Measuring Air Pressure 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure
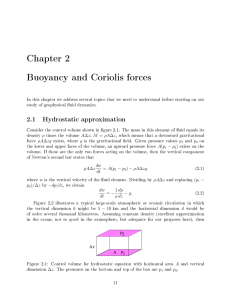
... The atmosphere balances these differences by acting as a giant heat-transfer system. This system moves warm air toward high latitudes and cool air toward the equator. Non-Rotating Earth Model • On a hypothetical non-rotating planet with a smooth surface of either all land or all water, two large ...
... The atmosphere balances these differences by acting as a giant heat-transfer system. This system moves warm air toward high latitudes and cool air toward the equator. Non-Rotating Earth Model • On a hypothetical non-rotating planet with a smooth surface of either all land or all water, two large ...
幻灯片 1
... Basic Concepts 1. A gas in a piston-cylinder device is compressed, and as a result its temperature rises. Is this a heat or work interaction? 2. On a P-v diagram, what does the area under the process curve represent? 3. Determine the energy required to accelerate a 2000-kg car from 20 to 70 km/h on ...
... Basic Concepts 1. A gas in a piston-cylinder device is compressed, and as a result its temperature rises. Is this a heat or work interaction? 2. On a P-v diagram, what does the area under the process curve represent? 3. Determine the energy required to accelerate a 2000-kg car from 20 to 70 km/h on ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... second when a tuning fork and a note are sounded together and six beats per second after the string is tightened. What should the tuner do next, tighten or loosen the string? Explain. Loosen. Since the beat frequency depends upon the difference between the two frequencies, you wish to go in the dire ...
... second when a tuning fork and a note are sounded together and six beats per second after the string is tightened. What should the tuner do next, tighten or loosen the string? Explain. Loosen. Since the beat frequency depends upon the difference between the two frequencies, you wish to go in the dire ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... second when a tuning fork and a note are sounded together and six beats per second after the string is tightened. What should the tuner do next, tighten or loosen the string? Explain. Loosen. Since the beat frequency depends upon the difference between the two frequencies, you wish to go in the di ...
... second when a tuning fork and a note are sounded together and six beats per second after the string is tightened. What should the tuner do next, tighten or loosen the string? Explain. Loosen. Since the beat frequency depends upon the difference between the two frequencies, you wish to go in the di ...
Chapter 1
... 17. The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers on the basis of temperature. List the names of these layers and their boundaries in order – from lowest to highest – and list as many characteristics of each as you can. ...
... 17. The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers on the basis of temperature. List the names of these layers and their boundaries in order – from lowest to highest – and list as many characteristics of each as you can. ...
Cikloni v zmernih širinah
... • a warm front moving to the northeast • a cold front moving to the southeast • region between warm and cold fronts is the "warm sector" • the central low pressure (low, which is deepening with time) • overrunning of warm air over the warm front • cold air surging southward behind the cold front • w ...
... • a warm front moving to the northeast • a cold front moving to the southeast • region between warm and cold fronts is the "warm sector" • the central low pressure (low, which is deepening with time) • overrunning of warm air over the warm front • cold air surging southward behind the cold front • w ...
Homework 6: Heat Transfer (Lowrie Chapter 4.2)
... (c) At what rate is heat flowing from the underlying mantle into the crust?, i.e., what is Q(z=35) km? Briefly explain why the difference between q0 and q(z=35) does (or does not) make sense given your estimate of H. 2) Recently, a new eruption site developed at Volcano National Park on the Big Isla ...
... (c) At what rate is heat flowing from the underlying mantle into the crust?, i.e., what is Q(z=35) km? Briefly explain why the difference between q0 and q(z=35) does (or does not) make sense given your estimate of H. 2) Recently, a new eruption site developed at Volcano National Park on the Big Isla ...
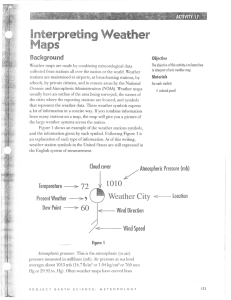
Fryterprettng V/eathen - Mrs. Battistone`s Earth Science Class
... alrow points the direction the wind is blowing, but wind direction is designated as the direction the wind is blowing from. Therefore, if an arrow points to the east, the wind direction is actually called "from the west." In Figure 1 above, the wind direction is from the south. See Figure 3 for the ...
... alrow points the direction the wind is blowing, but wind direction is designated as the direction the wind is blowing from. Therefore, if an arrow points to the east, the wind direction is actually called "from the west." In Figure 1 above, the wind direction is from the south. See Figure 3 for the ...
Key p.4-12, p.14-18
... **Complete the formula below** Total Energy = (kinetic energy + potential energy) x (#particles) **What would have more thermal energy, a cup of hot chocolate at 60°C or Elk Lake?** Elk Lake: it has lots of particles compared to hot chocolate cup ...
... **Complete the formula below** Total Energy = (kinetic energy + potential energy) x (#particles) **What would have more thermal energy, a cup of hot chocolate at 60°C or Elk Lake?** Elk Lake: it has lots of particles compared to hot chocolate cup ...
WINTER NIGHT HABITS OF BIRDS
... a cavity, and so on; by clouds overhead; and, in varying degrees, by the water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, even with a perfectly clear sky. If a bird is completely enclosed in a wooden box, or in a tree cavity, or cave, and if the temperature of the outer plumage surface is the same ...
... a cavity, and so on; by clouds overhead; and, in varying degrees, by the water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, even with a perfectly clear sky. If a bird is completely enclosed in a wooden box, or in a tree cavity, or cave, and if the temperature of the outer plumage surface is the same ...
Chapter 1 - Princeton University Press
... atmosphere. In these panels, white means that radiation is transmitted, and gray indicates that it is absorbed by interactions with molecules of the gases in air. Absorbed radiation is used to kick electrons into higher energy levels, and to increase vibrational and rotational frequencies of molecul ...
... atmosphere. In these panels, white means that radiation is transmitted, and gray indicates that it is absorbed by interactions with molecules of the gases in air. Absorbed radiation is used to kick electrons into higher energy levels, and to increase vibrational and rotational frequencies of molecul ...
high and low pressure systems. The belts which most influence us in
... Wind is the movement or flow of air. The large wind systems occur due to the different temperatures across the earth from the tropics to the poles. Air over the tropics heats up and rises. As it does so it cools and descends again and the cycle restarts. This simple pattern is complicated by the dif ...
... Wind is the movement or flow of air. The large wind systems occur due to the different temperatures across the earth from the tropics to the poles. Air over the tropics heats up and rises. As it does so it cools and descends again and the cycle restarts. This simple pattern is complicated by the dif ...
Weather Systems Level 4
... • Warm fronts – zones where a moving warm air mass replaces a cold air mass. In opposition to cold fronts, the air behind a warm front is warmer and moister than the air ahead of it, thus increasing the temperature and humidity as it passes through. • Isobars - lines that connect locations of equal ...
... • Warm fronts – zones where a moving warm air mass replaces a cold air mass. In opposition to cold fronts, the air behind a warm front is warmer and moister than the air ahead of it, thus increasing the temperature and humidity as it passes through. • Isobars - lines that connect locations of equal ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 20. A house has many windows that are single paned (a single sheet of glass). During the winter, a large amount of heat is transferred from the inside of a house to the outside environment through these windows. Of the following, which would be the best way to decrease the amount of heat transferred ...
... 20. A house has many windows that are single paned (a single sheet of glass). During the winter, a large amount of heat is transferred from the inside of a house to the outside environment through these windows. Of the following, which would be the best way to decrease the amount of heat transferred ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.