
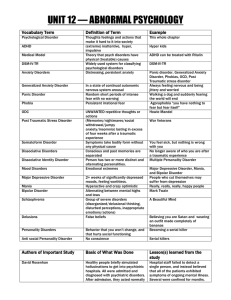
Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
unit 12 — abnormal psychology
... fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience Symptoms take bodily form without any physical cause Conscious and past memories are sep ...
... fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience Symptoms take bodily form without any physical cause Conscious and past memories are sep ...
Chapter 5 powerpoint
... A person has sudden, unexplained feelings of terror; a condition in which fear and anxiety get in the way of a person’s ability to function and enjoy life. ...
... A person has sudden, unexplained feelings of terror; a condition in which fear and anxiety get in the way of a person’s ability to function and enjoy life. ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 48
... phobia is diagnosed when there is an uncontrollable, irrational, intense desire to avoid the some object or situation. Even an image of the object can trigger a ...
... phobia is diagnosed when there is an uncontrollable, irrational, intense desire to avoid the some object or situation. Even an image of the object can trigger a ...
Panic Disorders
... misperceptions of underlying causes) on the one hand and physiological reactions on the other. Perceiving these bodily sensations as dire threats induces anxiety, which is accompanied by activation of the sympathetic nervous system. The changes in bodily sensations that trigger a panic attack may re ...
... misperceptions of underlying causes) on the one hand and physiological reactions on the other. Perceiving these bodily sensations as dire threats induces anxiety, which is accompanied by activation of the sympathetic nervous system. The changes in bodily sensations that trigger a panic attack may re ...
Psychological Disorders are - AKHSewing
... nervous system arousal (Sympathetic N.S.). Persistent symptoms: sweating, heart racing, dizziness, shaking accompanied by persistent negative feelings and fear…not triggered by specific events. ...
... nervous system arousal (Sympathetic N.S.). Persistent symptoms: sweating, heart racing, dizziness, shaking accompanied by persistent negative feelings and fear…not triggered by specific events. ...
THE CHILD
... adult roles • Individual therapy • Children often feel they are forced into therapy against his or her will • Nurses are seen as allies to caregivers that forced them into therapy • Nurse must avoid taking sides in order to develop trusting relationship • Communicate acceptance of child separate fro ...
... adult roles • Individual therapy • Children often feel they are forced into therapy against his or her will • Nurses are seen as allies to caregivers that forced them into therapy • Nurse must avoid taking sides in order to develop trusting relationship • Communicate acceptance of child separate fro ...
The Environmental Science of Mood Disorders
... • Patients with multiple unexplained complaints (somatizers) • Patients excessively worried about serious illness (hypochondriasis) • Patients with psychiatric disorders with somatic symptoms (depression; anxiety) ...
... • Patients with multiple unexplained complaints (somatizers) • Patients excessively worried about serious illness (hypochondriasis) • Patients with psychiatric disorders with somatic symptoms (depression; anxiety) ...
ap abnormal - HopewellPsychology
... sudden episodes (usually lasting a few minutes) of intense dread/fear 2. Non-specific: No particular trigger ...
... sudden episodes (usually lasting a few minutes) of intense dread/fear 2. Non-specific: No particular trigger ...
NUR 104 Mood disorder
... Types • Mild-a normal experience of living • Moderate- Now some problems grasping information(selective inattention) • Severe-Perceptual field very reduced problem solving impossible • Panic- Marked disturbed behavior • Running, shouting, screaming or with • drawal ...
... Types • Mild-a normal experience of living • Moderate- Now some problems grasping information(selective inattention) • Severe-Perceptual field very reduced problem solving impossible • Panic- Marked disturbed behavior • Running, shouting, screaming or with • drawal ...
AP_Chapter_16_psychological_disorders[1][1]
... sudden episodes (usually lasting a few minutes) of intense dread/fear 2. Non-specific: No particular trigger ...
... sudden episodes (usually lasting a few minutes) of intense dread/fear 2. Non-specific: No particular trigger ...
appsychchapt16
... Hyperalertness to danger. The individual often has difficulty shutting down the fightor-flight response that was activated during the event. This causes sleeplessness, ...
... Hyperalertness to danger. The individual often has difficulty shutting down the fightor-flight response that was activated during the event. This causes sleeplessness, ...
Day 7
... Often avoid social situations or endure them with great distress Generalized subtype – Social phobia across numerous social situations ...
... Often avoid social situations or endure them with great distress Generalized subtype – Social phobia across numerous social situations ...
Anxiety Disorders - Austin Community College
... – Natural environment; heights – Blood/injection – Situational/elevators ...
... – Natural environment; heights – Blood/injection – Situational/elevators ...
Adolescent Anxiety - Ilana Blatt
... • Probably a good sign that you need professional help • Exposure is an important part of CBT treatment for anxiety – controlled exposure to the feared situation/thought/experience until the person habituates • Habituation = Ride the anxiety wave! ...
... • Probably a good sign that you need professional help • Exposure is an important part of CBT treatment for anxiety – controlled exposure to the feared situation/thought/experience until the person habituates • Habituation = Ride the anxiety wave! ...
Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Depression and Anxiety
... • The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning • The symptoms are not due to the effects of alcohol or other substances or a medical condition (but comorbidity common) • Depressive episodes only, no manic, mixed, or hypomanic episodes • Symptoms not better accounte ...
... • The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning • The symptoms are not due to the effects of alcohol or other substances or a medical condition (but comorbidity common) • Depressive episodes only, no manic, mixed, or hypomanic episodes • Symptoms not better accounte ...
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY OF CHILDREN AND FAMILY
... focused on worrying about having a panic attack in a situation that will result in embarrassment, extreme discomfort, a heart attack or even worse. ...
... focused on worrying about having a panic attack in a situation that will result in embarrassment, extreme discomfort, a heart attack or even worse. ...
Depression and Anxiety Disorders
... Anxiety disorders include panic disorders, agoraphobia, social phobia, social anxiety disorder (SAD), simple phobia, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Symptoms include worry and nervousness, racing heart, breathlessnes ...
... Anxiety disorders include panic disorders, agoraphobia, social phobia, social anxiety disorder (SAD), simple phobia, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Symptoms include worry and nervousness, racing heart, breathlessnes ...
Anxiety and Somatoform Disorders
... A. Panic disorder 1. Recurrent and unexpected panic attacks are severe ...
... A. Panic disorder 1. Recurrent and unexpected panic attacks are severe ...
Anxiety disorder

Anxiety disorders are a category of mental disorders characterized by feelings of anxiety and fear, where anxiety is a worry about future events and fear is a reaction to current events. These feelings may cause physical symptoms, such as a racing heart and shakiness. There are a number of anxiety disorders: including generalized anxiety disorder, a specific phobia, social anxiety disorder, separation anxiety disorder, agoraphobia, and panic disorder among others. While each has its own characteristics and symptoms, they all include symptoms of anxiety.Anxiety disorders are partly genetic but may also be due to drug use including alcohol and caffeine, as well as withdrawal from certain drugs. They often occur with other mental disorders, particularly major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, certain personality disorders, and eating disorders. The term anxiety covers four aspects of experiences that an individual may have: mental apprehension, physical tension, physical symptoms and dissociative anxiety. The emotions present in anxiety disorders range from simple nervousness to bouts of terror. There are other psychiatric and medical problems that may mimic the symptoms of an anxiety disorder, such as hyperthyroidism.Common treatment options include lifestyle changes, therapy, and medications. Medications are typically recommended only if other measures are not effective. Anxiety disorders occur about twice as often in females as males, and generally begin during childhood. As many as 18% of Americans and 14% of Europeans may be affected by one or more anxiety disorders.










![AP_Chapter_16_psychological_disorders[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008609904_1-bcd0b4691952c52f8b5635246f54a50a-300x300.png)











