Multi-impulsive Eating Disorders
... starvation and the results of other eating disordered behaviours on the capacity to learn ...
... starvation and the results of other eating disordered behaviours on the capacity to learn ...
2006_08_31-DaSilva-Affective_and_personality_disorders
... C) The episode is associated with an unequivocal change in functioning that is uncharacteristic of the person when not symptomatic. D) The disturbance in mood and the change in functioning are observable by others. E) The mood disturbance not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occ ...
... C) The episode is associated with an unequivocal change in functioning that is uncharacteristic of the person when not symptomatic. D) The disturbance in mood and the change in functioning are observable by others. E) The mood disturbance not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occ ...
Anxiety Disorders - Psychology with Mr.Salacki
... Failure to strive to one’s potential or being out of touch with one’s feelings. ...
... Failure to strive to one’s potential or being out of touch with one’s feelings. ...
DSM-5 And Mood disorders - Institut universitaire en santé mentale
... D. The mood between temper outbursts is persistently irritable or angry most of the day, nearly every day, and is observable by others (e.g., parents, teachers, peers). E. Criteria A-D have been present for 12 or more months. Throughout that time, the individual has not had 3 or more consecutive mon ...
... D. The mood between temper outbursts is persistently irritable or angry most of the day, nearly every day, and is observable by others (e.g., parents, teachers, peers). E. Criteria A-D have been present for 12 or more months. Throughout that time, the individual has not had 3 or more consecutive mon ...
Current Topics in Complex Post
... being more frequently victimized sexually (Cortina & Kubiak, 2006), which carries the assumption that the impact of sexual abuse is categorically different than any other violation of one’s safety. However, the aforementioned symptoms which can be subsumed under the label of cPTSD are not exclusivel ...
... being more frequently victimized sexually (Cortina & Kubiak, 2006), which carries the assumption that the impact of sexual abuse is categorically different than any other violation of one’s safety. However, the aforementioned symptoms which can be subsumed under the label of cPTSD are not exclusivel ...
`Everybody looks at my pubic bone` — a case report of
... with some aspect of their face and have multiple perceived defects. The patient reported no particular reason for focusing on her pubic bone and one would have thought that dieting would probably have made her pubic bone more prominent. The onset of BDD usually occurs during adolescence, when indivi ...
... with some aspect of their face and have multiple perceived defects. The patient reported no particular reason for focusing on her pubic bone and one would have thought that dieting would probably have made her pubic bone more prominent. The onset of BDD usually occurs during adolescence, when indivi ...
Postnatal Anxiety
... Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a specific anxiety problem which can occur after a person experiences, or sees, a traumatic event, or series of traumatic events. A traumatic event is one that makes a person feel that their own life, or the lives of other people, is in serious danger. In som ...
... Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a specific anxiety problem which can occur after a person experiences, or sees, a traumatic event, or series of traumatic events. A traumatic event is one that makes a person feel that their own life, or the lives of other people, is in serious danger. In som ...
Panic Disorder and Panic Attacks
... anxiety, fear, or terror, people may also have many other symptoms, most of which are physical. In an attack you may feel several of the following: ...
... anxiety, fear, or terror, people may also have many other symptoms, most of which are physical. In an attack you may feel several of the following: ...
355 A
... this course will be taught in seminar format, students are expected to complete the assigned readings and to come to class prepared to discuss them. Students will be asked to respond to questions that have arisen from the readings. This is your opportunity to share your reactions and thoughts about ...
... this course will be taught in seminar format, students are expected to complete the assigned readings and to come to class prepared to discuss them. Students will be asked to respond to questions that have arisen from the readings. This is your opportunity to share your reactions and thoughts about ...
Mood Disorder Symptoms, Causes and E7҃ect
... Mood drug options include different types of antidepressants. You may be prescribed serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. SNRIs include duloxetine (Cymbalta) and venlafaxine (Effexor). Another available antidepressant is bupropion (Wellbutrin), which manipulates dopamine. ...
... Mood drug options include different types of antidepressants. You may be prescribed serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. SNRIs include duloxetine (Cymbalta) and venlafaxine (Effexor). Another available antidepressant is bupropion (Wellbutrin), which manipulates dopamine. ...
Take control of bipolar disorder
... we don’t know the exact cause, there is some research that suggests an underlying abnormality in the way some nerve cells in the brain function and communicate which makes some people more vulnerable to physical and psychological stress. ...
... we don’t know the exact cause, there is some research that suggests an underlying abnormality in the way some nerve cells in the brain function and communicate which makes some people more vulnerable to physical and psychological stress. ...
Analysis of Emotional Harm Claims
... Axis IV should be used by the plaintiff’s mental health professional to report psychosocial and environmental problems that may affect the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of mental disorders listed on Axes I and II. Positive stressors (e.g., a job promotion) should only be listed if they constit ...
... Axis IV should be used by the plaintiff’s mental health professional to report psychosocial and environmental problems that may affect the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of mental disorders listed on Axes I and II. Positive stressors (e.g., a job promotion) should only be listed if they constit ...
- Wiley Online Library
... decision making; however, cardiovascular symptoms are threat cues for patients with panic disorder (PD). Therefore, enhanced cardiac perception may aid intuitive decision making only in healthy individuals, but impair intuitive decision making in PD patients. Methods: PD patients and age- and sex-ma ...
... decision making; however, cardiovascular symptoms are threat cues for patients with panic disorder (PD). Therefore, enhanced cardiac perception may aid intuitive decision making only in healthy individuals, but impair intuitive decision making in PD patients. Methods: PD patients and age- and sex-ma ...
What is Mental Health First Aid?
... behaviour and fever • Psychological dependence produced by cocaine is believed to be among the strongest of all drugs ...
... behaviour and fever • Psychological dependence produced by cocaine is believed to be among the strongest of all drugs ...
Personality Disorders
... Inflexible and pervasive across a broad range of personal and social situations Clinically significant distress or impairment in one or more area of functioning The pattern is stable and of long duration, and its onset can be traced back at least to adolescence or early adulthood Not better accounte ...
... Inflexible and pervasive across a broad range of personal and social situations Clinically significant distress or impairment in one or more area of functioning The pattern is stable and of long duration, and its onset can be traced back at least to adolescence or early adulthood Not better accounte ...
Major Depressive Disorder in - ATTC Addiction Technology Transfer
... (M=6.2 vs. 7.6 weeks, t=2.3, df=524, p=0.02), were more likely to meet criteria for alcohol- (OR=1.8) or other substance dependence (OR=2.2) at 3-year follow-up, and evidenced declining functional outcomes on the ASI (drug, psychiatric) from baseline to FU. ...
... (M=6.2 vs. 7.6 weeks, t=2.3, df=524, p=0.02), were more likely to meet criteria for alcohol- (OR=1.8) or other substance dependence (OR=2.2) at 3-year follow-up, and evidenced declining functional outcomes on the ASI (drug, psychiatric) from baseline to FU. ...
Anorexia Nervosa
... • Anorexia Nervosa: Deep lack of control; flight from maturation; runs in families (genetics or modeling?); cognitive biases regarding weight and body shape. • Bulimia Nervosa: Little theory as of now. Restraint hypothesis: "catastrophic shifts" occur if restrained behavior (which creates an approac ...
... • Anorexia Nervosa: Deep lack of control; flight from maturation; runs in families (genetics or modeling?); cognitive biases regarding weight and body shape. • Bulimia Nervosa: Little theory as of now. Restraint hypothesis: "catastrophic shifts" occur if restrained behavior (which creates an approac ...
Personality Disorders
... genuine remorse for this behavior. Manipulative interactions with others make it difficult to decide whether or not complaints are genuine. About 3% of men, but only 1% of women have this disorder. Accounts for 3 out of every 4 penitentiary prisoners. More common among lower class populations and ru ...
... genuine remorse for this behavior. Manipulative interactions with others make it difficult to decide whether or not complaints are genuine. About 3% of men, but only 1% of women have this disorder. Accounts for 3 out of every 4 penitentiary prisoners. More common among lower class populations and ru ...
Somatization in childhood The child psychiatrist`s concern?
... When do these symptoms matter in children? • They are common and often multiple • When they are an expression of somatization and somatoform disorders they can be highly impairing and lead to multiple medical consultations • There is a strong association with anxiety and depressive disorders – acro ...
... When do these symptoms matter in children? • They are common and often multiple • When they are an expression of somatization and somatoform disorders they can be highly impairing and lead to multiple medical consultations • There is a strong association with anxiety and depressive disorders – acro ...
Chapter 7: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Posttraumatic s
... c. Negative emotions such as anger, shame, guilt, hopelessness, fear, and anxiety. d. Pathological “fear structures” that arouse anxiety when triggered. 7. Although more time-consuming, diagnostic interviews are considered to be a more valid diagnostic strategy for assessing PTSD than self-report me ...
... c. Negative emotions such as anger, shame, guilt, hopelessness, fear, and anxiety. d. Pathological “fear structures” that arouse anxiety when triggered. 7. Although more time-consuming, diagnostic interviews are considered to be a more valid diagnostic strategy for assessing PTSD than self-report me ...
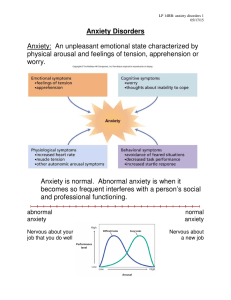
Anxiety: An unpleasant emotional state characterized
... Anxiety disorders: Disorders characterized by excessive anxiety in the absence of true danger. It is normal to be anxious in stressful or threatening situations. It is abnormal to feel strong chronic anxiety without cause. People often experience more than one type of anxiety disorder at a given tim ...
... Anxiety disorders: Disorders characterized by excessive anxiety in the absence of true danger. It is normal to be anxious in stressful or threatening situations. It is abnormal to feel strong chronic anxiety without cause. People often experience more than one type of anxiety disorder at a given tim ...
Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders
... • Overtalkative, overactive, elated, little need for sleep, etc. ...
... • Overtalkative, overactive, elated, little need for sleep, etc. ...
DSM-5 Released: The Big Changes
... research.). This exclusion was removed in the DSM5. Here are the reasons they gave: The first is to remove the implication that bereavement typically lasts only 2 months when both physicians and grief counselors recognize that the duration is more commonly 1–2 years. Second, bereavement is recogniz ...
... research.). This exclusion was removed in the DSM5. Here are the reasons they gave: The first is to remove the implication that bereavement typically lasts only 2 months when both physicians and grief counselors recognize that the duration is more commonly 1–2 years. Second, bereavement is recogniz ...
File
... Concept that diseases have physical causes Can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured Assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which may include treatment in a psychiatric hospital (p.533) ...
... Concept that diseases have physical causes Can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured Assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which may include treatment in a psychiatric hospital (p.533) ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.