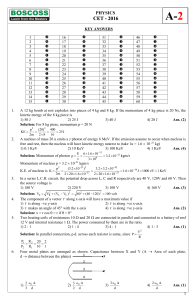
electrochemical processes in microfluidics systems under ac electric
... Red box area under 10x microscope, c): Side view of the device. Units for d): COMSOL simulation of the gradient of electric field in labeled area in Fig. 26b. All numbers are micrometers. ................ 129 Figure 27: Dye properties study a): Photobleaching property for FITC; b) Photobleaching pro ...
... Red box area under 10x microscope, c): Side view of the device. Units for d): COMSOL simulation of the gradient of electric field in labeled area in Fig. 26b. All numbers are micrometers. ................ 129 Figure 27: Dye properties study a): Photobleaching property for FITC; b) Photobleaching pro ...
Maxwell equation simulations of coherent optical photon emission from shock... * Evan J. Reed, Marin Soljačić,
... is not required when the system is coherently prepared as in, for example, so-called correlated spontaneous emission “lasers” 关8兴. In this section, we perform a quantum field theory analysis of a related system that yields the same emitted frequencies as the classical case, given in Eq. 共7兲. We begi ...
... is not required when the system is coherently prepared as in, for example, so-called correlated spontaneous emission “lasers” 关8兴. In this section, we perform a quantum field theory analysis of a related system that yields the same emitted frequencies as the classical case, given in Eq. 共7兲. We begi ...
Physical Science Physics - Department of Basic Education
... Break up your learning sections into manageable parts. Trying to learn too much at one time will only result in a tired, unfocused and anxious brain. ...
... Break up your learning sections into manageable parts. Trying to learn too much at one time will only result in a tired, unfocused and anxious brain. ...
Few-Electron Qubits in Silicon Quantum Electronic Devices
... In the following years of my PhD, I’ve also had the honor to be trained hand by hand by Professor Petta in many areas of experimental low temperature physics. These fields include but not limited to, nano/micro-fabrication skills, DC and RF measurement techniques, and cryogenics which is literally o ...
... In the following years of my PhD, I’ve also had the honor to be trained hand by hand by Professor Petta in many areas of experimental low temperature physics. These fields include but not limited to, nano/micro-fabrication skills, DC and RF measurement techniques, and cryogenics which is literally o ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... used electro-optical lenses to focus the beam [2]. Actually this idea originated from the fact that resolutionlimiting chromatic failures do not play a big role in such a microscope. Then the first scanning electron microscope was developed by Charles Oatley around 1953, and the first commercial SEM ...
... used electro-optical lenses to focus the beam [2]. Actually this idea originated from the fact that resolutionlimiting chromatic failures do not play a big role in such a microscope. Then the first scanning electron microscope was developed by Charles Oatley around 1953, and the first commercial SEM ...
PDF
... gives a field magnitude |E| < 105 V/m and field gradient magnitude |∇E| < 1011 V/m2 at ∼10 µm away from the biased electrodes. At this field strength, the induced dipole d1 ≈ 1 D , the permanent dipole d0 ≈ 200 D.15,19 The dielectrophoretic force ∇(d0E + d1E) is therefore dominated by the permanent ...
... gives a field magnitude |E| < 105 V/m and field gradient magnitude |∇E| < 1011 V/m2 at ∼10 µm away from the biased electrodes. At this field strength, the induced dipole d1 ≈ 1 D , the permanent dipole d0 ≈ 200 D.15,19 The dielectrophoretic force ∇(d0E + d1E) is therefore dominated by the permanent ...
10 10-0
... With the magnetic field pointing downward and the area vector A pointing upward, the magnetic flux is negative, i.e., ! B = " BA < 0 , where A is the area of the loop. As the magnet moves closer to the loop, the magnetic field at a point on the loop increases ( dB / dt > 0 ), producing more flux thr ...
... With the magnetic field pointing downward and the area vector A pointing upward, the magnetic flux is negative, i.e., ! B = " BA < 0 , where A is the area of the loop. As the magnet moves closer to the loop, the magnetic field at a point on the loop increases ( dB / dt > 0 ), producing more flux thr ...
Part 22 of the H chemical shifts
... The 1 H NMR spectra of a number of alcohols, diols and inositols are reported and assigned in CDCl3 , D2 O and DMSO-d6 (henceforth DMSO) solutions. These data were used to investigate the effects of the OH group on the 1 H chemical shifts in these molecules and also the effect of changing the solven ...
... The 1 H NMR spectra of a number of alcohols, diols and inositols are reported and assigned in CDCl3 , D2 O and DMSO-d6 (henceforth DMSO) solutions. These data were used to investigate the effects of the OH group on the 1 H chemical shifts in these molecules and also the effect of changing the solven ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.