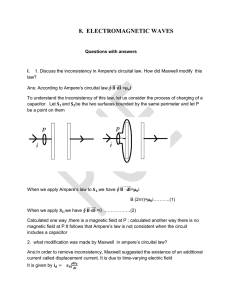
Batteries don`t store charge. They store energy. A chemical battery
... Lead Acid (Car) Battery The rxn on the right will not go in the direction indicated unless the electrolyte sol’n potential is closer than 1.685 V to the + electrode potential. i.e. the + electrode can be no more than 1.685 V higher in potential than the electrolyte sol’n. Pb+2 is in the form of sol ...
... Lead Acid (Car) Battery The rxn on the right will not go in the direction indicated unless the electrolyte sol’n potential is closer than 1.685 V to the + electrode potential. i.e. the + electrode can be no more than 1.685 V higher in potential than the electrolyte sol’n. Pb+2 is in the form of sol ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 8. Explain why a choke coil is preferred over ohmic resistance for diminishing current in an electrical circuit? 9. State the significance of Poynting vector. 10. Distinguish between antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. PART – B Answer ANY FOUR questions: ...
... 8. Explain why a choke coil is preferred over ohmic resistance for diminishing current in an electrical circuit? 9. State the significance of Poynting vector. 10. Distinguish between antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. PART – B Answer ANY FOUR questions: ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... • The biggest achievement of 19th century electromagnetic theory is the prediction and experimental verification that the electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space – This accomplishment • Opened a new world of communication • Yielded the prediction that the light is an EM wave ...
... • The biggest achievement of 19th century electromagnetic theory is the prediction and experimental verification that the electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space – This accomplishment • Opened a new world of communication • Yielded the prediction that the light is an EM wave ...
PHYS 1442-004, Dr. Brandt
... • The biggest achievement of 19th century electromagnetic theory is the prediction and experimental verification that the electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space – This accomplishment • Opened a new world of communication • Yielded the prediction that the light is an EM wave ...
... • The biggest achievement of 19th century electromagnetic theory is the prediction and experimental verification that the electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space – This accomplishment • Opened a new world of communication • Yielded the prediction that the light is an EM wave ...
PPT - University of Illinois Urbana
... From the construction, it is evident that the resultant force is directed away from the center of the square. The magnitude of this resultant force is given by ...
... From the construction, it is evident that the resultant force is directed away from the center of the square. The magnitude of this resultant force is given by ...
... A dielectric is a nonconducting material that, when placed between the plates of a capacitor, increases the capacitance. Dielectrics include rubber, glass, and waxed paper With a dielectric, the capacitance becomes C = κCo. The capacitance increases by the factor κ when the dielectric completely ...
Investigation of Deuteron-Deuteron Cold Fusion in a Cavity Abstract
... 14.4 eV/ (10-10 m) is a constant, not an unknown parameter. Since 'Cold fusion' of the two deuterons in a Deuterium molecule has never been observed, a lower limit for K = 9 (1/ fermi) [1 fermi = 10 -15 m] can be determined (see reference 3). In other words, K for the neutron exchange potential must ...
... 14.4 eV/ (10-10 m) is a constant, not an unknown parameter. Since 'Cold fusion' of the two deuterons in a Deuterium molecule has never been observed, a lower limit for K = 9 (1/ fermi) [1 fermi = 10 -15 m] can be determined (see reference 3). In other words, K for the neutron exchange potential must ...
Chapter 23
... (a) The value – 9.0 105 (in SI units) for small r leads to qcentral = – 7.97 106 C or roughly – 8.0 C. (b) The next (non-zero) value that takes is +4.0 105 (in SI units), which implies qenc 3.54 106 C. But we have already accounted for some of that charge in part (a), so the resul ...
... (a) The value – 9.0 105 (in SI units) for small r leads to qcentral = – 7.97 106 C or roughly – 8.0 C. (b) The next (non-zero) value that takes is +4.0 105 (in SI units), which implies qenc 3.54 106 C. But we have already accounted for some of that charge in part (a), so the resul ...
Huang Slides 1 V08
... The Electric Field • The electric field (in V/m) is defined as the force (in Newtons) per unit charge (in Coulombs). From this definition and Coulomb's law, the electric field E created by a single point charge Q at a distance r is ...
... The Electric Field • The electric field (in V/m) is defined as the force (in Newtons) per unit charge (in Coulombs). From this definition and Coulomb's law, the electric field E created by a single point charge Q at a distance r is ...
Powerpoint
... • Test charge is a small positive charge to sample the E-Field • Charge of test charge is small compared to source charges (source charges are the charges that generate the field) • E-field vectors • E-field is the force per charge • E-field vectors points away from + charges • E-field vectors point ...
... • Test charge is a small positive charge to sample the E-Field • Charge of test charge is small compared to source charges (source charges are the charges that generate the field) • E-field vectors • E-field is the force per charge • E-field vectors points away from + charges • E-field vectors point ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.