forms-of-energy-worksheet
... b. At a certain point the kinetic energy of a falling apple is5.2 J and its potential energy is 3.5 J. What is its mechanical energy? c. If an object’s mechanical energy is equal to its potential energy, how much kinetic energy does the object have? Explain. 2a. EXPLAIN Why do the particles of objec ...
... b. At a certain point the kinetic energy of a falling apple is5.2 J and its potential energy is 3.5 J. What is its mechanical energy? c. If an object’s mechanical energy is equal to its potential energy, how much kinetic energy does the object have? Explain. 2a. EXPLAIN Why do the particles of objec ...
MSSE 470S 5E Lesson Plan
... what they drew and how it makes sense with the form of energy on their piece of paper. I do not expect these presentations to be too in depth. They are meant to be quick and informal. After each student has gone, I will open the class up for discussion. The main terms/concepts I want them to take aw ...
... what they drew and how it makes sense with the form of energy on their piece of paper. I do not expect these presentations to be too in depth. They are meant to be quick and informal. After each student has gone, I will open the class up for discussion. The main terms/concepts I want them to take aw ...
Chapter 10: Thermodynamics
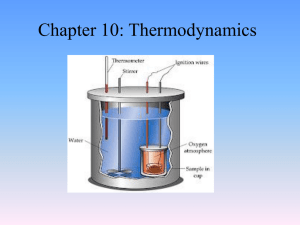
... • A total of 135 J of work is done on a gaseous refrigerant as it undergoes compression. If the internal energy of the gas increases by 114 J during the process, what is the total amount of energy transferred as heat? ...
... • A total of 135 J of work is done on a gaseous refrigerant as it undergoes compression. If the internal energy of the gas increases by 114 J during the process, what is the total amount of energy transferred as heat? ...
P K P K K K P P
... 22. Electrical Energy: the movement of electrons Example: electricity 23. Energy of microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, and light waves are all forms of _ electromagnetic _energy Energy Transformations (Conversions) 24. Define Energy transformation: begins with one energy and produces ...
... 22. Electrical Energy: the movement of electrons Example: electricity 23. Energy of microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, and light waves are all forms of _ electromagnetic _energy Energy Transformations (Conversions) 24. Define Energy transformation: begins with one energy and produces ...
Energy - Teacher Notes
... Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. When the kinetic energy of an object changes, work has been done on the object. Work is a scalar quantity. ...
... Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. When the kinetic energy of an object changes, work has been done on the object. Work is a scalar quantity. ...
Forms of Energy Test Review KEY
... Define the Forms of Potential Energy: 14. Chemical Energy: energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules Example: biomass, petroleum (gasoline), natural gas 15. Nuclear Energy: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Example: the sun (fusion), nuclear (fission) in power plants List two ways nuc ...
... Define the Forms of Potential Energy: 14. Chemical Energy: energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules Example: biomass, petroleum (gasoline), natural gas 15. Nuclear Energy: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Example: the sun (fusion), nuclear (fission) in power plants List two ways nuc ...
Work and Power
... Conservative Forces • Work done by conservative forces does not depend on the path taken: gravitation • For conservative forces, total work done on closed path is zero. • Conservative forces have no energy losses • Example: lifting object from floor to table involves same amount of work no matter w ...
... Conservative Forces • Work done by conservative forces does not depend on the path taken: gravitation • For conservative forces, total work done on closed path is zero. • Conservative forces have no energy losses • Example: lifting object from floor to table involves same amount of work no matter w ...
Period 6/7
... 26. Since liquid water has the highest specific heat naturally occurring substances, explain why the ocean temperatures are cool on the first day summer. ...
... 26. Since liquid water has the highest specific heat naturally occurring substances, explain why the ocean temperatures are cool on the first day summer. ...
8.1 kinetic and potential energy
... watching at the stars. Isn't that nice? Find their Gravitational Potental Energies. ...
... watching at the stars. Isn't that nice? Find their Gravitational Potental Energies. ...
PA2001: Energy and Momentum
... Power Power is defined as the rate of doing work Units are Joules/second (or Watts) ...
... Power Power is defined as the rate of doing work Units are Joules/second (or Watts) ...
Introduction in energy systems - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
... surrounding objects (Kelvin statement). Third law of thermodynamics The system is not possible cooled, in a finite number of steps, to absolute zero. ...
... surrounding objects (Kelvin statement). Third law of thermodynamics The system is not possible cooled, in a finite number of steps, to absolute zero. ...
My Work and Energy PPT(not used in class but very
... • An object raised to some height over the ground ...
... • An object raised to some height over the ground ...
energy - Science 6
... 2) A car turns electrical (spark) to thermal to chemical to thermal to mechanical and back to electrical! ...
... 2) A car turns electrical (spark) to thermal to chemical to thermal to mechanical and back to electrical! ...
Review questions:
... 1. Where on the graph would I put the independent variable? 2. Where on the graph would I put the dependent variable? 3. List and describe the 5 steps of the scientific method. 4. What is a hypothesis? 5. What are 2 things that all good hypotheses have to have/be? 6. What is a variable? 7. What is t ...
... 1. Where on the graph would I put the independent variable? 2. Where on the graph would I put the dependent variable? 3. List and describe the 5 steps of the scientific method. 4. What is a hypothesis? 5. What are 2 things that all good hypotheses have to have/be? 6. What is a variable? 7. What is t ...
Energy - DiMaggio
... Examples: toy at the top of staircase, book on bookshelf, apple on tree, stretched elastic) ...
... Examples: toy at the top of staircase, book on bookshelf, apple on tree, stretched elastic) ...
Types of Energy 1. potential energy – the energy stored in an object
... Types of Energy 1. potential energy – the energy stored in an object or material 2. kinetic energy – the energy of a moving object 3. mechanical energy – energy due to an object’s motion (which is kinetic energy) or an object’s position (which is potential energy) 4. electromagnetic energy – light e ...
... Types of Energy 1. potential energy – the energy stored in an object or material 2. kinetic energy – the energy of a moving object 3. mechanical energy – energy due to an object’s motion (which is kinetic energy) or an object’s position (which is potential energy) 4. electromagnetic energy – light e ...
The Nature of Matter - Plain Local Schools
... *The total amount of matter and energy in the always remains constant in the universe ...
... *The total amount of matter and energy in the always remains constant in the universe ...
Section_08_Conservat..
... The MHD equations can be written in the form of conservation laws that express the physical principles of conservation of mass, momentum and energy. As mentioned above, we already have the law of conservation of mass: ...
... The MHD equations can be written in the form of conservation laws that express the physical principles of conservation of mass, momentum and energy. As mentioned above, we already have the law of conservation of mass: ...
Thermochemistry - all things chemistry with dr. cody
... Calculate the enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of ethylene using the following thermochemical equations: C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) H = ? H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) C2H6(g) + 7/2 O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l) ...
... Calculate the enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of ethylene using the following thermochemical equations: C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) H = ? H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) C2H6(g) + 7/2 O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l) ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.