Lecture_5
... the charge on each plate if a 12-V battery is connected across the two plates? (c) What is the electric field between the plates? (d) Estimate the area of the plates needed to achieve a capacitance of 1 F, given the same air gap d. ...
... the charge on each plate if a 12-V battery is connected across the two plates? (c) What is the electric field between the plates? (d) Estimate the area of the plates needed to achieve a capacitance of 1 F, given the same air gap d. ...
Slide 1
... positive charge, anions induce negative charge) if the ion is in the higher dielectric regime (in the solution). ...
... positive charge, anions induce negative charge) if the ion is in the higher dielectric regime (in the solution). ...
Atomic Number and Mass Number
... In 1932, the English physicist James Chadwick carried out an experiment to show that neutrons exist. Chadwick concluded that the particles he produced were neutral because a charged object did not deflect their paths. A neutron is a neutral subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... In 1932, the English physicist James Chadwick carried out an experiment to show that neutrons exist. Chadwick concluded that the particles he produced were neutral because a charged object did not deflect their paths. A neutron is a neutral subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Document
... The charge is equal. However, the potential on the first is larger because the radius is larger. Because V is proportional to Q/r, with Q the same for both, and r, the distance away from the surface the same for both, Q/r is the same, thus V is the same [in “kQ/r” (potential of point charge) r is th ...
... The charge is equal. However, the potential on the first is larger because the radius is larger. Because V is proportional to Q/r, with Q the same for both, and r, the distance away from the surface the same for both, Q/r is the same, thus V is the same [in “kQ/r” (potential of point charge) r is th ...
Capacitance - the SASPhysics.com
... When t=RC, Q Q0 e i.e. Q=0.368Q0 RC is known as the Time constant Q=CV It is the time taken for the charge (and V=IR therefore also the voltage and current) to drop to 1/e of its initial value • In another period RC, the charge will have dropped to 1/e2 of its initial value • etc... • cf radioacti ...
... When t=RC, Q Q0 e i.e. Q=0.368Q0 RC is known as the Time constant Q=CV It is the time taken for the charge (and V=IR therefore also the voltage and current) to drop to 1/e of its initial value • In another period RC, the charge will have dropped to 1/e2 of its initial value • etc... • cf radioacti ...
Magnetic Force on a Current
... τ = I L2 B sin θ For different shapes, this becomes Section 20.5 τ = I A B sin θ ...
... τ = I L2 B sin θ For different shapes, this becomes Section 20.5 τ = I A B sin θ ...
Chapter 16 Notes
... • Use the following equations when working through the circuit diagrams: – Capacitance equation: C = Q / V – Capacitors in parallel: Ceq = C1 + C2 + … – Capacitors in parallel all have the same voltage differences as does the equivalent capacitance. – Capacitors in series: 1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + … – ...
... • Use the following equations when working through the circuit diagrams: – Capacitance equation: C = Q / V – Capacitors in parallel: Ceq = C1 + C2 + … – Capacitors in parallel all have the same voltage differences as does the equivalent capacitance. – Capacitors in series: 1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + … – ...
Hogan_E_AAC2013
... • Use of Rb plasma explored for mitigating head erosion and ion motion • For the beam and plasma parameters used, ionization of Rb 1+ ions leads to injection of RbII electrons in the wake in distributed fashion • Beam loading of the wake reduces the average transformer ratio from 1 to 0.85
• Sim ...
... • Use of Rb plasma explored for mitigating head erosion and ion motion • For the beam and plasma parameters used, ionization of Rb 1+ ions leads to injection of RbII electrons in the wake in distributed fashion • Beam loading of the wake reduces the average transformer ratio
atoms
... Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. They combine in simple whole number ratio, always with the same relative number and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms, changes in the way they are bonded together. The atoms t ...
... Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. They combine in simple whole number ratio, always with the same relative number and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms, changes in the way they are bonded together. The atoms t ...
PPA6_Lecture_Ch_18
... • Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge. • Conventional current is in the direction that positive charge would flow. ...
... • Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge. • Conventional current is in the direction that positive charge would flow. ...
The pKa value of a particular group is not the same in all molecules
... group is in part dependent on the environment of the group in a molecule. Let’s define another quantity characteristic of ionizing molecules. The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which the average net charge on a molecule is zero. ...
... group is in part dependent on the environment of the group in a molecule. Let’s define another quantity characteristic of ionizing molecules. The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which the average net charge on a molecule is zero. ...
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 18 Physics: Principles with
... • Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge. • Conventional current is in the direction that positive charge would flow. • Resistance is the ratio of voltage to current: ...
... • Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge. • Conventional current is in the direction that positive charge would flow. • Resistance is the ratio of voltage to current: ...
lesson homework Tuesday may 1st
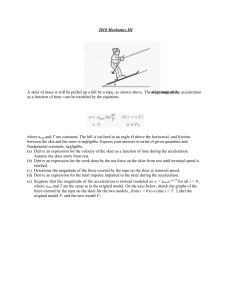
... where r is the distance from the center of the cloud. Express all algebraic answers in terms of Q, R, and fundamental constants (a) Determine the following as a function of r for r > R. i. The magnitude E of the electric field ii. The electric potential V (b) A proton is placed at point P shown abov ...
... where r is the distance from the center of the cloud. Express all algebraic answers in terms of Q, R, and fundamental constants (a) Determine the following as a function of r for r > R. i. The magnitude E of the electric field ii. The electric potential V (b) A proton is placed at point P shown abov ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.