5-Comparing Canadian Climates
... • The water in these currents differs from their surroundings due to differences in their temperatures and chemical composition. Water takes on the characteristics of the region it originated from. • They are driven by wind, and differences in temperature and salinity • Currents can move vast amount ...
... • The water in these currents differs from their surroundings due to differences in their temperatures and chemical composition. Water takes on the characteristics of the region it originated from. • They are driven by wind, and differences in temperature and salinity • Currents can move vast amount ...
Slideshow on Environmental Sustainability
... • If we are not all following our role as stewards in the global village, then we will not have a sustainable environment for our future children. • “We do not inherit the earth from our grandparents, we borrow it from our children.” • We must all do our part to keep our consumption of resources to ...
... • If we are not all following our role as stewards in the global village, then we will not have a sustainable environment for our future children. • “We do not inherit the earth from our grandparents, we borrow it from our children.” • We must all do our part to keep our consumption of resources to ...
STATION MODEL The "station" what ? Since we started offering you
... "river", rather, think of it like traffic on a highway - in some places the traffic speeds along and at other places the traffic slows down to perhaps to a crawl. The jetstream is no different now where it really speeds along in the upper atmosphere, meteorologists refer to it as a "divergent" area, ...
... "river", rather, think of it like traffic on a highway - in some places the traffic speeds along and at other places the traffic slows down to perhaps to a crawl. The jetstream is no different now where it really speeds along in the upper atmosphere, meteorologists refer to it as a "divergent" area, ...
Unit 6 Part 1 Notes
... The atmosphere is made of gases that take up space and transmit energy. ...
... The atmosphere is made of gases that take up space and transmit energy. ...
BataffoiiSp
... and the rest of the northern hemisphere directly, causing warm weather. In winter, when Earth orbits to the other side of the sun, the northern hemisphere tilts away from the sun. The seasons are reversed in the southern half of the globe. At what times of the year does the sun strike the northern a ...
... and the rest of the northern hemisphere directly, causing warm weather. In winter, when Earth orbits to the other side of the sun, the northern hemisphere tilts away from the sun. The seasons are reversed in the southern half of the globe. At what times of the year does the sun strike the northern a ...
Draft 2016 National Research Infrastructure Roadmap
... (HPC) to run model simulations; ii) high performance data management systems to curate and mine the large volumes of input and output data; iii) the software, i.e. the computer code, which comprises the model itself as well as the complex software that allows its execution in a variety of configurat ...
... (HPC) to run model simulations; ii) high performance data management systems to curate and mine the large volumes of input and output data; iii) the software, i.e. the computer code, which comprises the model itself as well as the complex software that allows its execution in a variety of configurat ...
SOL REVIEW #7: Atmosphere, Clouds, Weather
... the atmosphere. Two terms used to describe humidity are absolute humidity and relative humidity. Absolute humidity is the amount of water vapor divided by the amount of dry air in a certain volume of air at a particular temperature. The hotter the air is, the more water vapor it can hold. Relative h ...
... the atmosphere. Two terms used to describe humidity are absolute humidity and relative humidity. Absolute humidity is the amount of water vapor divided by the amount of dry air in a certain volume of air at a particular temperature. The hotter the air is, the more water vapor it can hold. Relative h ...
Clouds - TypePad
... No two clouds are exactly alike, and they are always changing their shape. The reason we have different types of clouds is that clouds formation takes place at different heights and ...
... No two clouds are exactly alike, and they are always changing their shape. The reason we have different types of clouds is that clouds formation takes place at different heights and ...
What is meteorology?
... property that gases have of being compressible, the whole atmosphere is in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium: this determines a horizontal stratification, in concentric ‘strata’, of the surfaces having not only a constant pressure (isobaric surfaces) and density, but also other magnitudes such as t ...
... property that gases have of being compressible, the whole atmosphere is in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium: this determines a horizontal stratification, in concentric ‘strata’, of the surfaces having not only a constant pressure (isobaric surfaces) and density, but also other magnitudes such as t ...
FREE Sample Here
... Much of Tibet lies at altitudes over 18,000 feet where the pressure is about 500 mb. At such altitudes, the Tibetans are above roughly a. 10 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. b. 25 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. c. 50 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. d. ...
... Much of Tibet lies at altitudes over 18,000 feet where the pressure is about 500 mb. At such altitudes, the Tibetans are above roughly a. 10 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. b. 25 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. c. 50 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. d. ...
Slide 1 - climateknowledge.org
... change as a society are best defined by human dimensions. Length of infrastructure investment, accumulation of wealth over a lifetime, ... ...
... change as a society are best defined by human dimensions. Length of infrastructure investment, accumulation of wealth over a lifetime, ... ...
solar radiation
... b. They are produced by the movement of air between the equator and the poles. c. They blow in a straight line from the poles toward the equator. d. They curve because of Earth’s rotation. ...
... b. They are produced by the movement of air between the equator and the poles. c. They blow in a straight line from the poles toward the equator. d. They curve because of Earth’s rotation. ...
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
... They are caused by the moon’s pull and Earth’s rotation, which are both predictable. about 12 noon The sun is much farther away from Earth than the moon is. Student should draw an oval showing high tides on the sides of Earth facing and opposite the moon. Yes, spring tides happen during the full moo ...
... They are caused by the moon’s pull and Earth’s rotation, which are both predictable. about 12 noon The sun is much farther away from Earth than the moon is. Student should draw an oval showing high tides on the sides of Earth facing and opposite the moon. Yes, spring tides happen during the full moo ...
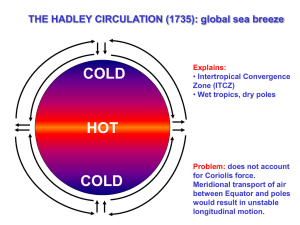
Chapter 2 WINDS Notes - Mr. Ruggiero`s Science 8-2
... patterns of the globe into 3 overall "cells" per hemisphere. That is why the winds in the tropics blow mainly east to west, and at mid latitudes, the winds blow mainly west to east. This also controls precipitation patterns on a large scale because air that is rising often loses its moisture as rain ...
... patterns of the globe into 3 overall "cells" per hemisphere. That is why the winds in the tropics blow mainly east to west, and at mid latitudes, the winds blow mainly west to east. This also controls precipitation patterns on a large scale because air that is rising often loses its moisture as rain ...
Atmosphere
... particles of air in the lowest layer of the atmosphere. For conduction to occur, substances must be in contact with one another. That's why conduction effects only a very thin atmospheric layer near earth's surface. ...
... particles of air in the lowest layer of the atmosphere. For conduction to occur, substances must be in contact with one another. That's why conduction effects only a very thin atmospheric layer near earth's surface. ...
Slide 1
... Remember to wait for the vocabulary word to pop up at the end! Can you guess it before it comes up? Created by P. Bordas MS, CCC-SLP ...
... Remember to wait for the vocabulary word to pop up at the end! Can you guess it before it comes up? Created by P. Bordas MS, CCC-SLP ...
Chapter 1 - U.S. Coast Guard Auxiliary
... weather phenomena so they can be safer and more effective in their roles. By necessity, it includes some very simple physical principles, but nothing above high school level. It will not make observers or forecasters of you, but will teach you how to make use of the vast stores of information ab ...
... weather phenomena so they can be safer and more effective in their roles. By necessity, it includes some very simple physical principles, but nothing above high school level. It will not make observers or forecasters of you, but will teach you how to make use of the vast stores of information ab ...
Earth and Environmental Science
... move freely (in the absence of obstacles). The Coriolis effect causes the path of a freely moving object to appear to curve. This is because Earth is rotating beneath the object. So even though the object's path is straight, it appears to curve. The curve appears to be to the right in the Northern H ...
... move freely (in the absence of obstacles). The Coriolis effect causes the path of a freely moving object to appear to curve. This is because Earth is rotating beneath the object. So even though the object's path is straight, it appears to curve. The curve appears to be to the right in the Northern H ...
Focus On Earth Science
... Local Winds and Eddies • Wind is air that is in motion relative to the surface. • An eddy is a current of air that runs counter to the main current. ...
... Local Winds and Eddies • Wind is air that is in motion relative to the surface. • An eddy is a current of air that runs counter to the main current. ...
Margaret Mead, American Anthropologist
... and went • These changes occur over hundreds or thousands of years • Scientists don’t know how quickly the Earth will warm or how severe the effects will be • In North America, tree swallows, Baltimore orioles and robins are nesting about 11 days earlier than they did 50 years ago; In Britain, at le ...
... and went • These changes occur over hundreds or thousands of years • Scientists don’t know how quickly the Earth will warm or how severe the effects will be • In North America, tree swallows, Baltimore orioles and robins are nesting about 11 days earlier than they did 50 years ago; In Britain, at le ...
FREE Sample Here
... Much of Tibet lies at altitudes over 18,000 feet where the pressure is about 500 mb. At such altitudes, the Tibetans are above roughly a. 10 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. b. 25 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. c. 50 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. d. ...
... Much of Tibet lies at altitudes over 18,000 feet where the pressure is about 500 mb. At such altitudes, the Tibetans are above roughly a. 10 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. b. 25 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. c. 50 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. d. ...
Meteorology Today 10E
... Much of Tibet lies at altitudes over 18,000 feet where the pressure is about 500 mb. At such altitudes, the Tibetans are above roughly a. 10 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. b. 25 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. c. 50 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. d. ...
... Much of Tibet lies at altitudes over 18,000 feet where the pressure is about 500 mb. At such altitudes, the Tibetans are above roughly a. 10 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. b. 25 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. c. 50 percent of the air molecules in the atmosphere. d. ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.