Earth`s Atmosphere 2017
... • Pollen—trees & flowers as they bloom in spring • Smoke—burning substances ...
... • Pollen—trees & flowers as they bloom in spring • Smoke—burning substances ...
Factors That Affect Climate
... • The temperate zones are between 23.5o and 66.5o north and between 23.5o and 66.5o south of the equator. The sun’s rays strike Earth at a smaller angle than near the equator. • Polar zones are between 66.5o north and south latitudes and the poles. The sun’s rays strike Earth at a very small angle i ...
... • The temperate zones are between 23.5o and 66.5o north and between 23.5o and 66.5o south of the equator. The sun’s rays strike Earth at a smaller angle than near the equator. • Polar zones are between 66.5o north and south latitudes and the poles. The sun’s rays strike Earth at a very small angle i ...
Some general facts about the Earth`s Atmosphere Layers of the
... the atmosphere is a dynamic system and most gases are continuously exchanged with the vegetation, oceans and organisms in a cycle gases are produced and removed from the atmosphere by chemical reaction, biological activity and physical processes. The lifetime of gases is highly variable and can rang ...
... the atmosphere is a dynamic system and most gases are continuously exchanged with the vegetation, oceans and organisms in a cycle gases are produced and removed from the atmosphere by chemical reaction, biological activity and physical processes. The lifetime of gases is highly variable and can rang ...
7th_Grade_files/10-Layers of the Atmosphere Reading for Foldable
... You live in the inner, or lowest, layer of Earth's atmosphere, the troposphere (TROH puh sfeer). Tropo- means "turning" or "changing." Conditions in the troposphere are more variable than in the other layers. The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere in which Earth's weather occurs. The depth o ...
... You live in the inner, or lowest, layer of Earth's atmosphere, the troposphere (TROH puh sfeer). Tropo- means "turning" or "changing." Conditions in the troposphere are more variable than in the other layers. The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere in which Earth's weather occurs. The depth o ...
SkyWatch
... The source of my early concern probably originated with my aunt. She lived with our family and kept the children, of whom there were eventually six, while my parents worked. It seemed to me as though she was always concerned that it might storm. She was obviously frightened by bad weather, but she d ...
... The source of my early concern probably originated with my aunt. She lived with our family and kept the children, of whom there were eventually six, while my parents worked. It seemed to me as though she was always concerned that it might storm. She was obviously frightened by bad weather, but she d ...
Wind Power - Join the pod
... strong, steady winds, although boats and caravans increasingly have small wind generators to help keep their batteries charged. ...
... strong, steady winds, although boats and caravans increasingly have small wind generators to help keep their batteries charged. ...
Atmosphere
... • The wind belts are named for the directions from which the winds come. • The westerly winds, for example, blow from west to east. These names hold for the winds in the wind belts of the Southern Hemisphere as well • Besides their effect on the global wind belts, the high and low pressure areas cre ...
... • The wind belts are named for the directions from which the winds come. • The westerly winds, for example, blow from west to east. These names hold for the winds in the wind belts of the Southern Hemisphere as well • Besides their effect on the global wind belts, the high and low pressure areas cre ...
Chapter 13 Section 3
... • Winter: drying grasses and fallen leaves decay and release carbon that was stored ▫ Causes CO2 levels to increase ...
... • Winter: drying grasses and fallen leaves decay and release carbon that was stored ▫ Causes CO2 levels to increase ...
AirPressureandWeatherPowerpoint
... and form _____________. storm clouds Low pressure areas, or lows, are shown by “L” symbols. Low barometric pressure supports unstable, and sometimes stormy weather conditions. ...
... and form _____________. storm clouds Low pressure areas, or lows, are shown by “L” symbols. Low barometric pressure supports unstable, and sometimes stormy weather conditions. ...
Document
... • Differences in heating on the earth’s surface • Wind flows from high pressure to low pressure • Ground heats surface air and then it rises • As it rises it begins to cool and fall back down ...
... • Differences in heating on the earth’s surface • Wind flows from high pressure to low pressure • Ground heats surface air and then it rises • As it rises it begins to cool and fall back down ...
extreme weather and climate change
... the jet stream. This and other natural and human-caused effects influence our weather patterns and extremes. ...
... the jet stream. This and other natural and human-caused effects influence our weather patterns and extremes. ...
Foehn Winds in Eastern Victoria
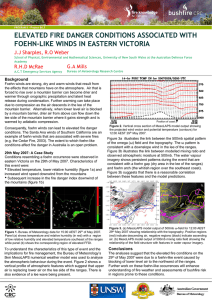
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
Wind-speed maps - Red Lodge Public Schools
... Air pressure depends on the density of the air, or how close together its molecules are. You know that a hard rubber ball is more dense than a Styrofoam ball and that ice cream is more dense that whipped cream. Air lower in the atmosphere is more dense than air above, so air pressure down low is gre ...
... Air pressure depends on the density of the air, or how close together its molecules are. You know that a hard rubber ball is more dense than a Styrofoam ball and that ice cream is more dense that whipped cream. Air lower in the atmosphere is more dense than air above, so air pressure down low is gre ...
Stratosphere (12 km – 50 km)
... Earth’s atmosphere is made up a few specific gasses. Nitrogen (N2) makes up 78% of the atmosphere, while Oxygen (O2) makes up 21% of the atmosphere. Both of these gasses are found throughout all the layers. Argon makes up 1% of the atmosphere, but it plays no significant role to life on Earth. Water ...
... Earth’s atmosphere is made up a few specific gasses. Nitrogen (N2) makes up 78% of the atmosphere, while Oxygen (O2) makes up 21% of the atmosphere. Both of these gasses are found throughout all the layers. Argon makes up 1% of the atmosphere, but it plays no significant role to life on Earth. Water ...
Layers of the Atmosphere
... weather weather occurs “Tropo” means turning or changing; named because conditions are always changing Shallowest layer of the atmosphere with almost all of the mass of the entire atmosphere… How is this possible? It is the most dense because gravity pull the molecules towards the surface. As altitu ...
... weather weather occurs “Tropo” means turning or changing; named because conditions are always changing Shallowest layer of the atmosphere with almost all of the mass of the entire atmosphere… How is this possible? It is the most dense because gravity pull the molecules towards the surface. As altitu ...
Airzone newsletter April 2010
... to other years. Deborah says the 2008 results were different from other years because of the large-scale weather patterns that were present at the time. “Certain weather conditions aggravate the air quality situation in winter, causing smoke to be trapped at the surface. These conditions include ver ...
... to other years. Deborah says the 2008 results were different from other years because of the large-scale weather patterns that were present at the time. “Certain weather conditions aggravate the air quality situation in winter, causing smoke to be trapped at the surface. These conditions include ver ...
Topic: Earth`s Atmosphere Essential Question: What are the
... Essential Question: What are the characteristics of the layers of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Composition air is made up of gases: nitrogen, oxygen and particles such as dust carried by the wind, salt picked up by the wind from ocean spray, water droplets, and ice crystals. Permanent atmospheric g ...
... Essential Question: What are the characteristics of the layers of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Composition air is made up of gases: nitrogen, oxygen and particles such as dust carried by the wind, salt picked up by the wind from ocean spray, water droplets, and ice crystals. Permanent atmospheric g ...
presentation file of the group
... Influences of assembly and breakup of supercontinents on hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere The assembly of a supercontinent may cause: 1. Decrease in total land areas 2. Low-rate oceanic production 3. Global sea level subsidence 4. Decrease of CO2 in atmosphere 5. Colder and dry weather - ‘Iceh ...
... Influences of assembly and breakup of supercontinents on hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere The assembly of a supercontinent may cause: 1. Decrease in total land areas 2. Low-rate oceanic production 3. Global sea level subsidence 4. Decrease of CO2 in atmosphere 5. Colder and dry weather - ‘Iceh ...
Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
... a. the dramatically lower temperatures in the area b. increased friction c. the comparatively high pressure gradient in the area d. the higher humidity associated with low pressures ...
... a. the dramatically lower temperatures in the area b. increased friction c. the comparatively high pressure gradient in the area d. the higher humidity associated with low pressures ...
ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE. The vertical distribution of
... Above the boundary layer the troposphere’s lapse rate averages about 6° to 7°C per kilometer, but the actual lapse rate in a given situation can be quite different. Sometimes the temperature is constant with height, or it may even increase with height in a shallow layer called an inversion. [See Inv ...
... Above the boundary layer the troposphere’s lapse rate averages about 6° to 7°C per kilometer, but the actual lapse rate in a given situation can be quite different. Sometimes the temperature is constant with height, or it may even increase with height in a shallow layer called an inversion. [See Inv ...
d64 - met ocean
... draw a diagram of a polar front depression, for both northern and southern hemispheres, showing isobars, warm and cold fronts, with circulation and warm sector draw a cross-section through a polar front depression, on the poleward and equatorial side of the centre, showing fronts, cloud and precipit ...
... draw a diagram of a polar front depression, for both northern and southern hemispheres, showing isobars, warm and cold fronts, with circulation and warm sector draw a cross-section through a polar front depression, on the poleward and equatorial side of the centre, showing fronts, cloud and precipit ...
Help - Fire Weather
... 0 = Clear - no clouds 1 = Scattered - 1 to 5 tenths of sky covered by clouds 2 = Broken - 6 to 9 tenths of sky covered by clouds 3 = Overcast - 10 tenths of sky covered by clouds 4 = Obscured - Upper level clouds not seen due to surface phenomena such as fog. Prob Pcp is the probability that precipi ...
... 0 = Clear - no clouds 1 = Scattered - 1 to 5 tenths of sky covered by clouds 2 = Broken - 6 to 9 tenths of sky covered by clouds 3 = Overcast - 10 tenths of sky covered by clouds 4 = Obscured - Upper level clouds not seen due to surface phenomena such as fog. Prob Pcp is the probability that precipi ...
SNC2P (3.3) Natural Climate Change
... • Moving continents lead to increases or decreases in volcanic activity as crustal plates move together or apart. Volcanic activity can release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contribute to global warming. It can also release massive clouds of dust and gas that linger in the atmosphere and ...
... • Moving continents lead to increases or decreases in volcanic activity as crustal plates move together or apart. Volcanic activity can release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contribute to global warming. It can also release massive clouds of dust and gas that linger in the atmosphere and ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.