Overview - RI
... The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by Atomic Structure so students can better understand why attraction and repulsion exist. Both Excited States and Photons and Spectroscopy are also supported by an understanding of Atomic Structure. Students will understand at a deeper level that atoms in their ...
... The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by Atomic Structure so students can better understand why attraction and repulsion exist. Both Excited States and Photons and Spectroscopy are also supported by an understanding of Atomic Structure. Students will understand at a deeper level that atoms in their ...
Part II
... • Capacitors can retain charge indefinitely even when not connected to a voltage source! ...
... • Capacitors can retain charge indefinitely even when not connected to a voltage source! ...
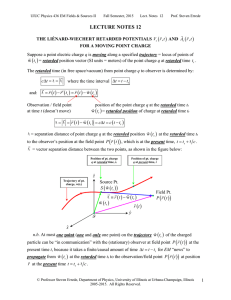
Lecture Notes 12: Lienard-Wiechert Retarded Potentials for Moving Point Charge, Retarded Electric and Magnetic Fields Associated with Moving Point Charge
... One might think that this problem would be understandable e.g. for a moving extended charge distribution, but that it would disappear/go away/vanish for point charges. However it doesn’t !!! In Maxwell’s equations of electrodynamics, formulated in terms of electric charge and current ...
... One might think that this problem would be understandable e.g. for a moving extended charge distribution, but that it would disappear/go away/vanish for point charges. However it doesn’t !!! In Maxwell’s equations of electrodynamics, formulated in terms of electric charge and current ...
by George Alexander The notion of a magnet with only one pole is
... to the heavy nuclei of elements like iron or oxygen, riddle materials like plastic and photographic film as easily as shotgun pellets p e n e t r a t e s t y r o f o a m . T o identify cosmic ray strikes, scientists are able to make the tracks in the plastic sheets visible by a chemical etching proc ...
... to the heavy nuclei of elements like iron or oxygen, riddle materials like plastic and photographic film as easily as shotgun pellets p e n e t r a t e s t y r o f o a m . T o identify cosmic ray strikes, scientists are able to make the tracks in the plastic sheets visible by a chemical etching proc ...
SAM Teachers Guide - RI
... The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by Atomic Structure so students can better understand why attraction and repulsion exist. Both Excited States and Photons and Spectroscopy are also supported by an understanding of Atomic Structure. Students will understand at a deeper level that atoms in ...
... The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by Atomic Structure so students can better understand why attraction and repulsion exist. Both Excited States and Photons and Spectroscopy are also supported by an understanding of Atomic Structure. Students will understand at a deeper level that atoms in ...
Overview - RI
... The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by Atomic Structure so students can better understand why attraction and repulsion exist. Both Excited States and Photons and Spectroscopy are also supported by an understanding of Atomic Structure. Students will understand at a deeper level that atoms in their ...
... The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by Atomic Structure so students can better understand why attraction and repulsion exist. Both Excited States and Photons and Spectroscopy are also supported by an understanding of Atomic Structure. Students will understand at a deeper level that atoms in their ...
feldspar, quartz
... region, electron work function, width of the forbidden gap, the concentration and mobility of the charge carriers, i.e., either electrons or holes, are taken into account by the theory. Minerals with different energetic levels donate or accept electron(s) when they are brought into intimate contact ...
... region, electron work function, width of the forbidden gap, the concentration and mobility of the charge carriers, i.e., either electrons or holes, are taken into account by the theory. Minerals with different energetic levels donate or accept electron(s) when they are brought into intimate contact ...
How pulsars work - SLAC
... Pair formation through CR (in young pulsars) or nonresonant inverse Compton scattering on thermal photons (most pulsars). Multiplicities due to ICS are smaller (102) than from CR. Hibschmann & Arons 01 ...
... Pair formation through CR (in young pulsars) or nonresonant inverse Compton scattering on thermal photons (most pulsars). Multiplicities due to ICS are smaller (102) than from CR. Hibschmann & Arons 01 ...
Electric fields are
... Electric Potential Energy can be considered unrealized kinetic energy for a particle in a fixed location. It takes work to move a particle from a position of lower potential energy to a position of higher potential energy. This increase in potential energy at rest may be converted to (or “realized a ...
... Electric Potential Energy can be considered unrealized kinetic energy for a particle in a fixed location. It takes work to move a particle from a position of lower potential energy to a position of higher potential energy. This increase in potential energy at rest may be converted to (or “realized a ...
Chapter 3 Electric Potential
... When moving from A to C, the change in potential is ∆VCA = − E0 y . On the other hand, when going from C to B, ∆VBC = 0 since the path is perpendicular to the direction of E . Thus, the same result is obtained irrespective of the path taken, consistent with the fact that E is conservative. Notice th ...
... When moving from A to C, the change in potential is ∆VCA = − E0 y . On the other hand, when going from C to B, ∆VBC = 0 since the path is perpendicular to the direction of E . Thus, the same result is obtained irrespective of the path taken, consistent with the fact that E is conservative. Notice th ...
5th lecture capacitors
... Let the electric charge on the first conductor +Q while –Q on the second one. In the following such a system will be called as electric capacitor or condenser. (The latter is considered an antiquated term in English, but most other languages use an equivalent, like the German word "Kondensator" or t ...
... Let the electric charge on the first conductor +Q while –Q on the second one. In the following such a system will be called as electric capacitor or condenser. (The latter is considered an antiquated term in English, but most other languages use an equivalent, like the German word "Kondensator" or t ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.