document
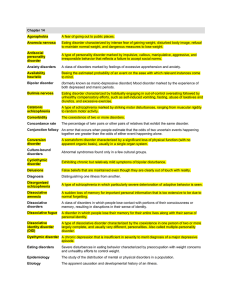
... feelings and behaviors that may be troublesome, selfdefeating, or self-destructive • Group therapy: involves treating a group of people who have similar problems and who meet regularly with a ...
... feelings and behaviors that may be troublesome, selfdefeating, or self-destructive • Group therapy: involves treating a group of people who have similar problems and who meet regularly with a ...
Lawyers and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
... call this vicarious traumatization. It is understood that professionals who work with people needing their help begin to experience the same emotions and even some of the same symptoms as their clients. Judges are particularly susceptible to vicarious trau matiz ation because they are exposed to ...
... call this vicarious traumatization. It is understood that professionals who work with people needing their help begin to experience the same emotions and even some of the same symptoms as their clients. Judges are particularly susceptible to vicarious trau matiz ation because they are exposed to ...
Psychological Disorders What is mental illness? Diagnostic and
... disorder, e.g., the anxiety or worry is not about having a panic attack (as in panic disorder), being embarrassed in public (as in social phobia), being contaminated (as in obsessive-compulsive disorder), being away from home or close relatives (as in Separation Anxiety Disorder), gaining weight (as ...
... disorder, e.g., the anxiety or worry is not about having a panic attack (as in panic disorder), being embarrassed in public (as in social phobia), being contaminated (as in obsessive-compulsive disorder), being away from home or close relatives (as in Separation Anxiety Disorder), gaining weight (as ...
Document
... When assessing psychiatric problems, you collect information about the person’s state of mind and thinking. Your actions and attitude often provide some of the therapy sought by the patient. Be prepared to spend some time with the patient as you assess his or her thinking. Dissociative disorders are ...
... When assessing psychiatric problems, you collect information about the person’s state of mind and thinking. Your actions and attitude often provide some of the therapy sought by the patient. Be prepared to spend some time with the patient as you assess his or her thinking. Dissociative disorders are ...
pptx
... MMPI • Example of an “empirically derived” test • Questions “earn” their way onto the final test by statistically differentiating different groups of people (people with and without depression, people with and without schizophrenia, people with and without alcohol problems, etc…) ...
... MMPI • Example of an “empirically derived” test • Questions “earn” their way onto the final test by statistically differentiating different groups of people (people with and without depression, people with and without schizophrenia, people with and without alcohol problems, etc…) ...
File
... – Localized: Unable to recall details for a particular event or brief period of time. – Generalized: Unable to recall all details from a person’s past. – Continuous: Unable to recall details from a specific event forward to the present. ...
... – Localized: Unable to recall details for a particular event or brief period of time. – Generalized: Unable to recall all details from a person’s past. – Continuous: Unable to recall details from a specific event forward to the present. ...
Depression 101
... than a specific medical condition. This related set of disorders are associated with chemical imbalance in the brain that affects many of our biologic and physical functions Stigma is due to fears about brain illness and leads to under-reporting of symptoms and undertreatment Anxiety and other c ...
... than a specific medical condition. This related set of disorders are associated with chemical imbalance in the brain that affects many of our biologic and physical functions Stigma is due to fears about brain illness and leads to under-reporting of symptoms and undertreatment Anxiety and other c ...
Glossary
... Eating disorder characterized by habitually engaging in out-of-control overeating followed by unhealthy compensatory efforts, such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, and excessive exercise. ...
... Eating disorder characterized by habitually engaging in out-of-control overeating followed by unhealthy compensatory efforts, such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, and excessive exercise. ...
Chapter 14 - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... Eating disorder characterized by habitually engaging in out-of-control overeating followed by unhealthy compensatory efforts, such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, and excessive exercise. ...
... Eating disorder characterized by habitually engaging in out-of-control overeating followed by unhealthy compensatory efforts, such as self-induced vomiting, fasting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, and excessive exercise. ...
CHAPTER 13 Long PRACTICE TEST
... Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the distinction between normal and abnormal behavior? a. A person might be considered normal in one culture and abnormal in another. b. Not all people whose behavior is abnormal experience personal distress. c. The most widely used criterion fo ...
... Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the distinction between normal and abnormal behavior? a. A person might be considered normal in one culture and abnormal in another. b. Not all people whose behavior is abnormal experience personal distress. c. The most widely used criterion fo ...
Abnormal test review -Know which collections of symptoms are
... For example: chemical imbalances in the brain are thought to be contributing factors in several disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar, OCD ...
... For example: chemical imbalances in the brain are thought to be contributing factors in several disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar, OCD ...
Mental Disorders
... and thinking processes. These people have difficulty thinking rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available. The most prevalent symptoms of these diseases are usually delu ...
... and thinking processes. These people have difficulty thinking rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available. The most prevalent symptoms of these diseases are usually delu ...
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
... that they have to be extra special just to be accepted. They may actually have very fragile self-esteem. A person with NPD may not show it, but is easily hurt and rejected. This often happens because their expectations are so high. Their relationships with other people tend to be very poor. Other po ...
... that they have to be extra special just to be accepted. They may actually have very fragile self-esteem. A person with NPD may not show it, but is easily hurt and rejected. This often happens because their expectations are so high. Their relationships with other people tend to be very poor. Other po ...
exploring psychology
... ANXIETY DISORDERS, OCD, AND PTSD (pp. 504, 510, 512–519, 540, 541, 557, 569–570, 574) Obsessive-compulsive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder are now classified separately from anxiety disorders. The criteria for posttraumatic stress disorder have been modified. Social phobia is now termed s ...
... ANXIETY DISORDERS, OCD, AND PTSD (pp. 504, 510, 512–519, 540, 541, 557, 569–570, 574) Obsessive-compulsive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder are now classified separately from anxiety disorders. The criteria for posttraumatic stress disorder have been modified. Social phobia is now termed s ...
Somatoform disorders
... – Obsessional personality, exaggerated health consciousness, alternative medical care common – High comorbidity with depression and anxiety disorders ...
... – Obsessional personality, exaggerated health consciousness, alternative medical care common – High comorbidity with depression and anxiety disorders ...
Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder
... Disorder Okeechobee Fla. Dyslimbia Press Inc. Kriesman J. J. and Strauss H: (1991 ) I Hate you -don’t leave me :Understanding the Borderline Personality New Your NY Avon Books Linehan M. M. (1993) Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Borderline Personality Disorder New York ...
... Disorder Okeechobee Fla. Dyslimbia Press Inc. Kriesman J. J. and Strauss H: (1991 ) I Hate you -don’t leave me :Understanding the Borderline Personality New Your NY Avon Books Linehan M. M. (1993) Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Borderline Personality Disorder New York ...
Personality Disorders
... Cluster B: The Dramatic, Emotional, or Erratic Ones Antisocial Personality Disorder Primary feature: complete disregard for others/rules (think: the sociopaths) Includes violence, law violations, lying/cheating, lack of remorse. May appear as very charming or cocky and hostile. The one diso ...
... Cluster B: The Dramatic, Emotional, or Erratic Ones Antisocial Personality Disorder Primary feature: complete disregard for others/rules (think: the sociopaths) Includes violence, law violations, lying/cheating, lack of remorse. May appear as very charming or cocky and hostile. The one diso ...
1 PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Agenda/Overview Mood
... Bipolar I differentiated from psychotic disorders by • rapid onset of symptoms • absence of prodromal signs of schizophrenia • quick return to previous level of functioning ...
... Bipolar I differentiated from psychotic disorders by • rapid onset of symptoms • absence of prodromal signs of schizophrenia • quick return to previous level of functioning ...
Perspectives ppt. - Ms. Engel @ South
... – However, for several people, anxiety or depression in moderation gives way to severe levels of these emotions, which can be maladaptive ...
... – However, for several people, anxiety or depression in moderation gives way to severe levels of these emotions, which can be maladaptive ...
Comparison of DSM-IV-TR Classification with DSM
... adolescents) of the disturbance, the person has never been without the symptoms in Criteria A and B for more than 2 months at a time. D. No Major Depressive Episode has been present during the first 2 years of the disturbance (1 year for children and adolescents); i.e., the disturbance is not better ...
... adolescents) of the disturbance, the person has never been without the symptoms in Criteria A and B for more than 2 months at a time. D. No Major Depressive Episode has been present during the first 2 years of the disturbance (1 year for children and adolescents); i.e., the disturbance is not better ...
Conduct Disorder - American Psychiatric Association
... Individuals with conduct disorder who meet criteria for the specifier have a relatively more severe form of the disorder and a different treatment response. Thus the specifier will allow clinicians to more accurately identify and diagnosis individuals who need more intensive and individualized treat ...
... Individuals with conduct disorder who meet criteria for the specifier have a relatively more severe form of the disorder and a different treatment response. Thus the specifier will allow clinicians to more accurately identify and diagnosis individuals who need more intensive and individualized treat ...
Notes 3-13
... terrified that the mafia was after him. He is convinced that the mafia has put cameras in his dormitory room. He occasionally hears the voices of two men talking when no one is around. His roommate states that for the past 2 months he has been increasingly withdrawn and suspicious. What is the most ...
... terrified that the mafia was after him. He is convinced that the mafia has put cameras in his dormitory room. He occasionally hears the voices of two men talking when no one is around. His roommate states that for the past 2 months he has been increasingly withdrawn and suspicious. What is the most ...
Chapter 16
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
Mental Health - Salesianum School
... • Having a phobia may produce the following signs and symptoms: • A persistent, irrational fear of a specific object, activity or situation. • An immediate response of uncontrollable anxiety when exposed to the object of fear. • A compelling desire to avoid and unusual measures taken to stay away fr ...
... • Having a phobia may produce the following signs and symptoms: • A persistent, irrational fear of a specific object, activity or situation. • An immediate response of uncontrollable anxiety when exposed to the object of fear. • A compelling desire to avoid and unusual measures taken to stay away fr ...