JSUNIL TUTORIAL,SAMASTIPUR ,BIHAR Class- X Subject – Science (ELECTRICITY)
... 3.A wire of resistivity rho is stretched to double its length. What will be its new resistance? ...
... 3.A wire of resistivity rho is stretched to double its length. What will be its new resistance? ...
$doc.title
... due to the electrons that are present simply because the material is purely crystalline (for example, Ge or Si) and not due to the presence of impurities. The only way in which conduction may take place is to provide the electrons with an energy equal to or greater than EG – thus enabling them to ju ...
... due to the electrons that are present simply because the material is purely crystalline (for example, Ge or Si) and not due to the presence of impurities. The only way in which conduction may take place is to provide the electrons with an energy equal to or greater than EG – thus enabling them to ju ...
Lab #1 – The Electric Field of Charged Particles
... The purpose of the scale factor will be explained later in this lab. e) In your create objects section, type code to create the first particle (the particles will represent atoms), give the atom the charge of 3 excess protons, and create the arrow you will use to visualize the E field: atom1 = spher ...
... The purpose of the scale factor will be explained later in this lab. e) In your create objects section, type code to create the first particle (the particles will represent atoms), give the atom the charge of 3 excess protons, and create the arrow you will use to visualize the E field: atom1 = spher ...
Physics 6B Electric Field Examples
... Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field produced by q1 and q2 at the origin. Find the net electric force on a charge q3=-0.6nC placed at the origin. b) The electric field near a single point charge is given by the formula: ...
... Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field produced by q1 and q2 at the origin. Find the net electric force on a charge q3=-0.6nC placed at the origin. b) The electric field near a single point charge is given by the formula: ...
Charge generation in Thunderstorms by collision of ice crystals with
... Small droplets having a radius of less than The relaxation time obtained by this method 180 ,u will coalesce with the raindrop. Larger ranges from I O - ~to 10-6 s within the ranges of droplets will travel through the raindrop and tern erature and frequency given above. T e relaxation time may also ...
... Small droplets having a radius of less than The relaxation time obtained by this method 180 ,u will coalesce with the raindrop. Larger ranges from I O - ~to 10-6 s within the ranges of droplets will travel through the raindrop and tern erature and frequency given above. T e relaxation time may also ...
W02D2_Presentation_answers
... The sheet in the middle is negatively charged with charge per unit area 2 , and the other two sheets are positively charged with area charge per unit ...
... The sheet in the middle is negatively charged with charge per unit area 2 , and the other two sheets are positively charged with area charge per unit ...
Powerpoint Slides
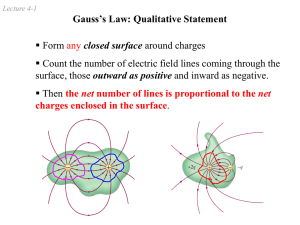
... the same relationship – there are lines (or, in three dimensions, surfaces) of constant potential. The electric field is perpendicular to these equipotential lines, and strongest where the lines are closest together. ...
... the same relationship – there are lines (or, in three dimensions, surfaces) of constant potential. The electric field is perpendicular to these equipotential lines, and strongest where the lines are closest together. ...
R - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... In general, charge density can vary with position. In this case, we can more carefully define density in terms of the charge in a very small volume at each point in space. The density then looks like a derivative: ...
... In general, charge density can vary with position. In this case, we can more carefully define density in terms of the charge in a very small volume at each point in space. The density then looks like a derivative: ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.