Minerals Study Guide The format on tests and quizzes is a variety of
... and free response questions. The questions are designed to assess whether you know the meanings of key terms, understand major concepts and how well you can apply your understanding to solving problems. Study your readings, assignments, review handouts, labs and class notes. Diagrams: diagram showin ...
... and free response questions. The questions are designed to assess whether you know the meanings of key terms, understand major concepts and how well you can apply your understanding to solving problems. Study your readings, assignments, review handouts, labs and class notes. Diagrams: diagram showin ...
- SlideBoom
... Recent studies have shown, however, that this color is due to the high concentration of iron. ...
... Recent studies have shown, however, that this color is due to the high concentration of iron. ...
MME 4713 Polymers D3
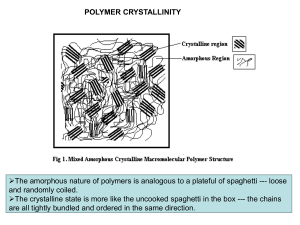
... The amorphous nature of polymers is analogous to a plateful of spaghetti --- loose and randomly coiled. The crystalline state is more like the uncooked spaghetti in the box --- the chains are all tightly bundled and ordered in the same direction. ...
... The amorphous nature of polymers is analogous to a plateful of spaghetti --- loose and randomly coiled. The crystalline state is more like the uncooked spaghetti in the box --- the chains are all tightly bundled and ordered in the same direction. ...
Section 4-2 What gives metals their distinctive properties?
... Characteristics of Metals • Elements that are shiny, malleable, ductile and good conductors of heat and electricity – Malleable – hammered or rolled into sheets – Ductile – can be drawn into wires ...
... Characteristics of Metals • Elements that are shiny, malleable, ductile and good conductors of heat and electricity – Malleable – hammered or rolled into sheets – Ductile – can be drawn into wires ...
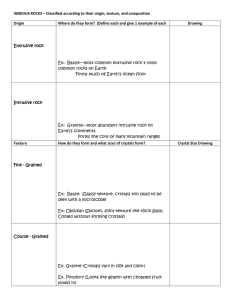
IGNEOUS ROCKS – Classified according to their origin, texture, and
... Ex: Granite—most abundant intrusive rock on Earth’s continents Forms the core of many mountain ranges Texture ...
... Ex: Granite—most abundant intrusive rock on Earth’s continents Forms the core of many mountain ranges Texture ...
Crystal

A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions, are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations.The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification.The word crystal is derived from the Ancient Greek word κρύσταλλος (krustallos), meaning both “ice” and “rock crystal”, from κρύος (kruos), ""icy cold, frost"".Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Examples of polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of solids is amorphous solids, where the atoms have no periodic structure whatsoever. Examples of amorphous solids include glass, wax, and many plastics.