Abnormal Psychology Project
... use the same story (first come, first serve). 2) Using your researched knowledge of the disorder, rewrite the story as it would be if the main character had that disorder. 3) Stories should NOT name the disorder, but should describe it within the story. 4) Type the finished story and include all gro ...
... use the same story (first come, first serve). 2) Using your researched knowledge of the disorder, rewrite the story as it would be if the main character had that disorder. 3) Stories should NOT name the disorder, but should describe it within the story. 4) Type the finished story and include all gro ...
Specific Disorders
... His problem is clearly organic -- he has some physical damage or deficiency. No one argues over such things as syphilis or head trauma. These are clearly brain pathologies and clearly the realm of the physician It is the so called functional psychoses Those with no known organic cause that are the a ...
... His problem is clearly organic -- he has some physical damage or deficiency. No one argues over such things as syphilis or head trauma. These are clearly brain pathologies and clearly the realm of the physician It is the so called functional psychoses Those with no known organic cause that are the a ...
Unit Eleven
... Normal or Not? The man in the example on the previous slide was interviewed by psychiatrists, diagnosed as paranoid schizophrenic, and ...
... Normal or Not? The man in the example on the previous slide was interviewed by psychiatrists, diagnosed as paranoid schizophrenic, and ...
Psychological Disorders
... Tend to be loners, have few friends Similar to symptoms of schizophrenia – without the hallucinations and delusions They stay in touch with reality ...
... Tend to be loners, have few friends Similar to symptoms of schizophrenia – without the hallucinations and delusions They stay in touch with reality ...
item[`#file`]->filename
... Slide 7: American Psychiatric Association, DSM-IV criteria, 1994. Slide 18: American Psychiatric Association, DSM-IV criteria, 1994. ...
... Slide 7: American Psychiatric Association, DSM-IV criteria, 1994. Slide 18: American Psychiatric Association, DSM-IV criteria, 1994. ...
- bYTEBoss
... excessive and unreasonable The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time consuming,and significantly interfere with normal routine ...
... excessive and unreasonable The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time consuming,and significantly interfere with normal routine ...
Chapter 7: Self & Moral Development
... • 13–18: 5.6% (girls 5.9%, boys 4.6%) Bipolar Disorder: • Diagnosis has increased dramatically, at least in part due to increased recognition that the disorder does occur in children • A high percentage also receive a comorbid diagnosis, often ADHD • Equal prevalence in males & females ...
... • 13–18: 5.6% (girls 5.9%, boys 4.6%) Bipolar Disorder: • Diagnosis has increased dramatically, at least in part due to increased recognition that the disorder does occur in children • A high percentage also receive a comorbid diagnosis, often ADHD • Equal prevalence in males & females ...
Mental Health - Springboro Community Schools
... 20. May involve hallucinations, delusions, disordered thinking, movement disorders, flat affect, social withdrawal, and cognitive deficits. Person is out of touch with reality and may perceive stimuli that don’t exist. 21. One of the most common mental disorders that develops in children. Children w ...
... 20. May involve hallucinations, delusions, disordered thinking, movement disorders, flat affect, social withdrawal, and cognitive deficits. Person is out of touch with reality and may perceive stimuli that don’t exist. 21. One of the most common mental disorders that develops in children. Children w ...
DEFINITION OF MENTAL ILLNESS
... Society sets standards for norm As society becomes more pluralistic, fewer behaviors will be considered abnormal Society can change criteria of normal or abnormal ...
... Society sets standards for norm As society becomes more pluralistic, fewer behaviors will be considered abnormal Society can change criteria of normal or abnormal ...
Interrater and Test-Retest Reliability
... social relationships and usually has no close friends. Is aloof and has no warm, tender feelings for other people. Schizotypal Personality Disorder - have the interpersonal difficulties of the schizoid personality and excessive social anxiety that does not diminish with familiarity. They have some ...
... social relationships and usually has no close friends. Is aloof and has no warm, tender feelings for other people. Schizotypal Personality Disorder - have the interpersonal difficulties of the schizoid personality and excessive social anxiety that does not diminish with familiarity. They have some ...
Psychological Disorders
... The medical model views abnormal behaviors as no different from illnesses and seeks to identify symptoms and prescribe medical treatments. ...
... The medical model views abnormal behaviors as no different from illnesses and seeks to identify symptoms and prescribe medical treatments. ...
ADHD vs. Mood Disorders - Columbia Associates in Psychiatry
... Family History – A helpful distinction between the two disorders is a family history. Since both have a familial inheritance, a detailed family history looking for symptoms or diagnosis of either disorder among blood relatives can be useful. If Bipolar Disorder is revealed, the childhood history of ...
... Family History – A helpful distinction between the two disorders is a family history. Since both have a familial inheritance, a detailed family history looking for symptoms or diagnosis of either disorder among blood relatives can be useful. If Bipolar Disorder is revealed, the childhood history of ...
Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders
... studies, and she’s on the verge of failing all her courses. This suggests that she may suffer from a (1) generalized anxiety disorder, which may lead to (2) physical problems, such as ulcers and high blood pressure. Because Carol cannot identify the cause of her tension, it would be described by Sig ...
... studies, and she’s on the verge of failing all her courses. This suggests that she may suffer from a (1) generalized anxiety disorder, which may lead to (2) physical problems, such as ulcers and high blood pressure. Because Carol cannot identify the cause of her tension, it would be described by Sig ...
MCQ PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
... c) there is up to a 25% incidence of secondary depression d) the diagnosis of schizophrenia can only be made after the illness has been going for 6 weeks e) the earlier the onset the worse the prognosis 13.Which is false with regards to dementia? a) there is a disturbance of cognitive and higher cor ...
... c) there is up to a 25% incidence of secondary depression d) the diagnosis of schizophrenia can only be made after the illness has been going for 6 weeks e) the earlier the onset the worse the prognosis 13.Which is false with regards to dementia? a) there is a disturbance of cognitive and higher cor ...
Chapter 16 Notes
... a. Self-Actualization – Humanistic view that to be normal or healthy involves full acceptance and expression of one’s own individuality and humanness i. Problem with this approach is that its hard to determine whether a person is actualizing themselves b. Labeling a person as mentally ill because of ...
... a. Self-Actualization – Humanistic view that to be normal or healthy involves full acceptance and expression of one’s own individuality and humanness i. Problem with this approach is that its hard to determine whether a person is actualizing themselves b. Labeling a person as mentally ill because of ...
Preparation for Lecture 13 (Chapter 14)
... committed murder. Also, mentally sick people have low chance of recovery and they are often stigmatized. Yet, many times, we cannot differentiate sane from insane. In this class, we will discuss the notion of abnormality, disorders, and therapies. ...
... committed murder. Also, mentally sick people have low chance of recovery and they are often stigmatized. Yet, many times, we cannot differentiate sane from insane. In this class, we will discuss the notion of abnormality, disorders, and therapies. ...
a severe mood disorder characterized by major
... Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression before age 30. B. Why women more than men? ...
... Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression before age 30. B. Why women more than men? ...
File
... •________ & Natural Selection causes anxiety for certain objects/ situations •Generalized anxiety, panic attacks, and even OCD are linked with ____ circuits like the ______________________ ...
... •________ & Natural Selection causes anxiety for certain objects/ situations •Generalized anxiety, panic attacks, and even OCD are linked with ____ circuits like the ______________________ ...
Psychological disorders
... • Twice as likely among female compared to male • Reasons: Conflicting roles of wife, lover and friend • Boys – twice as likely before puberty, Female – twice as likely after ...
... • Twice as likely among female compared to male • Reasons: Conflicting roles of wife, lover and friend • Boys – twice as likely before puberty, Female – twice as likely after ...
2. Personality Disorders
... following choices: – A) Social anxiety D) Hypochondriasis – B) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder E) Somatoform Disorder – C) Generalized anxiety disorder F) Agoraphobia ...
... following choices: – A) Social anxiety D) Hypochondriasis – B) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder E) Somatoform Disorder – C) Generalized anxiety disorder F) Agoraphobia ...
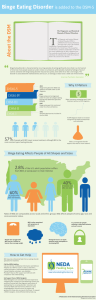
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
Group Powerpoint
... The primary cause of DID is severe and prolonged trauma experienced during childhood. This trauma is associated with emotional, physical or sexual abuse, or some combination of two or more. One theory is that young children, faced with a routine of torture, abuse, sexual abuse or neglect , dissociat ...
... The primary cause of DID is severe and prolonged trauma experienced during childhood. This trauma is associated with emotional, physical or sexual abuse, or some combination of two or more. One theory is that young children, faced with a routine of torture, abuse, sexual abuse or neglect , dissociat ...
Somatic Disorders DSM V Handout
... A. One or more symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function. B. Clinical findings provide evidence of incompatibility between the symptom and recognized neurological or medical conditions. C. The symptom or deficit is not better explained by another medical or mental disorder. D. The symp ...
... A. One or more symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function. B. Clinical findings provide evidence of incompatibility between the symptom and recognized neurological or medical conditions. C. The symptom or deficit is not better explained by another medical or mental disorder. D. The symp ...



![item[`#file`]->filename](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012354057_1-447b7c4c4656bac2ad46022937e666a7-300x300.png)