Bipolar Disorder and Substance Use Disorders
... more days than not, as indicated either by subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 years, but without a major depressive episode occurring. ...
... more days than not, as indicated either by subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 years, but without a major depressive episode occurring. ...
2017 Exam 1 Q`s and A`s - UCF College of Sciences
... 1. What is a clinical disorder? A constellation of symptoms [2] that significantly impairs [1] an individual’s ability to function and is characterized by a particular symptom picture with a specifiable onset [1], course [1], duration [1], outcome [1], and response to treatment [1], and associated f ...
... 1. What is a clinical disorder? A constellation of symptoms [2] that significantly impairs [1] an individual’s ability to function and is characterized by a particular symptom picture with a specifiable onset [1], course [1], duration [1], outcome [1], and response to treatment [1], and associated f ...
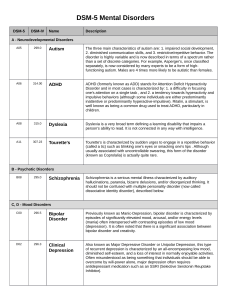
DSM V Mental Disorders
... Previously known as Manic-Depression, bipolar disorder is characterized by episodes of significantly elevated mood, arousal, and/or energy levels (mania) often interspersed with contrasting episodes of low mood (depression). It is often noted that there is a significant association between bipolar d ...
... Previously known as Manic-Depression, bipolar disorder is characterized by episodes of significantly elevated mood, arousal, and/or energy levels (mania) often interspersed with contrasting episodes of low mood (depression). It is often noted that there is a significant association between bipolar d ...
Psychosis in Children and Young People
... • Family members with high expressed emotion are hostile, very critical and not tolerant of the patient. They feel like they are helping by having this attitude. They not only criticise behaviours relating to the disorder but also other behaviours that are unique to the personality of the patient. ...
... • Family members with high expressed emotion are hostile, very critical and not tolerant of the patient. They feel like they are helping by having this attitude. They not only criticise behaviours relating to the disorder but also other behaviours that are unique to the personality of the patient. ...
Name
... treatment are available for patients with the disorder. It will make for a more interesting presentation if you find out some creative things about the disorder like any famous people who have had the disorder or what the extreme effects of the disorder can be if it is not treated. You may want to t ...
... treatment are available for patients with the disorder. It will make for a more interesting presentation if you find out some creative things about the disorder like any famous people who have had the disorder or what the extreme effects of the disorder can be if it is not treated. You may want to t ...
Brief Overview of Common Psychotropic Medications - CE
... schizopherenia as well as the newer aypical antipsychotics. The mechanism of action involves many brain receptors but these medications are typically associated with the blockage of dopamine or D2 receptors. These medications are still used especially in acute hospital settings although becoming les ...
... schizopherenia as well as the newer aypical antipsychotics. The mechanism of action involves many brain receptors but these medications are typically associated with the blockage of dopamine or D2 receptors. These medications are still used especially in acute hospital settings although becoming les ...
Integrating Interpersonal Social Rhythm Therapy and Eye Movement
... trauma and trauma-like symptoms. It is believed that insufficient processing of distressing experiences creates pathological symptoms and once satisfactorily processed, the memories are stored more adaptively, allowing for better functioning in the present (Shapiro, 2001). The Systematic Treatment E ...
... trauma and trauma-like symptoms. It is believed that insufficient processing of distressing experiences creates pathological symptoms and once satisfactorily processed, the memories are stored more adaptively, allowing for better functioning in the present (Shapiro, 2001). The Systematic Treatment E ...
chapter 16: psychological disorders
... Personality Disorders Personality disorders are psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. The most troubling of these disorders is the antisocial personality disorder, in which a person (usually a man) exhibits a lack of co ...
... Personality Disorders Personality disorders are psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. The most troubling of these disorders is the antisocial personality disorder, in which a person (usually a man) exhibits a lack of co ...
informativespeechoutline
... A. Using DSM criteria, the mental health professional must identify the criteria including, 1. Your symptoms are not caused by drugs, alcohol, cultural or religious practices, or medical condition. 2. Having recurrent gaps in memory of daily events, traumatic events, personal information, or everyd ...
... A. Using DSM criteria, the mental health professional must identify the criteria including, 1. Your symptoms are not caused by drugs, alcohol, cultural or religious practices, or medical condition. 2. Having recurrent gaps in memory of daily events, traumatic events, personal information, or everyd ...
exploring psychology
... disorder no longer exist. They have been incorporated into a single continuum of mild to severe autism spectrum disorder. ...
... disorder no longer exist. They have been incorporated into a single continuum of mild to severe autism spectrum disorder. ...
Drop the language of disorder Evidence
... medicalisation of their understandable responses to their experiences; responses that undoubtedly have distressing consequences which demand helping responses, but which are better understood as normal individual variation than as illnesses. DSM-V would, if implemented, see an increased emphasis on ...
... medicalisation of their understandable responses to their experiences; responses that undoubtedly have distressing consequences which demand helping responses, but which are better understood as normal individual variation than as illnesses. DSM-V would, if implemented, see an increased emphasis on ...
Chapter 16 PowerPoint Notes
... Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicols & Gottesman, 1983). Personality Disorders Personality disorders are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually witho ...
... Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicols & Gottesman, 1983). Personality Disorders Personality disorders are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually witho ...
Schizoaffective Disorder
... • Principle of hierarchy (K. Jaspers) schizophrenic symptoms primarily, mood symptoms secondly ...
... • Principle of hierarchy (K. Jaspers) schizophrenic symptoms primarily, mood symptoms secondly ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – They usually accept the loss with relative calm – They invent physical symptoms to gain freedom from an unbearable conflict ...
... – They usually accept the loss with relative calm – They invent physical symptoms to gain freedom from an unbearable conflict ...
Study Guide: Chapter 14 Introduction: Understanding Psychological
... Syndrome, discuss who it affects most, and explain one possible cause of the disorder. 28. Describe the different types of schizophrenia, discuss the prevalence of schizophrenia, and identify variations in the course of the disease. 29. Summarize the evidence for the various factors thought to be in ...
... Syndrome, discuss who it affects most, and explain one possible cause of the disorder. 28. Describe the different types of schizophrenia, discuss the prevalence of schizophrenia, and identify variations in the course of the disease. 29. Summarize the evidence for the various factors thought to be in ...
View Presentation
... Four Types of Anxiety Disorders • Phobic disorder - an anxiety disorder characterized by a persistent, inappropriate fear of an object or situation • Generalized anxiety disorder - a mental disorder that is characterized by a persistent, inappropriate anxiety for which there is no apparent cause • ...
... Four Types of Anxiety Disorders • Phobic disorder - an anxiety disorder characterized by a persistent, inappropriate fear of an object or situation • Generalized anxiety disorder - a mental disorder that is characterized by a persistent, inappropriate anxiety for which there is no apparent cause • ...
Psychopharmacology
... magnetic stimulation (fMS) or Vagal Nerve stimulation (VNS) may be considered. Psychotherapy has been shown to benefit the client on antidepressants. Monotherapy is not adequate because: o 55-65%o of clients show a partial or no response to meclication o 35-45 o/ohave active remission o Of these,33 ...
... magnetic stimulation (fMS) or Vagal Nerve stimulation (VNS) may be considered. Psychotherapy has been shown to benefit the client on antidepressants. Monotherapy is not adequate because: o 55-65%o of clients show a partial or no response to meclication o 35-45 o/ohave active remission o Of these,33 ...
Chapter 13 - Psychological Disorders
... Agoraphobia: Anxiety characterized by marked fear and avoidance of being alone in a place from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing (such as airplanes, tunnels, being in crowds) Social phobia: Fear of, and desire to avoid, situations in which one might be exposed to scrutiny by others ...
... Agoraphobia: Anxiety characterized by marked fear and avoidance of being alone in a place from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing (such as airplanes, tunnels, being in crowds) Social phobia: Fear of, and desire to avoid, situations in which one might be exposed to scrutiny by others ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1 - Brimley Area Schools
... despair last for more than a few weeks and interfere with daily activities and interests • It can be a serious health problem that affects one’s ability to concentrate, sleep, perform at school or work or handle everyday decisions ...
... despair last for more than a few weeks and interfere with daily activities and interests • It can be a serious health problem that affects one’s ability to concentrate, sleep, perform at school or work or handle everyday decisions ...
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION VI SEMESTER
... 49. _____________ is best known of depression specific psychotherapy for unipolar depression. a) Cognitive behavioral therapy b) Lithium therapy c) Interpersonal therapy d) Family therapy 50. __________ is used with seriously depressed patients who may present immediate and serious suicidal risk. a) ...
... 49. _____________ is best known of depression specific psychotherapy for unipolar depression. a) Cognitive behavioral therapy b) Lithium therapy c) Interpersonal therapy d) Family therapy 50. __________ is used with seriously depressed patients who may present immediate and serious suicidal risk. a) ...
Chapter14
... loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting. Memory loss may be for a single traumatic event or for an extended time period around the event. identity ...
... loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting. Memory loss may be for a single traumatic event or for an extended time period around the event. identity ...
Childhood Bipolar Disorder
... instruments, no- controls, no blindness to parental diagnosis, no direct evaluation of children). Very few follow –up studies ( a total of 20 children for a period of 1-3 years). Chang et al., 2001; DelBello and Geller, 2000; LaPalme et al 1994 ...
... instruments, no- controls, no blindness to parental diagnosis, no direct evaluation of children). Very few follow –up studies ( a total of 20 children for a period of 1-3 years). Chang et al., 2001; DelBello and Geller, 2000; LaPalme et al 1994 ...
An Update On Depressive Disorders
... 1. Not all people are happy all the time…actual very few are! 2. Dysthymia can be effectively treated (60% respond to cognitive therapyCBT; 60% respond to antidepressantsAD). 3. Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and obsessive personalities with their serious, somber demeanor are often misdiagnosed ...
... 1. Not all people are happy all the time…actual very few are! 2. Dysthymia can be effectively treated (60% respond to cognitive therapyCBT; 60% respond to antidepressantsAD). 3. Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and obsessive personalities with their serious, somber demeanor are often misdiagnosed ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.