR, ability to disentangle orbit orientation ...
... ―Standard siren‖ – neutron star binaries out to z~1, BH binaries anywhere Precision depends on SNR, ability to disentangle orbit orientation ...
Ch2a
... The Elevation of the North Pole Star The north pole star is always at an elevation, or altitude, a, above the northern horizon, that is equal to the latitude, of the observer. Circumpolar stars are stars which are always in view. They never set below the horizon. All stars with declinations ...
... The Elevation of the North Pole Star The north pole star is always at an elevation, or altitude, a, above the northern horizon, that is equal to the latitude, of the observer. Circumpolar stars are stars which are always in view. They never set below the horizon. All stars with declinations ...
Powerpoint - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... corresponds to material moving towards the observer (which would be blueshifted), while red corresponds to material moving away from the observer (red-shifted). Black contours indicate material hotter than 106 K. Line Profiles. This diagnostic shows the relative blue- or red-shift of an emission lin ...
... corresponds to material moving towards the observer (which would be blueshifted), while red corresponds to material moving away from the observer (red-shifted). Black contours indicate material hotter than 106 K. Line Profiles. This diagnostic shows the relative blue- or red-shift of an emission lin ...
Lecture7 - UCSB Physics
... age dating, are used to determine the rocks formed 4.56 x 109 years ago. ...
... age dating, are used to determine the rocks formed 4.56 x 109 years ago. ...
upperMS - CWRU Astronomy
... OBN stars come from mass loss in OB stars Say the CN cycle converts CN in the inner 60% of a star over 15% of its main sequence lifetime If 40% of the remaining mass can be removed in the final 85% of the lifetime, then it’s a nitrogen rich star It’s ok to lose this much mass and still be OB, but i ...
... OBN stars come from mass loss in OB stars Say the CN cycle converts CN in the inner 60% of a star over 15% of its main sequence lifetime If 40% of the remaining mass can be removed in the final 85% of the lifetime, then it’s a nitrogen rich star It’s ok to lose this much mass and still be OB, but i ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.