Document
... A tough seed coat surrounds and protects the embryo and keeps the contents of the seed from _____________________ out. • The embryo begins to grow when ____________________ are right. It does this by using nutrients from the stored food supply until it can carry out photosynthesis on its own. Angio ...
... A tough seed coat surrounds and protects the embryo and keeps the contents of the seed from _____________________ out. • The embryo begins to grow when ____________________ are right. It does this by using nutrients from the stored food supply until it can carry out photosynthesis on its own. Angio ...
Brazilian Cherry fact sheet
... outcompetes native shrubs and ground covers and can prevent tree seedling regeneration. Brazilian cherry is an invasive plant which can disrupt native flora communities and ecosystems. ...
... outcompetes native shrubs and ground covers and can prevent tree seedling regeneration. Brazilian cherry is an invasive plant which can disrupt native flora communities and ecosystems. ...
Biology 12.4 Plant Reproduction Reproduction 1. Asexual a
... 1. natural VR when the plant reproduces itself a. a portion of the plant can form a complete new plant b. underground roots and stems can develop new plants (mint, weeds, bulbs, potato tubers) c. runners are surface stems can develop into new plants (strawberry plants and spider plants) d. Adventiti ...
... 1. natural VR when the plant reproduces itself a. a portion of the plant can form a complete new plant b. underground roots and stems can develop new plants (mint, weeds, bulbs, potato tubers) c. runners are surface stems can develop into new plants (strawberry plants and spider plants) d. Adventiti ...
Plant Control and Hormones
... Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars made in the leaves down to the roots. 2. whether or not they make seeds. 3. whether or not they have flowers. The four groups ar ...
... Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars made in the leaves down to the roots. 2. whether or not they make seeds. 3. whether or not they have flowers. The four groups ar ...
An Overview of Plants Section 2 Seedless Plants
... a. Photosynthesis—process where plants use chlorophyll to make food b. Chlorophyll is found in a cell structure called a chloroplast. 3. Most of the space inside many plant cells is taken up by a large, membrane-bound structure called a central vacuole, which regulates water content. B. Scientists t ...
... a. Photosynthesis—process where plants use chlorophyll to make food b. Chlorophyll is found in a cell structure called a chloroplast. 3. Most of the space inside many plant cells is taken up by a large, membrane-bound structure called a central vacuole, which regulates water content. B. Scientists t ...
AP Biology
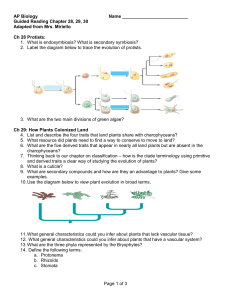
... 6. What are the five derived traits that appear in nearly all land plants but are absent in the charophyceans? 7. Thinking back to our chapter on classification – how is the clade terminology using primitive and derived traits a clear way of studying the evolution of plants? 8. What is a cuticle? 9. ...
... 6. What are the five derived traits that appear in nearly all land plants but are absent in the charophyceans? 7. Thinking back to our chapter on classification – how is the clade terminology using primitive and derived traits a clear way of studying the evolution of plants? 8. What is a cuticle? 9. ...
Answer Key
... seen help this tree reproduce? Attention: The Theobroma (cacao tree) may not be flowering during your field trip! This may be a good point to bring up with students. Plants are not always in flower. This is a cauliflorous plant, which means the flowers and fruit grow right on the trunk and woody bra ...
... seen help this tree reproduce? Attention: The Theobroma (cacao tree) may not be flowering during your field trip! This may be a good point to bring up with students. Plants are not always in flower. This is a cauliflorous plant, which means the flowers and fruit grow right on the trunk and woody bra ...
22.1 Study Workbook
... For Questions 1–8, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
... For Questions 1–8, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
seed dispersal
... How are new plants formed? • from seeds (sexual reproduction) • by producing things such as bulbs or tubers (asexual reproduction). ...
... How are new plants formed? • from seeds (sexual reproduction) • by producing things such as bulbs or tubers (asexual reproduction). ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... • Prompt: Give 2 reasons why flowers are important. What is the difference between pollen and seeds. ...
... • Prompt: Give 2 reasons why flowers are important. What is the difference between pollen and seeds. ...
Japanese Aucuba (Aucuba Japonica) - Garden Basics
... Japanese Aucuba is a shade tolerant, evergreen shrub that is often seen planted under large trees or as a foundation planting on the north and east sides of homes. It grows to fifteen feet in height with a rounded or upright-rounded shape. Leaves are shiny and green, and some cultivars have yellow o ...
... Japanese Aucuba is a shade tolerant, evergreen shrub that is often seen planted under large trees or as a foundation planting on the north and east sides of homes. It grows to fifteen feet in height with a rounded or upright-rounded shape. Leaves are shiny and green, and some cultivars have yellow o ...
the machair flora august
... this plant is more often found as a dense, cylindrical spike of pink flowers, sometimes up to 15cm long. Each individual little flower has spreading lateral sepals with the upper sepal and petals closed together to form a hood. The flowers are extremely fragrant. The linear leaves are unspotted and ...
... this plant is more often found as a dense, cylindrical spike of pink flowers, sometimes up to 15cm long. Each individual little flower has spreading lateral sepals with the upper sepal and petals closed together to form a hood. The flowers are extremely fragrant. The linear leaves are unspotted and ...
Japanese Honeysuckle, Garlic Mustard, Chinese and European Privet
... late fall foliar spray of 2% glyphosate, repeated control usually necessary. Similar Plants - Native honeysuckle have fused leaves through which the stem grows along newer growth. ...
... late fall foliar spray of 2% glyphosate, repeated control usually necessary. Similar Plants - Native honeysuckle have fused leaves through which the stem grows along newer growth. ...
Ch 22- Plant Diversity
... – Named for # of seed leaves, or cotyledon- first leaf or first pair of leaves produced by embryo of seed plant ...
... – Named for # of seed leaves, or cotyledon- first leaf or first pair of leaves produced by embryo of seed plant ...
Kingdom Plantae Ch 22
... Early Plants • For most of Earth’s history plants did not exist. Life was concentrated in oceans, lakes and streams…Oxygen came from algae and cyanobacteria • The first plants evolved from an organism much like the multicellular green algae living today. ...
... Early Plants • For most of Earth’s history plants did not exist. Life was concentrated in oceans, lakes and streams…Oxygen came from algae and cyanobacteria • The first plants evolved from an organism much like the multicellular green algae living today. ...
NONVASCULAR PLANTS
... • Non vascular plants do not have a vascular system • These plants do not have the xylem and phleom • Xylem: conducts water and dissolves nutrients • Phleom: conducts sugar and other metabolic products ...
... • Non vascular plants do not have a vascular system • These plants do not have the xylem and phleom • Xylem: conducts water and dissolves nutrients • Phleom: conducts sugar and other metabolic products ...
Garlic Mustard CONTROL Thetford
... Seeds ripen in long slender pods, average 100/plant (but can exceed1000s); seeds are mature by late July or August. ...
... Seeds ripen in long slender pods, average 100/plant (but can exceed1000s); seeds are mature by late July or August. ...
Japanese knotweed
... Japanese knotweed is an impressive plant that may grow ten feet in height with leaves up to 6 inches in length and 2 to 5 inches in width. Also called Mexican bamboo, because of its hollow stems, it was brought into this country as an ornamental. It can be found across the United States and as far n ...
... Japanese knotweed is an impressive plant that may grow ten feet in height with leaves up to 6 inches in length and 2 to 5 inches in width. Also called Mexican bamboo, because of its hollow stems, it was brought into this country as an ornamental. It can be found across the United States and as far n ...
diamond frost - Proven Winners
... DIAMOND FROST® Euphorbia hybrid ‘INNEUPHDIA’ USPP17567 Can2830 ...
... DIAMOND FROST® Euphorbia hybrid ‘INNEUPHDIA’ USPP17567 Can2830 ...
Plant Study Questions
... 67.Which two vascular tissues are found on a leaf? a. Xylem b. Phloem 68.Which organism is the ancestor of all plants? a. Green algae 69.Why do seeds need to travel? a. To find the right conditions to replant and grow 70.Where are two places that you can find seeds in angiosperms? a. Flowers b. frui ...
... 67.Which two vascular tissues are found on a leaf? a. Xylem b. Phloem 68.Which organism is the ancestor of all plants? a. Green algae 69.Why do seeds need to travel? a. To find the right conditions to replant and grow 70.Where are two places that you can find seeds in angiosperms? a. Flowers b. frui ...
Invasive Plants Fact Sheet - Friends of Hopewell Valley Open Space
... through June. Fruit: Small, black borne in clusters. Look-alikes: Goutweed also called Bishop's weed (Aegopodium podagraria) is a highly invasive, non-native groundcover or creeping plant with 9 leaflets on lower leaves. Upper leaves may be variable. Some varieties of this plant may have white edges ...
... through June. Fruit: Small, black borne in clusters. Look-alikes: Goutweed also called Bishop's weed (Aegopodium podagraria) is a highly invasive, non-native groundcover or creeping plant with 9 leaflets on lower leaves. Upper leaves may be variable. Some varieties of this plant may have white edges ...
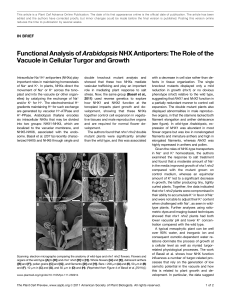
Functional Analysis ofArabidopsisNHX Antiporters
... and were not able to adjust their K+ content when challenged with Na+, as seen in wildtype plants. Further analyses using ratiometric dyes and imaging-based techniques showed that nhx1 nhx2 plants had both lower vacuolar pH and lower K+ concentration compared with the wild type. A typical mesophytic ...
... and were not able to adjust their K+ content when challenged with Na+, as seen in wildtype plants. Further analyses using ratiometric dyes and imaging-based techniques showed that nhx1 nhx2 plants had both lower vacuolar pH and lower K+ concentration compared with the wild type. A typical mesophytic ...
Types of Plants Notes - Teacher Copy
... Pollen grows tube to join egg (fertilization) forming seed ...
... Pollen grows tube to join egg (fertilization) forming seed ...
Unit 14 Plants Angiosperms Notes
... Flowering plants are the most widespread, diverse, and colorful members of the plant kingdom. Adapted to all corners of the world Species far outnumber the nonflowering plants Familiar with: fruit trees, vegetables, cereal grain, wildflowers ...
... Flowering plants are the most widespread, diverse, and colorful members of the plant kingdom. Adapted to all corners of the world Species far outnumber the nonflowering plants Familiar with: fruit trees, vegetables, cereal grain, wildflowers ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.