PowerPoint Lecture - UCSD Department of Physics
... When net force is not zero • When an object experiences a non-zero net force, it must accelerate • Newton’s second law: F = m·a Force = mass times acceleration • The same force makes a small object accelerate more than it would a more massive object – hit a golf ball and a bowling ball with a golf c ...
... When net force is not zero • When an object experiences a non-zero net force, it must accelerate • Newton’s second law: F = m·a Force = mass times acceleration • The same force makes a small object accelerate more than it would a more massive object – hit a golf ball and a bowling ball with a golf c ...
Notes - 5
... We sometimes want to determine the electric potential between two points. This is known as the potential difference. For example, given two points A and B, the potential difference between A and B is: ...
... We sometimes want to determine the electric potential between two points. This is known as the potential difference. For example, given two points A and B, the potential difference between A and B is: ...
99MC
... It is accelerating towards the center of the earth at all times. It must be in circular orbit above the earth’s equator. It is always vertically above the same place in the earth’s surface. It must be rotating in the same sense and with the same angular speed as the earth. It is at a height where it ...
... It is accelerating towards the center of the earth at all times. It must be in circular orbit above the earth’s equator. It is always vertically above the same place in the earth’s surface. It must be rotating in the same sense and with the same angular speed as the earth. It is at a height where it ...
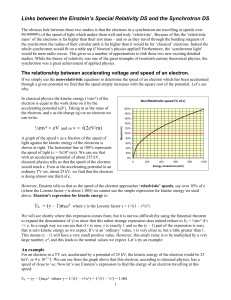
Links between the Einstein`s Special Relativity DS and
... We said above that the reason the electrons don’t exceed the speed of light is that their mass increases with increased total energy. In fact, Einstein did not like to talk of an increase in the mass of a relativistic object, only the increasing energy and momentum. Indeed modern particle physicists ...
... We said above that the reason the electrons don’t exceed the speed of light is that their mass increases with increased total energy. In fact, Einstein did not like to talk of an increase in the mass of a relativistic object, only the increasing energy and momentum. Indeed modern particle physicists ...
Ch 14 Work, Power and Simple Machines
... world, we have to take it into consideration… – The work done by this frictional force changes KE into thermal energy. – When the energy lost to frictional forces is accounted for all energy is conserved! ...
... world, we have to take it into consideration… – The work done by this frictional force changes KE into thermal energy. – When the energy lost to frictional forces is accounted for all energy is conserved! ...
How much kinetic energy does the mass have
... How much kinetic energy does the mass have when traveling at twice this speed? Four times as much: Ek = 4 (450J) = 1800 J ...
... How much kinetic energy does the mass have when traveling at twice this speed? Four times as much: Ek = 4 (450J) = 1800 J ...
L 1-3
... Diatomic Molecule with a oscillating dipole moment can absorb electromagnetic radiation via their rotational motion. Eg: CO, NO, and HCl ...
... Diatomic Molecule with a oscillating dipole moment can absorb electromagnetic radiation via their rotational motion. Eg: CO, NO, and HCl ...
The Nature of Energy
... make their own food through a series of chemical reactions. • It also stimulates chemical reactions in your eyes so that you can see. ...
... make their own food through a series of chemical reactions. • It also stimulates chemical reactions in your eyes so that you can see. ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... heat to the surroundings. The piston moves downward as the gases react to form a solid. As the volume of the gas decreases under the constant pressure of the atmosphere, the surroundings do 480 J of work on the system. What is the change in the internal energy of the system? ...
... heat to the surroundings. The piston moves downward as the gases react to form a solid. As the volume of the gas decreases under the constant pressure of the atmosphere, the surroundings do 480 J of work on the system. What is the change in the internal energy of the system? ...
Section 1 Powerpoint
... • How are energy and work related? • What factors does the kinetic energy of an object depend on? • How is gravitational potential energy determined? • What are the major forms of energy? ...
... • How are energy and work related? • What factors does the kinetic energy of an object depend on? • How is gravitational potential energy determined? • What are the major forms of energy? ...
jeopardy_Ch._3_Energy 370.5 KB - chamilton
... The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Energy can, however, change from one for to another. When a log burns, the chemical energy in the log is converted to electromagnetic energy (light and heat) and some sound energy that are given off. The chemi ...
... The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Energy can, however, change from one for to another. When a log burns, the chemical energy in the log is converted to electromagnetic energy (light and heat) and some sound energy that are given off. The chemi ...
Anthropology of Physics: Energy, Matter and Culture
... predicted of these individuals when say what they are, by giving their species (e.g. “a man’ a “horse”) or their genus. So in this category of substance we have both the primary substances and certain special universals, called “secondary substances”, that are predicted of them. The remaining catego ...
... predicted of these individuals when say what they are, by giving their species (e.g. “a man’ a “horse”) or their genus. So in this category of substance we have both the primary substances and certain special universals, called “secondary substances”, that are predicted of them. The remaining catego ...
NAME - Net Start Class
... c. a bike rider in a race d. a stretched rubber band 5. Which one is an example of potential energy? a. the wind b. a battery c. a child sliding down a slide d. boiling water 6. Where do you have the most potential energy? a. at the bottom of a hill b. on the 2nd turn of the rollercoaster c. at the ...
... c. a bike rider in a race d. a stretched rubber band 5. Which one is an example of potential energy? a. the wind b. a battery c. a child sliding down a slide d. boiling water 6. Where do you have the most potential energy? a. at the bottom of a hill b. on the 2nd turn of the rollercoaster c. at the ...
Seeing Energy in Everything
... Types of Heat Transfer: Conduction is heat transfer between two objects that are touching each other. When two objects touch and one has a higher temperature than the other; heat is transferred to the object with the lower temperature. When you touch something hot it feels hot because heat is being ...
... Types of Heat Transfer: Conduction is heat transfer between two objects that are touching each other. When two objects touch and one has a higher temperature than the other; heat is transferred to the object with the lower temperature. When you touch something hot it feels hot because heat is being ...
Standard 1
... spontaneously splits itself into a slightly lighter nucleus and a very light helium nucleus. P.2.10 Describe how later, Austrian and German scientists showed that when uranium is struck by neutrons, it splits into two nearly equal parts plus two or three extra neutrons. Note that Lise Meitner, an Au ...
... spontaneously splits itself into a slightly lighter nucleus and a very light helium nucleus. P.2.10 Describe how later, Austrian and German scientists showed that when uranium is struck by neutrons, it splits into two nearly equal parts plus two or three extra neutrons. Note that Lise Meitner, an Au ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.