Handout
... illnesses, personality disorders, and medical problems related to mental illness (Axis I, II, III.) • The organization is different in order to correspond better to ICD and to reflect a developmental perspective. • There are three sections: – 1) Introduction and instructions – 2) The Disorders – 3) ...
... illnesses, personality disorders, and medical problems related to mental illness (Axis I, II, III.) • The organization is different in order to correspond better to ICD and to reflect a developmental perspective. • There are three sections: – 1) Introduction and instructions – 2) The Disorders – 3) ...
anxiety disorders (cont.)
... • Other problems and disorders: Axes II, III, IV, V – Axis IV: psychosocial and environmental problems • refers to psychosocial and environmental problems that may affect the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of mental disorders in Axes I and II – Axis V: global assessment of functioning scale • u ...
... • Other problems and disorders: Axes II, III, IV, V – Axis IV: psychosocial and environmental problems • refers to psychosocial and environmental problems that may affect the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of mental disorders in Axes I and II – Axis V: global assessment of functioning scale • u ...
Mental Disorders
... motivation, short-term memory and some emotions, as well as immune function and motor control. Scientists say the amount of dopamine receptors and the level of dopamine released effects how attentive a person is. An inefficiency of these variables causes ADHD. The way that dopamine and dopamine rece ...
... motivation, short-term memory and some emotions, as well as immune function and motor control. Scientists say the amount of dopamine receptors and the level of dopamine released effects how attentive a person is. An inefficiency of these variables causes ADHD. The way that dopamine and dopamine rece ...
DSM-IV-TR
... Cognitive Model – The model suggests that people’s thoughts and beliefs are central to abnormal behavior. ( the primary goal of treatment using the cognitive model is to explicitly teach new and more adaptive ways of thinking) Humanistic Model – It suggests that individuals can, by and large, set th ...
... Cognitive Model – The model suggests that people’s thoughts and beliefs are central to abnormal behavior. ( the primary goal of treatment using the cognitive model is to explicitly teach new and more adaptive ways of thinking) Humanistic Model – It suggests that individuals can, by and large, set th ...
Personality disorders - Faribault Area Learning Center
... • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close relationships often precede depression • With each new generation, depression is striking earlier and affecting more people ...
... • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close relationships often precede depression • With each new generation, depression is striking earlier and affecting more people ...
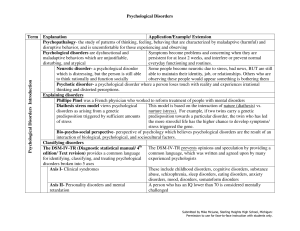
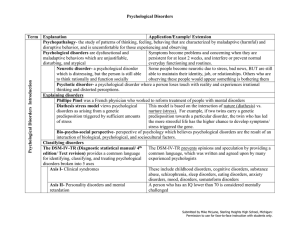
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
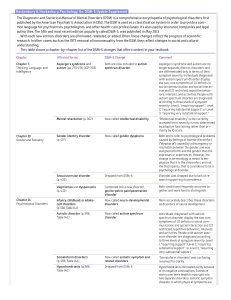
13A-Psychdisorder-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
Study Guide Final 12-13-2005 - Logan Class of December 2011
... begin in childhood may disappear as the individual grows older. Fear of certain types of animals is the most common Specific Phobia. The disorder can be comorbid with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia. ...
... begin in childhood may disappear as the individual grows older. Fear of certain types of animals is the most common Specific Phobia. The disorder can be comorbid with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia. ...
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is
... present but their significance is exaggerated; and illness anxiety disorder, in which individuals worry excessively about being ill despite an absence of physical symptoms. Both disorders involve an anxious preoccupation or worry about health concerns. ...
... present but their significance is exaggerated; and illness anxiety disorder, in which individuals worry excessively about being ill despite an absence of physical symptoms. Both disorders involve an anxious preoccupation or worry about health concerns. ...
the fatal addiction to plastic surgery
... largely ignored. However, it has been estimated that 1 to 2 percent of the general population has BDD, which is nearly 5 million people in the United States alone. BDD is aptly described as the disease of “imagined ugliness.” Most of us pay attention to our appearance but BDD sufferers worry excessi ...
... largely ignored. However, it has been estimated that 1 to 2 percent of the general population has BDD, which is nearly 5 million people in the United States alone. BDD is aptly described as the disease of “imagined ugliness.” Most of us pay attention to our appearance but BDD sufferers worry excessi ...
THE WORLD OF ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
... acknowledge the need for prevention? How does insurance coverage relate to mental health treatment? ...
... acknowledge the need for prevention? How does insurance coverage relate to mental health treatment? ...
Neurotic disorders
... important recent event, which is not due to organic mental disorder and is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness or fatigue. The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat experiences, or unexpected bereavements, and used to be partial and selective. ...
... important recent event, which is not due to organic mental disorder and is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness or fatigue. The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat experiences, or unexpected bereavements, and used to be partial and selective. ...
Explaining Psychological Disorders
... Agoraphobia – intense and irrational fear of separation from _________ or being somewhere from which one cannot __________ ...
... Agoraphobia – intense and irrational fear of separation from _________ or being somewhere from which one cannot __________ ...
Section 9: Basic Psychiatric Terminology
... Must have experienced, witnessed or been confronted with a life ...
... Must have experienced, witnessed or been confronted with a life ...
Psychotic Disorders
... medications are D2 antagonists drugs that increase dopamine cause psychosis (amphetamines) nigrostriatal, mesolimibic, mesocortical tracts Serotonin data from effective medications GABA - inhibitory neurotransmitter loss of cell bodies in hippocampus ...
... medications are D2 antagonists drugs that increase dopamine cause psychosis (amphetamines) nigrostriatal, mesolimibic, mesocortical tracts Serotonin data from effective medications GABA - inhibitory neurotransmitter loss of cell bodies in hippocampus ...
Psychological Disord..
... caring parent; emotionally rewarding • Mothers may rub child skin to produce rash; give child drugs to induce vomiting; or more severe injuries • Mothers were themselves often abused as children; had problems with their mother • Will usually deny condition ...
... caring parent; emotionally rewarding • Mothers may rub child skin to produce rash; give child drugs to induce vomiting; or more severe injuries • Mothers were themselves often abused as children; had problems with their mother • Will usually deny condition ...
An Integrated Approach, 2E Chapter 33
... sense of feeling empty or having no feelings. Some individuals, particularly adolescents, may exhibit irritability rather than sadness. Major depressive episodes frequently develop over a few days or weeks and without treatment commonly last for ...
... sense of feeling empty or having no feelings. Some individuals, particularly adolescents, may exhibit irritability rather than sadness. Major depressive episodes frequently develop over a few days or weeks and without treatment commonly last for ...
Personality Disorder
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
6 Emotional stress and psychical trauma
... important recent event, which is not due to organic mental disorder and is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness or fatigue. The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat experiences, or unexpected bereavements, and used to be partial and selective. ...
... important recent event, which is not due to organic mental disorder and is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness or fatigue. The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat experiences, or unexpected bereavements, and used to be partial and selective. ...
Journal of Homosexuality Sociocultural Interpretations of Social
... of care, den Boer et al. (2000) indicate there may be a place for combined pharmaceutical agents. Cognitive-behavioral therapies are also identified as effective treatment agents (Ballenger et al., 1998; den Boer, 2000). THE CURRENT STATUS OF SOCIAL PHOBIA In general, Social Phobia is not well-under ...
... of care, den Boer et al. (2000) indicate there may be a place for combined pharmaceutical agents. Cognitive-behavioral therapies are also identified as effective treatment agents (Ballenger et al., 1998; den Boer, 2000). THE CURRENT STATUS OF SOCIAL PHOBIA In general, Social Phobia is not well-under ...
SOMATIC SYMPTOM and RELATED DISORDERS
... A. One or more somatic symptoms that are distressing B. Excessive thoughts, feelings or behaviours to the symptoms as manifested by at least one of the following: 1. persistent or disproportionate thoughts about the seriousness of the illness 2. persistently high level of anxiety about the symptoms ...
... A. One or more somatic symptoms that are distressing B. Excessive thoughts, feelings or behaviours to the symptoms as manifested by at least one of the following: 1. persistent or disproportionate thoughts about the seriousness of the illness 2. persistently high level of anxiety about the symptoms ...
Signs and Symptoms in Psychiatry
... la belle indifference Inappropriate attitude of calm or lack of concern about one's disability. May be seen in patients with conversion disorder. labile affect Affective expression characterized by rapid and abrupt changes, unrelated to external stimuli. Lilliputian hallucination Visual sensation t ...
... la belle indifference Inappropriate attitude of calm or lack of concern about one's disability. May be seen in patients with conversion disorder. labile affect Affective expression characterized by rapid and abrupt changes, unrelated to external stimuli. Lilliputian hallucination Visual sensation t ...
Anxiety Disorders
... the first place, then a person will experience increasing anxiety. This person will end up either demonstrating obvious signs of anxiety, or he/she will engage in certain, usually bizarre, behaviors in an attempt to alleviate the anxiety. These include panic, amnesia, obsessions, compulsive behavior ...
... the first place, then a person will experience increasing anxiety. This person will end up either demonstrating obvious signs of anxiety, or he/she will engage in certain, usually bizarre, behaviors in an attempt to alleviate the anxiety. These include panic, amnesia, obsessions, compulsive behavior ...