Annual Plant List for the South Plains
... Bloom spring and fall; deadhead for best results, takes some shade ...
... Bloom spring and fall; deadhead for best results, takes some shade ...
Chrysanthemums
... • Temperature • 1. Starting mum temp – 65-68°F at night – 70-75°F during the day ...
... • Temperature • 1. Starting mum temp – 65-68°F at night – 70-75°F during the day ...
Growing pumpkins and other vine crops in Wisconsin
... The growth habit of individual plants may either be determinate (shoot tip ends in a flower) with a bushy growth habit or indeterminate (shoot tips grow continuously with flowers in leaf axils) with a prostrate and spreading growth habit (figure 1). Leaves are borne singly and may be simple or lobed ...
... The growth habit of individual plants may either be determinate (shoot tip ends in a flower) with a bushy growth habit or indeterminate (shoot tips grow continuously with flowers in leaf axils) with a prostrate and spreading growth habit (figure 1). Leaves are borne singly and may be simple or lobed ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... that will restrict the cloning of human beings. Bioethics is the study of moral issues in the fields of medical treatment and research. Although there are many ways of analyzing bioethical issues, there are certain steps that are common to all discussions. In this investigation, you will consider the ...
... that will restrict the cloning of human beings. Bioethics is the study of moral issues in the fields of medical treatment and research. Although there are many ways of analyzing bioethical issues, there are certain steps that are common to all discussions. In this investigation, you will consider the ...
A-1-3A Foliage Plants - Cornell Cooperative Extension of Nassau
... Medium indirect light, normal room temperature. Keep soil barely moist. Repot infrequently (may slow down growth). Grows tall fast and can be pruned back. Most graceful of palms, but intolerant of low light. Examine periodically for spider mites. ...
... Medium indirect light, normal room temperature. Keep soil barely moist. Repot infrequently (may slow down growth). Grows tall fast and can be pruned back. Most graceful of palms, but intolerant of low light. Examine periodically for spider mites. ...
Tissue systems
... polymer of glucose) • Cell walls of cellulose = fibrous (not branched) polysaccharide = accounts for the relative rigidity of the cell wall • Cell division by formation of cell plate • Most extant plant species are terrestrial (many characteristics that are adapted for terrestrial life) • Separated ...
... polymer of glucose) • Cell walls of cellulose = fibrous (not branched) polysaccharide = accounts for the relative rigidity of the cell wall • Cell division by formation of cell plate • Most extant plant species are terrestrial (many characteristics that are adapted for terrestrial life) • Separated ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... that will restrict the cloning of human beings. Bioethics is the study of moral issues in the fields of medical treatment and research. Although there are many ways of analyzing bioethical issues, there are certain steps that are common to all discussions. In this investigation, you will consider the ...
... that will restrict the cloning of human beings. Bioethics is the study of moral issues in the fields of medical treatment and research. Although there are many ways of analyzing bioethical issues, there are certain steps that are common to all discussions. In this investigation, you will consider the ...
Instructor`s Manual to accompany Principles of Life
... Shoots are composed of repeating units called phytomers; shoots grow by adding more phytomers. The vascular tissue is arranged in bundles in the stem. Leaf anatomy is well suited for photosynthesis, including adaptations for intercepting sunlight, efficient gas exchange while limiting water loss, an ...
... Shoots are composed of repeating units called phytomers; shoots grow by adding more phytomers. The vascular tissue is arranged in bundles in the stem. Leaf anatomy is well suited for photosynthesis, including adaptations for intercepting sunlight, efficient gas exchange while limiting water loss, an ...
new-plants - roisenbiology
... phosphorylation in response to the appropriate light conditions. • The activation of these transcription factors depends on their phosphorylation by protein kinases activated by cGMP or Ca2+ ...
... phosphorylation in response to the appropriate light conditions. • The activation of these transcription factors depends on their phosphorylation by protein kinases activated by cGMP or Ca2+ ...
A abiotic factor Nonliving component in the environment. abscisic
... beta-carotene Yellow to red pigment in plants; one of the most important of the carotenoids; converts to vitamin A in the body. biennial Plant that completes its life cycle within two growing seasons; example: carrot. binomial Two-word scientific name. biodiesel A vegetable oil product used as a cle ...
... beta-carotene Yellow to red pigment in plants; one of the most important of the carotenoids; converts to vitamin A in the body. biennial Plant that completes its life cycle within two growing seasons; example: carrot. binomial Two-word scientific name. biodiesel A vegetable oil product used as a cle ...
Chapter 9 THE KINGDOM PLANTAE
... So, how do we distinguish plants from multicellular algae? First, plants as we are defining them are nearly all terrestrial organisms, although some plants, such as water lilies, have returned secondarily to water during their evolution. Living on land poses very different problems from living in wa ...
... So, how do we distinguish plants from multicellular algae? First, plants as we are defining them are nearly all terrestrial organisms, although some plants, such as water lilies, have returned secondarily to water during their evolution. Living on land poses very different problems from living in wa ...
Artificial Selection in Brassica rapa
... absolutely restricted to offspring of parents that meet the desired criteria (rarely is natural selection such an all-or-none phenomenon). In artificial selection, humans are doing the selecting—purposely restricting breeding to individuals with certain characteristics. In natural selection, the “en ...
... absolutely restricted to offspring of parents that meet the desired criteria (rarely is natural selection such an all-or-none phenomenon). In artificial selection, humans are doing the selecting—purposely restricting breeding to individuals with certain characteristics. In natural selection, the “en ...
Drosera anglica - English sundew
... and Pinguicula vulgaris (butterwort), sundews are carnivorous plants, capturing insects (primarily) with their nectar-like, mucilaginous secretions to supplement nutrients, such as nitrogen, that are otherwise in low availability in their habitats. Sundew leaves curl around their insect prey, when c ...
... and Pinguicula vulgaris (butterwort), sundews are carnivorous plants, capturing insects (primarily) with their nectar-like, mucilaginous secretions to supplement nutrients, such as nitrogen, that are otherwise in low availability in their habitats. Sundew leaves curl around their insect prey, when c ...
Wild-Food Plants in Southern Ethiopia: Reflections on the role of
... 1. Introduction and background For many years the importance of wild plants in subsistence agriculture in the developing world as a food supplement and as a means of survival during times of drought and famine has been overlooked. Generally, the consumption of such so-called ‘wild-food’ has been and ...
... 1. Introduction and background For many years the importance of wild plants in subsistence agriculture in the developing world as a food supplement and as a means of survival during times of drought and famine has been overlooked. Generally, the consumption of such so-called ‘wild-food’ has been and ...
Coral Honeysuckle, Lonicera sempervirens
... stem—leaves of lower nodes may have petioles up to 1 cm long, whereas leaves of upper nodes can be sessile and directly below the flowers often confluent/perfoliate. Often some leaves persist all winter long, but the degree of winter leaf retention varies with latitude and severity of winter. The in ...
... stem—leaves of lower nodes may have petioles up to 1 cm long, whereas leaves of upper nodes can be sessile and directly below the flowers often confluent/perfoliate. Often some leaves persist all winter long, but the degree of winter leaf retention varies with latitude and severity of winter. The in ...
Document
... shallow water, so it’s reasonable to assume that the common ancestor that diverged into plants & charophyts may have as well • Surviving in shallow water requires organisms to resist occasional drying • Natural selection would favor individuals can survive periods of not being submerged in water ...
... shallow water, so it’s reasonable to assume that the common ancestor that diverged into plants & charophyts may have as well • Surviving in shallow water requires organisms to resist occasional drying • Natural selection would favor individuals can survive periods of not being submerged in water ...
WATER PLANTS
... Pitcher Plant. A small and squat carnivorous plant with a large lip, usually called the hood. It features an upright lid with a pair of ear-like wings on each side of the hood. Its purplish-red and the hood is beautifully veined with tree-like patterns. In spring, a single purplish-red, fragrant flo ...
... Pitcher Plant. A small and squat carnivorous plant with a large lip, usually called the hood. It features an upright lid with a pair of ear-like wings on each side of the hood. Its purplish-red and the hood is beautifully veined with tree-like patterns. In spring, a single purplish-red, fragrant flo ...
Who`s the Father? Dihybrid
... expressed. In the homozygous recessive form (anl/anl), anthocyanin expression is completely suppressed, and the plants appear a bright green color (which is the “non-purple stem ” phenotype). If the genotype is heterozygous (anl/ANL) or homozygous dominant (ANL/ANL), then anthocyanin is expressed at ...
... expressed. In the homozygous recessive form (anl/anl), anthocyanin expression is completely suppressed, and the plants appear a bright green color (which is the “non-purple stem ” phenotype). If the genotype is heterozygous (anl/ANL) or homozygous dominant (ANL/ANL), then anthocyanin is expressed at ...
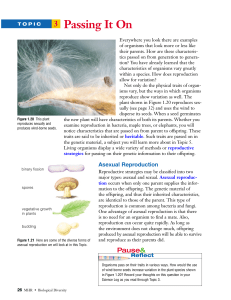
Chapter 10: Plant Reproduction
... plants do not produce seeds, how do growers get new plants? Growers can produce new plants by asexual reproduction because many plant cells have the ability to grow into a variety of cell types. New plants can be grown from just a few cells in the laboratory. Under the right conditions, an entire pl ...
... plants do not produce seeds, how do growers get new plants? Growers can produce new plants by asexual reproduction because many plant cells have the ability to grow into a variety of cell types. New plants can be grown from just a few cells in the laboratory. Under the right conditions, an entire pl ...
(Diagnostic fea. families 4(madhumita))
... which is commonly known as the legume family, pea family, bean family or pulse family •Fabaceae is the third largest family of flowering plants, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species. •The species of this family are found throughout the ...
... which is commonly known as the legume family, pea family, bean family or pulse family •Fabaceae is the third largest family of flowering plants, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species. •The species of this family are found throughout the ...
Reproductive and physiological responses to simulated climate
... The cost of reproduction in plants is typically defined as reproductive effort (RE), or the relative amount of available C that has been allocated to reproductive tissues (Reekie & Bazzaz, 1987; Bazzaz & Ackerly, 1992). Carbon is the standard currency for estimating RE because it is assumed to be an ...
... The cost of reproduction in plants is typically defined as reproductive effort (RE), or the relative amount of available C that has been allocated to reproductive tissues (Reekie & Bazzaz, 1987; Bazzaz & Ackerly, 1992). Carbon is the standard currency for estimating RE because it is assumed to be an ...
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the sitgma of a flower
... form fruits and seeds When the male cells meet with the female cell, it is called fertilization. This is also called sexual reproduction because male and female sex cells are involved ...
... form fruits and seeds When the male cells meet with the female cell, it is called fertilization. This is also called sexual reproduction because male and female sex cells are involved ...
LAB QUIZ III - Montana State University Billings
... family. Some species (e.g. Veronica), have four petals, but many have irregular shaped flowers with five petals, often joined to form a bell or tube, sometimes with two lips. In some species (e.g. Linaria), there is a long hollow spur with honey to attract pollinators. There are two long and two sho ...
... family. Some species (e.g. Veronica), have four petals, but many have irregular shaped flowers with five petals, often joined to form a bell or tube, sometimes with two lips. In some species (e.g. Linaria), there is a long hollow spur with honey to attract pollinators. There are two long and two sho ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.