Relative Intensities of the lines in a Zeeman pattern
... to t, the field lines must adjust such that those inside a distance ct are directed away from the instantaneous position of the source charge while the lines outside a distance c(t+t) are directed away from the instantaneous position that the charge would have had if it had not been accelerated. B ...
... to t, the field lines must adjust such that those inside a distance ct are directed away from the instantaneous position of the source charge while the lines outside a distance c(t+t) are directed away from the instantaneous position that the charge would have had if it had not been accelerated. B ...
Standardized Test Prep Chapter 17
... • Resistance is the opposition presented to electric current by a material or device. • The SI units for resistance is the ohm (Ω) and is equal to one volt per ampere. • Resistance ...
... • Resistance is the opposition presented to electric current by a material or device. • The SI units for resistance is the ohm (Ω) and is equal to one volt per ampere. • Resistance ...
Physics Ch 17 pp notes
... • Resistance is the opposition presented to electric current by a material or device. • The SI units for resistance is the ohm (Ω) and is equal to one volt per ampere. • Resistance ...
... • Resistance is the opposition presented to electric current by a material or device. • The SI units for resistance is the ohm (Ω) and is equal to one volt per ampere. • Resistance ...
N - Mr Bernabo at Affton High School
... The earth is also a magnet. It has North and South Magnetic Poles (a little off from geographic poles) ...
... The earth is also a magnet. It has North and South Magnetic Poles (a little off from geographic poles) ...
CBSE-SAMPLE PAPER 1 -2011 -Class XII
... Q. 2. What is the force experienced by a positively charges particle Q moving at right angles to a uniform electric field E. Q. 3. What is the order of voltages that can be built up using a Van De Graff generator? Q. 4. What is the angle b/w Electric field and Dipole moment at an axial point? Q. 5 ...
... Q. 2. What is the force experienced by a positively charges particle Q moving at right angles to a uniform electric field E. Q. 3. What is the order of voltages that can be built up using a Van De Graff generator? Q. 4. What is the angle b/w Electric field and Dipole moment at an axial point? Q. 5 ...
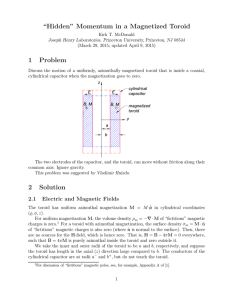
“Hidden” Momentum in a Magnetized Toroid 1 Problem 2
... work done by the electric field on the moving charges that comprise the electrical current [6, 30, 40, 41, 42]. This is appealing from the point of view of mechanics, but leaves open the question of where does the energy gained by the charges come from? A tacit view associated with the work done by t ...
... work done by the electric field on the moving charges that comprise the electrical current [6, 30, 40, 41, 42]. This is appealing from the point of view of mechanics, but leaves open the question of where does the energy gained by the charges come from? A tacit view associated with the work done by t ...
5.03 Magnetospheric Contributions to the Terrestrial Magnetic Field
... internal fields generated by every other moving particle, all equations are coupled and have to be solved simultaneously. Such a full solution is not only too difficult to obtain, but also of no practical use, since most of the time one is interested in knowing average quantities like density and te ...
... internal fields generated by every other moving particle, all equations are coupled and have to be solved simultaneously. Such a full solution is not only too difficult to obtain, but also of no practical use, since most of the time one is interested in knowing average quantities like density and te ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.