plant
... • Most plants have mycorrhizae, symbiotic fungi associated with their roots, in which the fungi – Absorb water and essential minerals from the soil – Provide these materials to the plant – Are nourished by sugars produced by the plant ...
... • Most plants have mycorrhizae, symbiotic fungi associated with their roots, in which the fungi – Absorb water and essential minerals from the soil – Provide these materials to the plant – Are nourished by sugars produced by the plant ...
July/August 2013 - Florida Council of Bromeliad Societies
... Puya the most ancient has 219 species. The largest of these, Puya Raimondi, grows at 12000 feet, can be 10 meters high and takes 80-100 years to bloom. You can find Puya in the high plains and peaks of Santiago Chile. Mostly big and spiky, some have soft leaves and some are twisted and tangled like ...
... Puya the most ancient has 219 species. The largest of these, Puya Raimondi, grows at 12000 feet, can be 10 meters high and takes 80-100 years to bloom. You can find Puya in the high plains and peaks of Santiago Chile. Mostly big and spiky, some have soft leaves and some are twisted and tangled like ...
plant biology
... prevent overheating) and restrict water loss. In some plants these hairs are sticky or toxic, so provide protection. Epidermal cells of the root produce root hairs that increase the surface area for absorption of water. Some epidermis cells on leaves (mainly on lower surface) and green stems form ti ...
... prevent overheating) and restrict water loss. In some plants these hairs are sticky or toxic, so provide protection. Epidermal cells of the root produce root hairs that increase the surface area for absorption of water. Some epidermis cells on leaves (mainly on lower surface) and green stems form ti ...
Wildflower Identification
... • Bright pink to lilac-purple blossoms almost 1 inch across with a four petaled flower. • Flowers on the bottom of the stem bloom first and them over several weeks they bloom going to the top. ...
... • Bright pink to lilac-purple blossoms almost 1 inch across with a four petaled flower. • Flowers on the bottom of the stem bloom first and them over several weeks they bloom going to the top. ...
The Discovery of C4 Photosynthesis
... C4 plants are capable of higher rates of leaf photosynthesis than C3 plants, especially at higher temperatures, show higher water-use efficiency and are commonly more tolerant to drought. They grow more rapidly and produce more dry matter than C 3 plants under appropriate conditions. These featrures ...
... C4 plants are capable of higher rates of leaf photosynthesis than C3 plants, especially at higher temperatures, show higher water-use efficiency and are commonly more tolerant to drought. They grow more rapidly and produce more dry matter than C 3 plants under appropriate conditions. These featrures ...
2005 Georgia Gold Medal Winners
... During recent years, plant breeders have made great strides in developing new plants with outstanding seasonal characteristics that give them improved landscape appeal. Examples are Rose Creek and Canyon Creek Abelias, exciting new selections from the breeding program of Dr. Michael Dirr at the Univ ...
... During recent years, plant breeders have made great strides in developing new plants with outstanding seasonal characteristics that give them improved landscape appeal. Examples are Rose Creek and Canyon Creek Abelias, exciting new selections from the breeding program of Dr. Michael Dirr at the Univ ...
PDF - CLIMBERS - University of Michigan
... crimson in the fall. The petioles are long, slender, usually 4-12 cm in length, and glabrous or sparsely pubescent. They are usually light green becoming bright orange-red in the fall. Leaves have been seen bearing mites, although no mite domatia are found on the leaves (RJB pers. obs.). The stems a ...
... crimson in the fall. The petioles are long, slender, usually 4-12 cm in length, and glabrous or sparsely pubescent. They are usually light green becoming bright orange-red in the fall. Leaves have been seen bearing mites, although no mite domatia are found on the leaves (RJB pers. obs.). The stems a ...
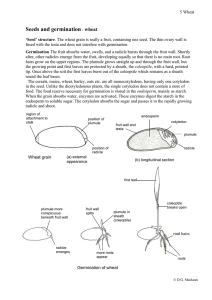
Seeds and germination - wheat
... after, other radicles emerge from the fruit, developing equally so that there is no main root. Root hairs grow on the upper regions. The plumule grows straight up and through the fruit wall, but the growing point and first leaves are protected by a sheath, the coleoptile, with a hard, pointed tip. O ...
... after, other radicles emerge from the fruit, developing equally so that there is no main root. Root hairs grow on the upper regions. The plumule grows straight up and through the fruit wall, but the growing point and first leaves are protected by a sheath, the coleoptile, with a hard, pointed tip. O ...
Plant Classification - Miss Stanley Cyber Classroom
... The first leaf is often a fanshaped blade. The second leaf is usually a fiddlehead, a coiled young leaf. Some fiddleheads are edible and used in salads. ...
... The first leaf is often a fanshaped blade. The second leaf is usually a fiddlehead, a coiled young leaf. Some fiddleheads are edible and used in salads. ...
Reading Project Where the Lilies Bloom
... epigastrium; pain radiating from the navel over the abdomen; soreness in the region of the liver, extending to the umbilicus; enlargement of the of the liver, determined by percussion; nausea; occasional vomiting; constipation with dry faeces, temperature slightly above normal; skin usually yellow." ...
... epigastrium; pain radiating from the navel over the abdomen; soreness in the region of the liver, extending to the umbilicus; enlargement of the of the liver, determined by percussion; nausea; occasional vomiting; constipation with dry faeces, temperature slightly above normal; skin usually yellow." ...
Acmispon glaber (Vogel) Brouillet, CALIFORNIA BROOM
... Lotus scoparius. This is a “broom” plant with small trifoliolate leaves and flexible, photosynthetic stems, and it is an important nitrogen fixer for the communities. Two varieties are currently recognized; the widespread typical variety tends to have relatively long flowers in which the keel is app ...
... Lotus scoparius. This is a “broom” plant with small trifoliolate leaves and flexible, photosynthetic stems, and it is an important nitrogen fixer for the communities. Two varieties are currently recognized; the widespread typical variety tends to have relatively long flowers in which the keel is app ...
Holiday Flowering Plants
... temperatures rise above 70°; do not be surprised if your plants appear to be dying. Rest assured they are merely ‘resting’ in the heat. ...
... temperatures rise above 70°; do not be surprised if your plants appear to be dying. Rest assured they are merely ‘resting’ in the heat. ...
Awabuki Sweet Viburnum
... riparian and swamp forest communities in the Sunshine Coast, Brisbane, Por t Macquarie and Coffs Harbour areas in recent years. As it is fast-growing and readily spread by animals that eat its fruit, it has the potential to become a serious environmental weed in these habitats. ...
... riparian and swamp forest communities in the Sunshine Coast, Brisbane, Por t Macquarie and Coffs Harbour areas in recent years. As it is fast-growing and readily spread by animals that eat its fruit, it has the potential to become a serious environmental weed in these habitats. ...
Iolanthe Magnolia - Garden Supply Co
... Iolanthe Magnolia is a multi-stemmed deciduous shrub with a shapely oval form. Its relatively coarse texture can be used to stand it apart from other landscape plants with finer foliage. This is a relatively low maintenance shrub, and should only be pruned after flowering to avoid removing any of th ...
... Iolanthe Magnolia is a multi-stemmed deciduous shrub with a shapely oval form. Its relatively coarse texture can be used to stand it apart from other landscape plants with finer foliage. This is a relatively low maintenance shrub, and should only be pruned after flowering to avoid removing any of th ...
PREFACE Botany is a fundamental course for the specialty of
... characteristics and functions of plant cells, tissues and organs, and master basic knowledge and skills of morphological anatomy associated with vegetative and reproductive organs after students complete the course. Students are required to have a preliminary understanding of various plant groups an ...
... characteristics and functions of plant cells, tissues and organs, and master basic knowledge and skills of morphological anatomy associated with vegetative and reproductive organs after students complete the course. Students are required to have a preliminary understanding of various plant groups an ...
Unit 10: Soybean Diseases
... One of the most serious SB diseases in the U.S. Occurs when exposed to cool, wet conditions, on poorly drained soils Can kill seed and seedlings during germination and emergence Seedlings wilt and appear water-soaked Disease attaching older plants ...
... One of the most serious SB diseases in the U.S. Occurs when exposed to cool, wet conditions, on poorly drained soils Can kill seed and seedlings during germination and emergence Seedlings wilt and appear water-soaked Disease attaching older plants ...
New Plants Alive title page BL11F 2003 - UWI St. Augustine
... simply taking up the space between other, outwardly more important tissues. But parenchyma cells do contribute support if they are turgid. The swollen protoplast of each cell presses outwards against the cell wall, and all of the parenchyma cells together press out against the restraining layer of c ...
... simply taking up the space between other, outwardly more important tissues. But parenchyma cells do contribute support if they are turgid. The swollen protoplast of each cell presses outwards against the cell wall, and all of the parenchyma cells together press out against the restraining layer of c ...
Prentice Hall Biology - Jamestown School District
... 2. With your partner, list three items that plants must get from animals—either directly or indirectly. Student lists will vary, but should include some of the following items: water, carbon dioxide, nutrients (from decaying animals), soil. 3. Using your answers to questions 1 and 2, construct a dia ...
... 2. With your partner, list three items that plants must get from animals—either directly or indirectly. Student lists will vary, but should include some of the following items: water, carbon dioxide, nutrients (from decaying animals), soil. 3. Using your answers to questions 1 and 2, construct a dia ...
Magnification changer with magnification scale
... No flowers, fruits, and seeds having true leaves (Seedless Plants), can see sorus of the back side of leaves. Like all other vascular plants, they have a life cycle referred to as alternation of generations, characterized by a diploid sporophytic and a haploid gametophytic phase. Unlike the gymn ...
... No flowers, fruits, and seeds having true leaves (Seedless Plants), can see sorus of the back side of leaves. Like all other vascular plants, they have a life cycle referred to as alternation of generations, characterized by a diploid sporophytic and a haploid gametophytic phase. Unlike the gymn ...
The Morphology and Anatomy of Utricularia Transrugosa Stapf.
... The vegetative morphology of Utricularia cannot be likened to that o f any other flowering plant. In order to avoid confusion, the terms leaf, stolon and rhizoid will be used in this report, though it must be remembered that in Utricularia the distinctions between these three are ill-defined. The ve ...
... The vegetative morphology of Utricularia cannot be likened to that o f any other flowering plant. In order to avoid confusion, the terms leaf, stolon and rhizoid will be used in this report, though it must be remembered that in Utricularia the distinctions between these three are ill-defined. The ve ...
notes - Australian Plant Society
... Prostanthera=gk. prostheke, an appendage + anther , Prostanthera is a genus of about 100 species of native Australian plants, they are small to medium shrubs with aromatic foliage, with square stems, some are prostrate with wiry, twiggy branches. This genus is under revision, it is expected changes ...
... Prostanthera=gk. prostheke, an appendage + anther , Prostanthera is a genus of about 100 species of native Australian plants, they are small to medium shrubs with aromatic foliage, with square stems, some are prostrate with wiry, twiggy branches. This genus is under revision, it is expected changes ...
How Much Does Acid Rain Hinder the Growth Height of Brassica
... and deposited material from the atmosphere that contains a high acidity level of nitric and sulfuric acid.” The acidity of the mixture can stunt the growth of plants due to the lack of nutrients and the effect of the mixture on the tissue and roots of the plant. However, there are several other fact ...
... and deposited material from the atmosphere that contains a high acidity level of nitric and sulfuric acid.” The acidity of the mixture can stunt the growth of plants due to the lack of nutrients and the effect of the mixture on the tissue and roots of the plant. However, there are several other fact ...
Plant Kingdom
... How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. ...
... How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.