Aalborg Universitet Unification and CPH Theory Javadi, Hossein; Forouzbakhsh, Farshid
... Electromagnetic energy converts to matter and anti-matter such as charged particles. Charged particles use gravitons and generate electromagnetic field by. In fact a charged particle is a generator to producing virtual photons, that they are negative and positive photons. This looking shows how two ...
... Electromagnetic energy converts to matter and anti-matter such as charged particles. Charged particles use gravitons and generate electromagnetic field by. In fact a charged particle is a generator to producing virtual photons, that they are negative and positive photons. This looking shows how two ...
Destabilisation of colloidal suspensions
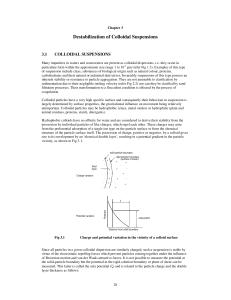
... medium they reduce the double layer thickness, while the adsorption of ions of opposite charge by a colloid reduces its own net charge. This influence of added electrolyte charge on colloid stability is shown graphically in Fig 3.2. It has been found that the effectiveness of added ions of opposite ...
... medium they reduce the double layer thickness, while the adsorption of ions of opposite charge by a colloid reduces its own net charge. This influence of added electrolyte charge on colloid stability is shown graphically in Fig 3.2. It has been found that the effectiveness of added ions of opposite ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Physics with Calculus II
... Investigate the functioning of motor, generator, and transformer. Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: a. ...
... Investigate the functioning of motor, generator, and transformer. Learning objectives What you will learn as you master the competency: a. ...
Chapter 4 Electrical Interaction Forces: From
... 4.4 Polarization Force Density As ions migrate through a liquid under the influence of an electric field, they impart a net force density ρ e E to the liquid. This is a consequence of the collisions between the individual ions and the neutral liquid molecules. An additional force density of electric ...
... 4.4 Polarization Force Density As ions migrate through a liquid under the influence of an electric field, they impart a net force density ρ e E to the liquid. This is a consequence of the collisions between the individual ions and the neutral liquid molecules. An additional force density of electric ...
document
... We will not be considering the cases with mutual capacitance. To eliminate mutual capacitance we'll again assume we have a uniformly transposed line, using similar arguments to the case of inductance. For the previous three conductor example: qa ...
... We will not be considering the cases with mutual capacitance. To eliminate mutual capacitance we'll again assume we have a uniformly transposed line, using similar arguments to the case of inductance. For the previous three conductor example: qa ...
EE369 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS
... We will not be considering the cases with mutual capacitance. To eliminate mutual capacitance we'll again assume we have a uniformly transposed line, using similar arguments to the case of inductance. For the previous three conductor example: qa ...
... We will not be considering the cases with mutual capacitance. To eliminate mutual capacitance we'll again assume we have a uniformly transposed line, using similar arguments to the case of inductance. For the previous three conductor example: qa ...
New emerging experimental results (ref) in the last couple of
... experimental observations is obtained. We assume that the interaction of the gold/monolayer interface with the vacuum causes a change in the local ZPE. The change in ZPE will redefine in terms the basic electronic properties of the system. Due to interaction of the interface electrons with the vacuu ...
... experimental observations is obtained. We assume that the interaction of the gold/monolayer interface with the vacuum causes a change in the local ZPE. The change in ZPE will redefine in terms the basic electronic properties of the system. Due to interaction of the interface electrons with the vacuu ...
(positive) charge flows into the battery via the negative terminal and
... A battery has two terminals, a higher potential terminal, often called the positive terminal, and a lower potential terminal, often called the negative terminal. When a battery is connected across a resistor, positive charge (in the conventional charge flow model) flows through the battery; it flows ...
... A battery has two terminals, a higher potential terminal, often called the positive terminal, and a lower potential terminal, often called the negative terminal. When a battery is connected across a resistor, positive charge (in the conventional charge flow model) flows through the battery; it flows ...
Powerpoint
... Changes in Electric Potential Energy elta PEe For each situation below, identify which arrangement (final or initial) has more electrical potential energy within the system of charges and their field. ...
... Changes in Electric Potential Energy elta PEe For each situation below, identify which arrangement (final or initial) has more electrical potential energy within the system of charges and their field. ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.