Applied quantum mechanics 1 Applied Quantum Mechanics
... (d) Show that E kinetic = – E potential 2 (which is a result predicted by the virial theorem). (e) Show that the peak in radial probability occurs at r = a B Z . (f) Show that the expectation value r = 3a B 2Z . (g) Show that the expectation value of momentum p = 0 . Problem 11.3 T ...
... (d) Show that E kinetic = – E potential 2 (which is a result predicted by the virial theorem). (e) Show that the peak in radial probability occurs at r = a B Z . (f) Show that the expectation value r = 3a B 2Z . (g) Show that the expectation value of momentum p = 0 . Problem 11.3 T ...
Problem: Runners at a marathon race are assigned consecutive
... of the entrants with a mathematical bent noticed that the sum of the numbers less than or equal to his own was equal to the sum of the numbers greater. If there were more than 10 runners but less than 100, what number was he and how many runners were there in the race? Solution: We consider a more g ...
... of the entrants with a mathematical bent noticed that the sum of the numbers less than or equal to his own was equal to the sum of the numbers greater. If there were more than 10 runners but less than 100, what number was he and how many runners were there in the race? Solution: We consider a more g ...
Chapter 5 Quiz Graph - Crestwood Local Schools
... 5. If the system 3x + 5y = 16 and 8x – 5y = 28 is solved by elimination, what is the value of x? a. 4 b. 5 c. -6 d. 7 5. ________ 6. If the system 2x – 5y = 1 and -3x + 7y = -3 is to be solved by elimination of the variable x, and the first equation is multiplied by 3, then by which number should th ...
... 5. If the system 3x + 5y = 16 and 8x – 5y = 28 is solved by elimination, what is the value of x? a. 4 b. 5 c. -6 d. 7 5. ________ 6. If the system 2x – 5y = 1 and -3x + 7y = -3 is to be solved by elimination of the variable x, and the first equation is multiplied by 3, then by which number should th ...
Title: Systems of Linear Equations – Elimination (Addition) Method
... Purpose: This is intended to refresh your knowledge about solving systems of linear equations using the elimination (addition) method, along with analyzing the solution. Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two ...
... Purpose: This is intended to refresh your knowledge about solving systems of linear equations using the elimination (addition) method, along with analyzing the solution. Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two ...
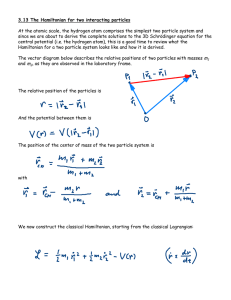
3.13 The Hamiltonian for two interacting particles At the atomic scale
... This is the same expression for H that we were using all along, since section 3.4, but now, instead of the mass of a single particle m , we have the so called reduced mass μ for two particles in relative motion. We will continue where we left off in section 3.12 but will now use the reduced mass in ...
... This is the same expression for H that we were using all along, since section 3.4, but now, instead of the mass of a single particle m , we have the so called reduced mass μ for two particles in relative motion. We will continue where we left off in section 3.12 but will now use the reduced mass in ...
KTH | SI3005 Qualitative and Approximate Methods in Theoretical
... The course is devoted to some "tools of the trade" in theoretical physics, the methods that are widely used by experienced theorists but rarely taught in a single course. These are the qualitative and approximate methods that allow one to reveal the characteristic features of the studied problem and ...
... The course is devoted to some "tools of the trade" in theoretical physics, the methods that are widely used by experienced theorists but rarely taught in a single course. These are the qualitative and approximate methods that allow one to reveal the characteristic features of the studied problem and ...