Part 2
... Integrating div F over the entire enclosed volume must match the net flux out through the boundary S of the volume V. Gauss’ divergence theorem then follows: ...
... Integrating div F over the entire enclosed volume must match the net flux out through the boundary S of the volume V. Gauss’ divergence theorem then follows: ...
Chapter 25: Capacitance - Farmingdale State College
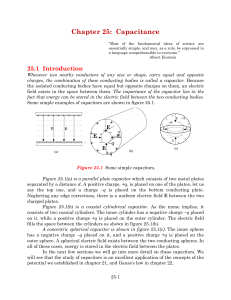
... consists of two coaxial cylinders. The inner cylinder has a negative charge −q placed on it, while a positive charge +q is placed on the outer cylinder. The electric field fills the space between the cylinders as shown in figure 25.1(b). A concentric spherical capacitor is shown in figure 25.1(c). T ...
... consists of two coaxial cylinders. The inner cylinder has a negative charge −q placed on it, while a positive charge +q is placed on the outer cylinder. The electric field fills the space between the cylinders as shown in figure 25.1(b). A concentric spherical capacitor is shown in figure 25.1(c). T ...
Electric field dependence of magnetic properties
... In the first definition of hab,gd the electric dipole polarizability tensor aab is introduced. The second definition, taken from Eq. ~3! above, is directly related to the technique used in this work to compute hab,gd , in the sense that hab,gd is obtained by numerical differentiation of analytically ...
... In the first definition of hab,gd the electric dipole polarizability tensor aab is introduced. The second definition, taken from Eq. ~3! above, is directly related to the technique used in this work to compute hab,gd , in the sense that hab,gd is obtained by numerical differentiation of analytically ...
Use of Spatially Non-Uniform Electric Fields for Contact-Free Assembly of Three-Dimensional
... Chapter 4: Wood, J. A. and Docoslis, A. Assembly of Colloidal Structures using AC Electrokinetic Forces from Non-Uniform Electric Fields. Manuscript in preparation for submission. A version of Chapter 5 has been submitted for publication: Wood, J. A. and Docoslis, A. (2011). AC Electrokinetic Templa ...
... Chapter 4: Wood, J. A. and Docoslis, A. Assembly of Colloidal Structures using AC Electrokinetic Forces from Non-Uniform Electric Fields. Manuscript in preparation for submission. A version of Chapter 5 has been submitted for publication: Wood, J. A. and Docoslis, A. (2011). AC Electrokinetic Templa ...
Solve
... one nitrogen atom; this must be NO2. For the two-atom molecules depicted, each is composed of one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom; this must be written as NO. Therefore, the answer is (c) a mixture of NO 2 and NO. Think About It Even though there are 11 red spheres depicted with 7 blue spheres, th ...
... one nitrogen atom; this must be NO2. For the two-atom molecules depicted, each is composed of one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom; this must be written as NO. Therefore, the answer is (c) a mixture of NO 2 and NO. Think About It Even though there are 11 red spheres depicted with 7 blue spheres, th ...
on the function and evolution of electric organs in fish
... to be 4-2 mm.; this diameter decreases both anteriorly and posteriorly. These figures are for a specimen 89 cm. in length. The maximal length of an electroplate is given as 1 -2 cm. According to Dahlgren (1914) the electric tissue of Gymnarchus is developed by the differentiation of striated muscle ...
... to be 4-2 mm.; this diameter decreases both anteriorly and posteriorly. These figures are for a specimen 89 cm. in length. The maximal length of an electroplate is given as 1 -2 cm. According to Dahlgren (1914) the electric tissue of Gymnarchus is developed by the differentiation of striated muscle ...
J. SEMICONDUCTING AND METALLIC POLYMERS: THE FOURTH GENERATION OF POLYMERIC MATERIALS
... counter-ion acts like a "surfactant" in that the charged head-group is ionically bound to the oppositely charged protonated PANI chain, and the "tail" is chosen to be compatible with non-polar or weakly polar organic liquids (in the case of solutions) or the host polymer (in the case of blends). The ...
... counter-ion acts like a "surfactant" in that the charged head-group is ionically bound to the oppositely charged protonated PANI chain, and the "tail" is chosen to be compatible with non-polar or weakly polar organic liquids (in the case of solutions) or the host polymer (in the case of blends). The ...
TEAL
... Figure 2.4-2: Loop flux function for r < a ...................................................................... 32 Figure 2.4-3: Loop flux function for r > a. .................................................................... 32 Figure 2.4-4: Field line for a loop with a flux function value of 2 ...
... Figure 2.4-2: Loop flux function for r < a ...................................................................... 32 Figure 2.4-3: Loop flux function for r > a. .................................................................... 32 Figure 2.4-4: Field line for a loop with a flux function value of 2 ...
Picosecond dynamics of surface electron transfer processes: Surface
... or the energy relaxation of the carrier through optical phonon emission. The space charge region (depletion layer) ofthe semiconductor is expected to be highly quantized due to the confining potential formed by the space charge field and the Helmholtz barrier. 6 These quantization effects should cha ...
... or the energy relaxation of the carrier through optical phonon emission. The space charge region (depletion layer) ofthe semiconductor is expected to be highly quantized due to the confining potential formed by the space charge field and the Helmholtz barrier. 6 These quantization effects should cha ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.