Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres What is an atmosphere? Earth`s
... What is the main reason why Venus is hotter than Earth? a) Venus is closer to the Sun than Earth. b) Venus is more reflective than Earth. c) Venus is less reflective than Earth. d) Greenhouse effect is much stronger on Venus than on Earth. e) Human activity has led to declining temperatures on Earth ...
... What is the main reason why Venus is hotter than Earth? a) Venus is closer to the Sun than Earth. b) Venus is more reflective than Earth. c) Venus is less reflective than Earth. d) Greenhouse effect is much stronger on Venus than on Earth. e) Human activity has led to declining temperatures on Earth ...
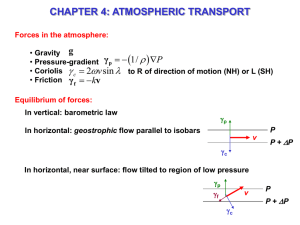
Wind
... During the next few billion years, water vapor condensed to form rain and oceans, which began to dissolve carbon dioxide. Approximately 50% of the carbon dioxide would be absorbed into the oceans. One of the earliest types of bacteria are the cyanobacteria. Fossil evidence indicates that these bacte ...
... During the next few billion years, water vapor condensed to form rain and oceans, which began to dissolve carbon dioxide. Approximately 50% of the carbon dioxide would be absorbed into the oceans. One of the earliest types of bacteria are the cyanobacteria. Fossil evidence indicates that these bacte ...
The Troposphere The Stratosphere The Mesosphere The
... You live in the inner, or lowest, layer of Earth’s atmosphere, the troposphere (TROH puh sfeer). Tropo- means “turning” or “changing.” Conditions in the troposphere are more variable than in the other layers. The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere in which Earth’s weather occurs. The depth o ...
... You live in the inner, or lowest, layer of Earth’s atmosphere, the troposphere (TROH puh sfeer). Tropo- means “turning” or “changing.” Conditions in the troposphere are more variable than in the other layers. The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere in which Earth’s weather occurs. The depth o ...
Weather Pre-Reading Activity - team7-1
... The “greenhouse effect” is Earth’s heating process in which gases in the atmosphere trap thermal energy. These gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane. These gases, also known as “greenhouse gases,” are sometimes the end result of burning fossil fuels such as gas, oil, ...
... The “greenhouse effect” is Earth’s heating process in which gases in the atmosphere trap thermal energy. These gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane. These gases, also known as “greenhouse gases,” are sometimes the end result of burning fossil fuels such as gas, oil, ...
Earth`s Amazing Atmosphere
... 8. The jet stream, a fast moving current of air responsible for moving storm systems over the land, travels through the stratosphere. Draw the symbol for the jet stream in the stratosphere. 9. Occasionally, the sun shoots outs streams of highly charged particles. When these particles contact the Ear ...
... 8. The jet stream, a fast moving current of air responsible for moving storm systems over the land, travels through the stratosphere. Draw the symbol for the jet stream in the stratosphere. 9. Occasionally, the sun shoots outs streams of highly charged particles. When these particles contact the Ear ...
Unit 4: Oceans, Atmosphere, and Weather
... Scientists believe that Earth in its earliest years was a horribly hot and violent place. Asteroids, comets, and other chunks of space debris left over from the solar system's formation continually bombarded the young planet, releasing huge amounts of heat. The decay of radioactive elements inside t ...
... Scientists believe that Earth in its earliest years was a horribly hot and violent place. Asteroids, comets, and other chunks of space debris left over from the solar system's formation continually bombarded the young planet, releasing huge amounts of heat. The decay of radioactive elements inside t ...
Atmosphere Assessment
... 14. Global winds are created as a result of a. The unequal heating of land and water b. The unequal heating of Earth due to its spherical shape c. The spinning of Earth d. The atmosphere 15. Sea breezes and land breezes are created as a result of a. The unequal heating of land and water b. The unequ ...
... 14. Global winds are created as a result of a. The unequal heating of land and water b. The unequal heating of Earth due to its spherical shape c. The spinning of Earth d. The atmosphere 15. Sea breezes and land breezes are created as a result of a. The unequal heating of land and water b. The unequ ...
Lesson Presentation
... Snow, ice, water, vegetation, and bare soil all reflect different amounts of solar radiation back to space. They also heat up at different rates. For example, dry land heats up rapidly and gives most of that heat back into the atmosphere. Water temperature changes slowly and stores heat, releasi ...
... Snow, ice, water, vegetation, and bare soil all reflect different amounts of solar radiation back to space. They also heat up at different rates. For example, dry land heats up rapidly and gives most of that heat back into the atmosphere. Water temperature changes slowly and stores heat, releasi ...
AVIATION WEATHER
... Water absorbs and radiates energy with temperature changes that are less than land. Topographical Variation – Large, deep bodies of water minimize temperature changes while large continents incur greater temperature changes – Wet soil (marshes, swamps) minimize temperature changes nearly as much as ...
... Water absorbs and radiates energy with temperature changes that are less than land. Topographical Variation – Large, deep bodies of water minimize temperature changes while large continents incur greater temperature changes – Wet soil (marshes, swamps) minimize temperature changes nearly as much as ...
Unit 7 Test Name: ATMOSPHERE and WEATHER QUIZ CLIMATE
... c. amount of gases b. temperature d. type of gases 14. As you hike up a mountain, which of the following decreases? a. temperature c. sunlight b. altitude d. none of the above 15. This layer of the atmosphere contains ozone that filters UV radiation. a. troposphere c. mesosphere b. stratosphere d. t ...
... c. amount of gases b. temperature d. type of gases 14. As you hike up a mountain, which of the following decreases? a. temperature c. sunlight b. altitude d. none of the above 15. This layer of the atmosphere contains ozone that filters UV radiation. a. troposphere c. mesosphere b. stratosphere d. t ...
Atmosphere Basics
... components and are only present at extremely low densities. This is the area where many satellites orbit the Earth. ...
... components and are only present at extremely low densities. This is the area where many satellites orbit the Earth. ...
Academic Earth/Space Science Date: March 19, 2014 ET Topic: U
... Describe how changes in concentration of minor components (e.g., O2, CO2, ozone, dust, pollution) in Earth's atmosphere are linked to climate change. S11.D.2.1.2 -- Important Compare the transmission, reflection, absorption, and radiation of solar energy to and by the Earth's surface under different ...
... Describe how changes in concentration of minor components (e.g., O2, CO2, ozone, dust, pollution) in Earth's atmosphere are linked to climate change. S11.D.2.1.2 -- Important Compare the transmission, reflection, absorption, and radiation of solar energy to and by the Earth's surface under different ...
ID - ReviewEarthScience.com
... warm air at Earth’s surface to rise high above the ground where it expands and cools. Then it sinks back to the surface where it is warmed, and the process continues. Generally, temperature and pressure in the troposphere decrease with height. But this relationship is reversed in a temperature inver ...
... warm air at Earth’s surface to rise high above the ground where it expands and cools. Then it sinks back to the surface where it is warmed, and the process continues. Generally, temperature and pressure in the troposphere decrease with height. But this relationship is reversed in a temperature inver ...
Air
... largely because of human activities. The “zig-zag,” up-and-down motion of the graph represents seasonal cycles due to photosynthetic activity (the processing of CO2 by ...
... largely because of human activities. The “zig-zag,” up-and-down motion of the graph represents seasonal cycles due to photosynthetic activity (the processing of CO2 by ...
Page 1 of 3 Curriculum: Susquenita Curriculum PENNSYLVANIA
... Describe how changes in concentration of minor components (e.g., O2, CO2, ozone, dust, pollution) in Earth's atmosphere are linked to climate change. S11.D.2.1.2 -- Important Compare the transmission, reflection, absorption, and radiation of solar energy to and by the Earth's surface under different ...
... Describe how changes in concentration of minor components (e.g., O2, CO2, ozone, dust, pollution) in Earth's atmosphere are linked to climate change. S11.D.2.1.2 -- Important Compare the transmission, reflection, absorption, and radiation of solar energy to and by the Earth's surface under different ...
Chapter 1 Composition
... in this stable layer. They are rare and called nacreous, or mother-of-pearl clouds. These clouds are thought to be made of ice crystals. They indicate that some water vapour is still present in this layer (although not much )Because they have a soft pearly luster as viewed from the surface of the ea ...
... in this stable layer. They are rare and called nacreous, or mother-of-pearl clouds. These clouds are thought to be made of ice crystals. They indicate that some water vapour is still present in this layer (although not much )Because they have a soft pearly luster as viewed from the surface of the ea ...
chapter10AtmosphersT..
... each of the two large “no-rotation” cells breaks into three smaller cells ...
... each of the two large “no-rotation” cells breaks into three smaller cells ...
Light: The Cosmic Messenger
... each of the two large “no-rotation” cells breaks into three smaller cells ...
... each of the two large “no-rotation” cells breaks into three smaller cells ...
Rain shadow effect
... Cold air is more compressed than warm air and is therefore denser. Thus, cold air falls down toward the earth, pressing down on the earth to create zones of high pressure. High pressure zones are represented by H on the weather map. Since the air in a high pressure zone is falling down toward the ea ...
... Cold air is more compressed than warm air and is therefore denser. Thus, cold air falls down toward the earth, pressing down on the earth to create zones of high pressure. High pressure zones are represented by H on the weather map. Since the air in a high pressure zone is falling down toward the ea ...
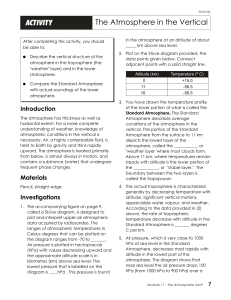
ACTIVITY The Atmosphere in the Vertical
... However, the 100-hPa pressure drop from 400 hPa to 300 hPa occurs over a vertical distance of about (1) (2) (3) km. The same pressure drop from 200 hPa to 100 hPa takes place over a vertical distance of nearly (1)(2)(3)(4)(5) km. 6. The diagram shows that air pressure of 500 hPa (half that at sea le ...
... However, the 100-hPa pressure drop from 400 hPa to 300 hPa occurs over a vertical distance of about (1) (2) (3) km. The same pressure drop from 200 hPa to 100 hPa takes place over a vertical distance of nearly (1)(2)(3)(4)(5) km. 6. The diagram shows that air pressure of 500 hPa (half that at sea le ...
Review Questions
... 22. What two factors primarily affect climate? 23. What happens to temperature as one increases latitude? Altitude? 24. Describe the general pattern of the climate zones. i.e. What do they follow? 25. Explain how topography effects climate. 26. Explain how latitude determines the amount of solar ene ...
... 22. What two factors primarily affect climate? 23. What happens to temperature as one increases latitude? Altitude? 24. Describe the general pattern of the climate zones. i.e. What do they follow? 25. Explain how topography effects climate. 26. Explain how latitude determines the amount of solar ene ...
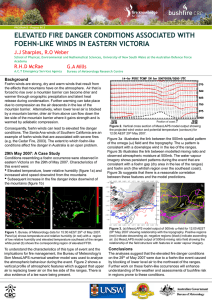
Foehn winds and effect on fire weather: Victorian Case Study File
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
... Consequently, foehn winds can lead to elevated fire danger conditions. The Santa Ana winds of Southern California are an example of foehn winds that are associated with severe fires (e.g. the Cedar Fire, 2003). The extent to which foehn-like conditions affect fire danger in Australia is an open prob ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.