IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Patients with depression often have features of anxiety disorders, and those with anxiety disorders commonly also have depression. Both disorders may occur together, meeting criteria for both. Bipolar Affective Disorder, too, can have features of Anxiety Disorder (Panic Disorder most commonly). It c ...
... Patients with depression often have features of anxiety disorders, and those with anxiety disorders commonly also have depression. Both disorders may occur together, meeting criteria for both. Bipolar Affective Disorder, too, can have features of Anxiety Disorder (Panic Disorder most commonly). It c ...
Problem 33- hallucinations
... activities of daily living (ADLs) e.g. hygiene, budgeting, cooking etc. Cognitive impairments: concentration and memory deficits Frontal lobe deficits: inability to formulate and execute complex plans Thought disorder: derailment ...
... activities of daily living (ADLs) e.g. hygiene, budgeting, cooking etc. Cognitive impairments: concentration and memory deficits Frontal lobe deficits: inability to formulate and execute complex plans Thought disorder: derailment ...
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder PTSD
... depression, and insomnia often experienced with PTSD, and in some cases, it may help relieve the distress and emotional numbness caused by trauma memories. Several kinds of antidepressant drugs have contributed to patient improvement in most (but not all) clinical trials, and some other classes of d ...
... depression, and insomnia often experienced with PTSD, and in some cases, it may help relieve the distress and emotional numbness caused by trauma memories. Several kinds of antidepressant drugs have contributed to patient improvement in most (but not all) clinical trials, and some other classes of d ...
1 - U-System
... 33. For the same patient listed in question 32: Which of the following best describes symptom production and motivation in this teenage? a. Symptom production conscious, motivation primarily conscious b. Symptom production unconscious, motivation primarily conscious c. Symptom production conscious, ...
... 33. For the same patient listed in question 32: Which of the following best describes symptom production and motivation in this teenage? a. Symptom production conscious, motivation primarily conscious b. Symptom production unconscious, motivation primarily conscious c. Symptom production conscious, ...
ICD-9-CM coding for ADHD
... Use additional code(s) to identify any associated injuries 995.59 Other child abuse and neglect Multiple forms of abuse Use additional code to identify intent of neglect (E904.0,E968.4) ...
... Use additional code(s) to identify any associated injuries 995.59 Other child abuse and neglect Multiple forms of abuse Use additional code to identify intent of neglect (E904.0,E968.4) ...
Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness
... Other specified disorder or Unspecified disorder type are to be used if the diagnosis of a client is too uncertain because of: 1. Behaviors which are associated with a classification are seen but there is uncertainty regarding the diagnostic category due to the fact that The client presents some s ...
... Other specified disorder or Unspecified disorder type are to be used if the diagnosis of a client is too uncertain because of: 1. Behaviors which are associated with a classification are seen but there is uncertainty regarding the diagnostic category due to the fact that The client presents some s ...
Ch02 - Myweb @ CW Post
... • Exclusion criteria were eliminated from the DSM-III-R, except those used to rule out an organic causes of disorder. • The elimination of exclusion criteria lead to an increase in rates of comorbidity, or the co-occurrence of two or more disorders. DSM-IV (APA, 1994) • Revisions were more data dr ...
... • Exclusion criteria were eliminated from the DSM-III-R, except those used to rule out an organic causes of disorder. • The elimination of exclusion criteria lead to an increase in rates of comorbidity, or the co-occurrence of two or more disorders. DSM-IV (APA, 1994) • Revisions were more data dr ...
Social Anxiety Disorder Brochure
... life. A mental health professional can provide a diagnosis and individualized treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment provide the best hope for preventing the onset of other related disorders. A variety of treatment options are scientifically proven to be effective. One evidence-based treatmen ...
... life. A mental health professional can provide a diagnosis and individualized treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment provide the best hope for preventing the onset of other related disorders. A variety of treatment options are scientifically proven to be effective. One evidence-based treatmen ...
the fatal addiction to plastic surgery
... thoughts. These flaws may be non-existent or minimal but you cannot reassure a BDD victim. BDD patients may compulsively remove their skin, attempt self surgeries and even amputations in extreme cases. These obsessive concerns cause significant emotional distress (e.g. depression) and often signific ...
... thoughts. These flaws may be non-existent or minimal but you cannot reassure a BDD victim. BDD patients may compulsively remove their skin, attempt self surgeries and even amputations in extreme cases. These obsessive concerns cause significant emotional distress (e.g. depression) and often signific ...
Mood Disorders
... recurrent depressive episodes. Both biological and social factors play a part in these patterns. For example, women who experience severe premenstrual mood changes are more vulnerable to other mood disorders including postpartum depression. For bipolar disorder, men and woman are equally represented ...
... recurrent depressive episodes. Both biological and social factors play a part in these patterns. For example, women who experience severe premenstrual mood changes are more vulnerable to other mood disorders including postpartum depression. For bipolar disorder, men and woman are equally represented ...
ANXIETY
... migraines, diabetes, heart and respiratory diseases, reported that on days when they feel anxious or depressed, there is a moderate (38%) to severe (12%) change in their physical symptoms or aches and pains. ...
... migraines, diabetes, heart and respiratory diseases, reported that on days when they feel anxious or depressed, there is a moderate (38%) to severe (12%) change in their physical symptoms or aches and pains. ...
anxiety - Science Mission
... migraines, diabetes, heart and respiratory diseases, reported that on days when they feel anxious or depressed, there is a moderate (38%) to severe (12%) change in their physical symptoms or aches and pains. ...
... migraines, diabetes, heart and respiratory diseases, reported that on days when they feel anxious or depressed, there is a moderate (38%) to severe (12%) change in their physical symptoms or aches and pains. ...
Let`s Talk About Binge Eating Disorder
... Binge-eating disorder (BED) can be challenging to identify. Its prevalence in the general population is about 2%,[1] and according to the newly released 5th edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), BED has a distinct clinical profile from bulimia nervosa, which i ...
... Binge-eating disorder (BED) can be challenging to identify. Its prevalence in the general population is about 2%,[1] and according to the newly released 5th edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), BED has a distinct clinical profile from bulimia nervosa, which i ...
Panic Disorder
... Naltrexone blocks opiate receptors and works by decreasing the craving for alcohol, resulting in fewer relapses. Most, but not all, studies found that naltrexone decreases relapses but the effect is modest (12-20%). Combining naltrexone therapy with cognitive behavioral therapy enhanced benefit. One ...
... Naltrexone blocks opiate receptors and works by decreasing the craving for alcohol, resulting in fewer relapses. Most, but not all, studies found that naltrexone decreases relapses but the effect is modest (12-20%). Combining naltrexone therapy with cognitive behavioral therapy enhanced benefit. One ...
Slide 1
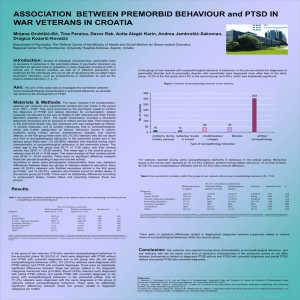
... Materials & Methods: The study included 415 compensationseeking war veterans who experienced combat and war stress in the period from 1991 – 1995. They were examined by the psychiatric expert to confirm the diagnosis of PTSD and related disorders for compensation- related purposes, as required by th ...
... Materials & Methods: The study included 415 compensationseeking war veterans who experienced combat and war stress in the period from 1991 – 1995. They were examined by the psychiatric expert to confirm the diagnosis of PTSD and related disorders for compensation- related purposes, as required by th ...
Overview of Psychopathologies and Their Treatments
... work without getting distracted. Rare in childhood. Reactive attachment disorder-may show social inhibition but is not interested in relationships compared with ADHD. Anxiety disorders-inattention is not the search for novel or preoccupation with something but due to worry or rumination. Depressive ...
... work without getting distracted. Rare in childhood. Reactive attachment disorder-may show social inhibition but is not interested in relationships compared with ADHD. Anxiety disorders-inattention is not the search for novel or preoccupation with something but due to worry or rumination. Depressive ...
Psych_Disorders_12
... • Charles is the third of seven children. He attended school in the suburbs of a large city, where he made average grades. He dated a bit in high school and had several close friends. During vacations, he worked in his father’s garage, learning all he could about automobiles. After high school, Cha ...
... • Charles is the third of seven children. He attended school in the suburbs of a large city, where he made average grades. He dated a bit in high school and had several close friends. During vacations, he worked in his father’s garage, learning all he could about automobiles. After high school, Cha ...
powerpoint - CRE Learning Home
... • Acute stress disorder is caused by exposure to trauma, which is defined as a stressor that causes intense fear and, usually, involves threats to life or serious injury to oneself or others. ...
... • Acute stress disorder is caused by exposure to trauma, which is defined as a stressor that causes intense fear and, usually, involves threats to life or serious injury to oneself or others. ...
fostering connections: responding to reactive attachment disorder
... • Because the majority of brain growth and development takes place during these first years, early developmental trauma and neglect have a ‘disproportionate influence on brain organization and later brain functioning’” ...
... • Because the majority of brain growth and development takes place during these first years, early developmental trauma and neglect have a ‘disproportionate influence on brain organization and later brain functioning’” ...
Preview the test
... a) Be diagnosed with ODD and DMDD b) Be diagnosed with whichever is the primary diagnosis c) Only be diagnosed with ODD d) Only be diagnosed with DMDD 28) An individual who is completely convinced that their hoarding behavior is not problematic despite evidence to the contrary would be given which s ...
... a) Be diagnosed with ODD and DMDD b) Be diagnosed with whichever is the primary diagnosis c) Only be diagnosed with ODD d) Only be diagnosed with DMDD 28) An individual who is completely convinced that their hoarding behavior is not problematic despite evidence to the contrary would be given which s ...
Prototype for a Scientific Classification of Mental Disorders – website
... What about the word classification? This is a formalised type of description. I ask: ‘Can description ever be neutral with respect to theory? I don’t believe so. Carl Linnaeus – the seventeenth century Swedish scholar who classified plants - he also classified diseases - held that classification sho ...
... What about the word classification? This is a formalised type of description. I ask: ‘Can description ever be neutral with respect to theory? I don’t believe so. Carl Linnaeus – the seventeenth century Swedish scholar who classified plants - he also classified diseases - held that classification sho ...
Preview the test
... 4) The DAST is highly reliable and corresponds well with the DSM diagnosis of substance use, however it does not a) address the impact substance use is having on a person’s life. b) obtain information regarding specific substances used. c) it does not attempt to discern if multiple substances are us ...
... 4) The DAST is highly reliable and corresponds well with the DSM diagnosis of substance use, however it does not a) address the impact substance use is having on a person’s life. b) obtain information regarding specific substances used. c) it does not attempt to discern if multiple substances are us ...
the powerpoint - Pennsylvania Psychological Association
... Other specified DID covers: Identity disturbance due to prolonged and intensive coercive persuasion through brainwashing, tor ture, and political imprisonment. DSM-5 of fers insight into triggers for decompensation through a developmental lens including a DID-af flicted client’s: 1) removal from ...
... Other specified DID covers: Identity disturbance due to prolonged and intensive coercive persuasion through brainwashing, tor ture, and political imprisonment. DSM-5 of fers insight into triggers for decompensation through a developmental lens including a DID-af flicted client’s: 1) removal from ...