May 2014
... that releases detectable signs of their existence into space L = the length of time for which such civilizations release detectable signals into space Now we have photographed other planets orbiting other stars, detected other planets through radial velocity (star wobble – and blue/red shift of the ...
... that releases detectable signs of their existence into space L = the length of time for which such civilizations release detectable signals into space Now we have photographed other planets orbiting other stars, detected other planets through radial velocity (star wobble – and blue/red shift of the ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... entropy that not all of this gas will be accreted into the halo. • Photoionization heating by UV background: the strength of the effect fails to reconcile the models with the ...
... entropy that not all of this gas will be accreted into the halo. • Photoionization heating by UV background: the strength of the effect fails to reconcile the models with the ...
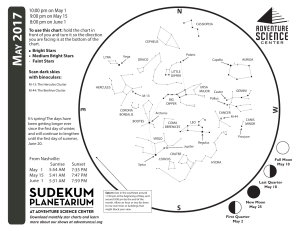
1705 chart front
... your binocular view on Jupiter, try leaning them up against the side of a building or another steady surface. A small telescope not only shows the moons of Jupiter, but also its cloud bands. Jupiter has stripes! Look for our own Moon next to Jupiter on May 7. Look to the east for the constellation H ...
... your binocular view on Jupiter, try leaning them up against the side of a building or another steady surface. A small telescope not only shows the moons of Jupiter, but also its cloud bands. Jupiter has stripes! Look for our own Moon next to Jupiter on May 7. Look to the east for the constellation H ...
Document
... o Observed rates of period change are consistent with Classic Cepheids during their first crossing of the instability gap, whereas models have the rate of change for Polaris at four times what is observed. ...
... o Observed rates of period change are consistent with Classic Cepheids during their first crossing of the instability gap, whereas models have the rate of change for Polaris at four times what is observed. ...
AST1001.ch10
... predicted number More recent observations also found a deficit of neutrinos. A new theory of the neutrino predicts that they have mass and can change form. This theory agrees with the observed neutrino numbers. ...
... predicted number More recent observations also found a deficit of neutrinos. A new theory of the neutrino predicts that they have mass and can change form. This theory agrees with the observed neutrino numbers. ...
The Stars and the Solar System
... many ways. Sailors studied them to find their way at night. Farmer’s used them to mark the seasons and signal when to plant or harvest their ...
... many ways. Sailors studied them to find their way at night. Farmer’s used them to mark the seasons and signal when to plant or harvest their ...
Simple astronomy within the solar system
... Next the two amateurs determine the distance to the sun by using the known data about the moon’s orbit as shown in the illustration. At a particular time the sun, moon, and earth are in positions such that the shadow edge coincides with a major diameter of the moon (which to an observer appears to b ...
... Next the two amateurs determine the distance to the sun by using the known data about the moon’s orbit as shown in the illustration. At a particular time the sun, moon, and earth are in positions such that the shadow edge coincides with a major diameter of the moon (which to an observer appears to b ...
Basic data of CoRoT-Exo-2b - tls
... (infrared spectra with high spectra resolution needed) Determine the mass and the radius of the host star accurately (optical spectra with high spectral resolution and high signal to noise needed, in practise 2 to 4 ...
... (infrared spectra with high spectra resolution needed) Determine the mass and the radius of the host star accurately (optical spectra with high spectral resolution and high signal to noise needed, in practise 2 to 4 ...
Night Sky Checklist April–May–June Unaided Eye Astronomy
... light years distant. The group is visible to the unaided eye under clear skies well away from lights, and is a striking site in binoculars. Omega Centauri is a globular cluster, a family of close to a million stars whose gravity holds the whole group together in what appears in binoculars or a low p ...
... light years distant. The group is visible to the unaided eye under clear skies well away from lights, and is a striking site in binoculars. Omega Centauri is a globular cluster, a family of close to a million stars whose gravity holds the whole group together in what appears in binoculars or a low p ...
THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... sense (think why?). The further the (angular) distance of the star from the pole star, the greater its radius of the traced circle. When the angular distance increases to 90º, the traced circle becomes a great circle – the celestial equator. If we extend the plane containing the equator in space, th ...
... sense (think why?). The further the (angular) distance of the star from the pole star, the greater its radius of the traced circle. When the angular distance increases to 90º, the traced circle becomes a great circle – the celestial equator. If we extend the plane containing the equator in space, th ...
WHERE DO ELEMENTS COME FROM?
... • Nuclear reaction: Elements are fused inside stars to form heavier elements from hydrogen • Along with others, it was shown that the abundance of elements in the universe can be explained mostly by stellar fusion… Margaret Burbidge Geoffrey Burbidge Willy Fowler Fred Hoyle ...
... • Nuclear reaction: Elements are fused inside stars to form heavier elements from hydrogen • Along with others, it was shown that the abundance of elements in the universe can be explained mostly by stellar fusion… Margaret Burbidge Geoffrey Burbidge Willy Fowler Fred Hoyle ...
PHYS3380_102615_bw
... Original cloud large and diffuse - begins to collapse. Final density, shape, size, and temperature the result of three processes: • Heating - cloud heats up due to conservation of energy - as cloud shrank, gravitational energy converted to kinetic energy - collisions convert KE into random motions ...
... Original cloud large and diffuse - begins to collapse. Final density, shape, size, and temperature the result of three processes: • Heating - cloud heats up due to conservation of energy - as cloud shrank, gravitational energy converted to kinetic energy - collisions convert KE into random motions ...
Outline - March 16, 2010 Interstellar Medium (ISM) Why should you
... Center of a collapsing cloud becomes denser and hotter. The energy is gravitational. Half the gravitational energy goes into heating the collapsing clout, the other half escapes as light. The central object is called a “protostar”, and they are very bright! (Because they have very large radii.) ...
... Center of a collapsing cloud becomes denser and hotter. The energy is gravitational. Half the gravitational energy goes into heating the collapsing clout, the other half escapes as light. The central object is called a “protostar”, and they are very bright! (Because they have very large radii.) ...
Stars
... ______ 8. The colors that appear when a chemical element emits light are called a. continuous lines. b. absorption lines. c. color lines. d. emission lines. ______ 9. Each element in a hot gas can be identified by a. a unique set of bright emission lines. b. a unique set of bright absorption lines. ...
... ______ 8. The colors that appear when a chemical element emits light are called a. continuous lines. b. absorption lines. c. color lines. d. emission lines. ______ 9. Each element in a hot gas can be identified by a. a unique set of bright emission lines. b. a unique set of bright absorption lines. ...
Interactive Vocabulary Review for Outer Space Indicator
... A natural, luminous, celestial body is better known as a STAR! ...
... A natural, luminous, celestial body is better known as a STAR! ...
Jeopardy - Cloudfront.net
... a. absorption spectrum of elements to the emission spectra of a star b. continuous spectrum of elements to the emission spectra of a star c. emission spectrum of elements to the absorption spectra of a star d. emission spectrum of elements to continuous spectra of a star ...
... a. absorption spectrum of elements to the emission spectra of a star b. continuous spectrum of elements to the emission spectra of a star c. emission spectrum of elements to the absorption spectra of a star d. emission spectrum of elements to continuous spectra of a star ...
Classnotes 9_159 - University of Texas Astronomy
... Around the turn of the century, it was appreciated that atoms consist of electrically charged particles, both positive and negative. The physicist J.J. Thomson proposed a model for the structure of the atom based upon a relatively large, positively charged, amorphous mass in which much smaller, nega ...
... Around the turn of the century, it was appreciated that atoms consist of electrically charged particles, both positive and negative. The physicist J.J. Thomson proposed a model for the structure of the atom based upon a relatively large, positively charged, amorphous mass in which much smaller, nega ...
Name - Physics
... 2. An elevator weighing 10,000 N is supported by a steel cable. Determine the tension in the cable when the elevator is accelerated upward at 3.0 m/s2. ...
... 2. An elevator weighing 10,000 N is supported by a steel cable. Determine the tension in the cable when the elevator is accelerated upward at 3.0 m/s2. ...
Stars on the HR Diagram
... knowledge astronomers acquire about stars is through mathematical comparison of data derived from the light (radiation) from stars. The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram, widely used in astronomy, is a scatter plot with a distribution of data points that describe a relationship between physical aspec ...
... knowledge astronomers acquire about stars is through mathematical comparison of data derived from the light (radiation) from stars. The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram, widely used in astronomy, is a scatter plot with a distribution of data points that describe a relationship between physical aspec ...
The Sun - GeoScience
... 1. Where is our Sun located in our solar system? Click on “Interior” from the list on the left 2. a. Name the inner most layer of the sun. b. What occurs in this layer? Click on “Surface of the Sun” in the text 3. What is the name of the ‘surface of the sun’? 4. What form of the Sun’s energy do we r ...
... 1. Where is our Sun located in our solar system? Click on “Interior” from the list on the left 2. a. Name the inner most layer of the sun. b. What occurs in this layer? Click on “Surface of the Sun” in the text 3. What is the name of the ‘surface of the sun’? 4. What form of the Sun’s energy do we r ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.