of a mineral? - Bakersfield College
... •4 oxygens with 1 silicon •building block for all silicate minerals •very strong bond – hard to break •(Si04)-4 unstable, wants to combine with metals “triangles” put together – very stable makes tough, hard minerals ...
... •4 oxygens with 1 silicon •building block for all silicate minerals •very strong bond – hard to break •(Si04)-4 unstable, wants to combine with metals “triangles” put together – very stable makes tough, hard minerals ...
Igneous Rocks
... formed”, is a rock type that forms from the solidification of a molten mineral solution. ...
... formed”, is a rock type that forms from the solidification of a molten mineral solution. ...
LCD Television Technology
... such as LCD televisions and LCD monitors Has a naturally crystalline structure Reacts to electric currents in particular ways, usually by untwisting to different degrees depending on the voltage of the current it is exposed to ...
... such as LCD televisions and LCD monitors Has a naturally crystalline structure Reacts to electric currents in particular ways, usually by untwisting to different degrees depending on the voltage of the current it is exposed to ...
igneous rocks
... meaning “Fire formed”, is a rock type that forms from the solidification of a molten mineral solution. ...
... meaning “Fire formed”, is a rock type that forms from the solidification of a molten mineral solution. ...
001 Mineral Name and Class: Quartz, Tectosilicate Chemical
... Chemical Formula: SiO2 Crystal System: Hexagonal Rock Formation Associated with: Bar Harbor Formation (found on top of) Collection Location: C.O.A. Beach Bar Harbor, Maine 44.39˚ N, 68.22˚ W Description: Quartz is known for its hardness of 7 used in the Mohs Hardness Scale. It ...
... Chemical Formula: SiO2 Crystal System: Hexagonal Rock Formation Associated with: Bar Harbor Formation (found on top of) Collection Location: C.O.A. Beach Bar Harbor, Maine 44.39˚ N, 68.22˚ W Description: Quartz is known for its hardness of 7 used in the Mohs Hardness Scale. It ...
Minerals
... at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
... at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
Minerals - Center for Mathematics & Science Education CMSE
... at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
... at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
Rock and Minerals Powerpoint
... at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
... at this level of consumption the average newborn infant will need a lifetime supply of: -795 lbs of lead (car batteries, electric components) -757 lbs of zinc (to make brass, rubber, paints) -1500lbs of copper (electrical motors, wirings ...
Igneous Rocks
... Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks are formed by crystallization from magma. They include two types; Volcanic or extrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and crystallizes on the surface of the Earth. Pluto ...
... Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks are formed by crystallization from magma. They include two types; Volcanic or extrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and crystallizes on the surface of the Earth. Pluto ...
Minerals - Madison Public Schools
... inorganic solid that has a definite crystalline structure. • All minerals contain one or more of the 92 naturally occurring elements. ...
... inorganic solid that has a definite crystalline structure. • All minerals contain one or more of the 92 naturally occurring elements. ...
Growth Of Zinc Oxide Crystals By Accelerated Evoporation
... (2nd B), now 12th, group). The native doping of ...
... (2nd B), now 12th, group). The native doping of ...
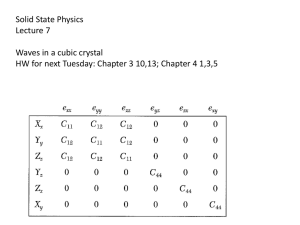
Solid State Physics Lectures 7 Waves in a cubic crystal
... We can measure phonon dispersion (in other words, w vs K) for phonons by INELASTIC SCATTERING (for example, of neutrons.) We need to measure how much energy the neutron loses, and how it’s ...
... We can measure phonon dispersion (in other words, w vs K) for phonons by INELASTIC SCATTERING (for example, of neutrons.) We need to measure how much energy the neutron loses, and how it’s ...
or here in RTF format
... Describe the overall texture of the specimen, and try to decide if it's an igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary rock. eg "a foliated metamorphic rock with 2-3mm porphyroblasts and tight small-scale folds" (4) Decide how many different phases are present, and estimate the volume % of each using the st ...
... Describe the overall texture of the specimen, and try to decide if it's an igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary rock. eg "a foliated metamorphic rock with 2-3mm porphyroblasts and tight small-scale folds" (4) Decide how many different phases are present, and estimate the volume % of each using the st ...
Chapter 5.1: Minerals
... begin to break down chemically. • The temperature and pressure becomes great enough to change the mineral in a solid state. • The free atoms, ions, and molecules recombine forming new minerals. ...
... begin to break down chemically. • The temperature and pressure becomes great enough to change the mineral in a solid state. • The free atoms, ions, and molecules recombine forming new minerals. ...
No Slide Title
... Certain groups of directions are equivalent; they are only different because of the way we constructed the coordinates. In cubic lattices, [100] is equivalent to [010] if we redefine the coordinate system (or rotate the unit cell). Equivalent groups of equivalent directions are written in
(exa ...
... Certain groups of directions are equivalent; they are only different because of the way we constructed the coordinates. In cubic lattices, [100] is equivalent to [010] if we redefine the coordinate system (or rotate the unit cell). Equivalent groups of equivalent directions are written in
1 • Welcome to the GIA Junior Gemologist Program
... • Some magma may feed volcanoes on the Earth's surface, but most remains trapped below, where it cools very slowly over thousands or millions of years until it solidifies (hardens) • When magma cools and hardens slowly, the individual minerals in it form large grains (or crystals) that are easy to s ...
... • Some magma may feed volcanoes on the Earth's surface, but most remains trapped below, where it cools very slowly over thousands or millions of years until it solidifies (hardens) • When magma cools and hardens slowly, the individual minerals in it form large grains (or crystals) that are easy to s ...
Crystal chemistry - thephysicsteacher.ie
... Profile: Julia studied chemistry, physics and maths at A level. She then completed a degree in chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Nottingham in the UK. Julia has worked in protein purification for a number of years, including spending time at the chemical company called Bayer in Califor ...
... Profile: Julia studied chemistry, physics and maths at A level. She then completed a degree in chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Nottingham in the UK. Julia has worked in protein purification for a number of years, including spending time at the chemical company called Bayer in Califor ...
Day 8
... What are the three types of rock? igneous, metamorphic & sedimentary What's the major difference between the three types? The major difference is in how they form. ...
... What are the three types of rock? igneous, metamorphic & sedimentary What's the major difference between the three types? The major difference is in how they form. ...
Mineral & Rock
... The Organics Class: The "Minerals" composed of organic chemicals! The Mineraloids: The "Minerals" that lack crystal structure! ...
... The Organics Class: The "Minerals" composed of organic chemicals! The Mineraloids: The "Minerals" that lack crystal structure! ...
Crystal

A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions, are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations.The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification.The word crystal is derived from the Ancient Greek word κρύσταλλος (krustallos), meaning both “ice” and “rock crystal”, from κρύος (kruos), ""icy cold, frost"".Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Examples of polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of solids is amorphous solids, where the atoms have no periodic structure whatsoever. Examples of amorphous solids include glass, wax, and many plastics.