Chapter 42a
... nutty... There are all kinds of interesting questions that come from a knowledge of science, which only adds to the excitement and mystery of a flower. It only adds. Richard Feynman, What Do You Care What Other People Think? (1989, p. 11) Main concepts: • The cell is the basic unit of all living thi ...
... nutty... There are all kinds of interesting questions that come from a knowledge of science, which only adds to the excitement and mystery of a flower. It only adds. Richard Feynman, What Do You Care What Other People Think? (1989, p. 11) Main concepts: • The cell is the basic unit of all living thi ...
chapt 22
... Gametes unite to form a zygote. Zygote divides by mitosis to form the sporophyte generation. ...
... Gametes unite to form a zygote. Zygote divides by mitosis to form the sporophyte generation. ...
Neodypsis decaryi (Triangle Palm) Size/Shape
... This palm is endemic to the Madagascar, and it thrives in poor, dry soils. Its usual heights is 3-5 m with a crown spread of 5-7 m, and it grows best in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. The tall, stiff feather-shape leaves can grow to 3 m long. Fronds grow from the top portion of the trunk i ...
... This palm is endemic to the Madagascar, and it thrives in poor, dry soils. Its usual heights is 3-5 m with a crown spread of 5-7 m, and it grows best in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. The tall, stiff feather-shape leaves can grow to 3 m long. Fronds grow from the top portion of the trunk i ...
Neodypsis decaryi (Triangle Palm) Size/Shape
... This palm is endemic to the Madagascar, and it thrives in poor, dry soils. Its usual heights is 3-5 m with a crown spread of 5-7 m, and it grows best in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. The tall, stiff feather-shape leaves can grow to 3 m long. Fronds grow from the top portion of the trunk i ...
... This palm is endemic to the Madagascar, and it thrives in poor, dry soils. Its usual heights is 3-5 m with a crown spread of 5-7 m, and it grows best in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. The tall, stiff feather-shape leaves can grow to 3 m long. Fronds grow from the top portion of the trunk i ...
Kingdom Plantaenew
... cover the outer surface. • Vascular Tissue: specialized transport cells 1. Xylem: carries water and nutrients up from the roots. (tracheids and vessel elements) 2. Phloem: carries sugars down from leaves (sieve tube elements and companion cells) • Ground Tissue: contains photosynthesizing cells and ...
... cover the outer surface. • Vascular Tissue: specialized transport cells 1. Xylem: carries water and nutrients up from the roots. (tracheids and vessel elements) 2. Phloem: carries sugars down from leaves (sieve tube elements and companion cells) • Ground Tissue: contains photosynthesizing cells and ...
BIT Assignment
... • You may examine the real specimens displayed. • Homework – Textbook Page 37-38, HKCEE 1985 1(a) and HKCEE 1987 1(a) ...
... • You may examine the real specimens displayed. • Homework – Textbook Page 37-38, HKCEE 1985 1(a) and HKCEE 1987 1(a) ...
leaves - SBI3USylviaFall2010
... • When stomata are open water is lost (transpiration) and the plant can exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide through diffusion. • When stomata are closed the plant conserves water, but can not exchange gases. • Guard cells located on either side of the stomata regulate the opening and closing of the s ...
... • When stomata are open water is lost (transpiration) and the plant can exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide through diffusion. • When stomata are closed the plant conserves water, but can not exchange gases. • Guard cells located on either side of the stomata regulate the opening and closing of the s ...
CATHERINE - PUPApprentice0910
... It is the part of the embryo that first grows downward into the soil form a stem of the seedling. This hold the plant in place and gathers moisture and food in the soil. ...
... It is the part of the embryo that first grows downward into the soil form a stem of the seedling. This hold the plant in place and gathers moisture and food in the soil. ...
General Biology 101 - Linn
... Chapter Outlines Starr & Taggert 10th edition Chapter 23 Introduction – Pioneers in a New World It is thought that plants first colonized the land around 700 million years ago. There are fossils of these first pioneers. Today cyanobacteria (photosynthetic prokaryotes) and green algae grow as mats in ...
... Chapter Outlines Starr & Taggert 10th edition Chapter 23 Introduction – Pioneers in a New World It is thought that plants first colonized the land around 700 million years ago. There are fossils of these first pioneers. Today cyanobacteria (photosynthetic prokaryotes) and green algae grow as mats in ...
Evolution_LauraD
... published • 1874, second edition of Descent of Man is published • 1876, published autobiography ...
... published • 1874, second edition of Descent of Man is published • 1876, published autobiography ...
plant reproduction
... There are also plants that do not flower BUT still produce seeds….(ahhh, so many kinds of plants – isn’t it fascinating!) Gymnosperms are vascular plants that produce seeds, but do not produce flowers. Coniferous trees, such as pine trees, are examples of gymnosperms. Look at the seed of a pine tre ...
... There are also plants that do not flower BUT still produce seeds….(ahhh, so many kinds of plants – isn’t it fascinating!) Gymnosperms are vascular plants that produce seeds, but do not produce flowers. Coniferous trees, such as pine trees, are examples of gymnosperms. Look at the seed of a pine tre ...
Plant Biology Review ()
... equipped with buds on the surface • Runners (like strawberries) – horizontal stems that can give rise to new roots and shoots • Bulbs – underground buds (contains several buds that can be new plants) • Grafting – two young plants are joined ...
... equipped with buds on the surface • Runners (like strawberries) – horizontal stems that can give rise to new roots and shoots • Bulbs – underground buds (contains several buds that can be new plants) • Grafting – two young plants are joined ...
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Welcome to UCSC
... 4. Splashing rain water is important for this plants sexual reproduction compared to more ancestral plants which needed to be submerged in water to reproduce sexually? Which statement below is false? A. Being able to reproduce out of water enabled plants to become established on land. B. Being able ...
... 4. Splashing rain water is important for this plants sexual reproduction compared to more ancestral plants which needed to be submerged in water to reproduce sexually? Which statement below is false? A. Being able to reproduce out of water enabled plants to become established on land. B. Being able ...
Revision (Respiration, Photosynthesis,Dispersal
... more water is drawn up the xylem. • But plants also need to have water evaporate from their leaves to cool themselves down. So they need to strike a balance between water gain and water loss. • Plants control the amount of water lost through transpiration by opening and closing their stomata. Two gu ...
... more water is drawn up the xylem. • But plants also need to have water evaporate from their leaves to cool themselves down. So they need to strike a balance between water gain and water loss. • Plants control the amount of water lost through transpiration by opening and closing their stomata. Two gu ...
Mini-Lesson: Punnett Squares
... Each parent of an organism contributes a gene with two alleles that may be dominant or recessive. A dominant trait will always be expressed over a recessive trait. This can be illustrated with a simple chart called a Punnett Square: Pea Plant Examples Plant 1 = Dominant Tall (TT) = Tall Plant Plant ...
... Each parent of an organism contributes a gene with two alleles that may be dominant or recessive. A dominant trait will always be expressed over a recessive trait. This can be illustrated with a simple chart called a Punnett Square: Pea Plant Examples Plant 1 = Dominant Tall (TT) = Tall Plant Plant ...
Plant Hormones and Response – Part 1 I. Plant Hormones A. Auxin
... 1. For example, Bolting – This process is triggered by water (ligand) entering the seed. 2. For example, Greening (Fig: 39.4) – The plant begins producing chloroplasts in response to sunlight. C. Hormones are released to target tissues to relay information. (Remember, only need small amounts cell ...
... 1. For example, Bolting – This process is triggered by water (ligand) entering the seed. 2. For example, Greening (Fig: 39.4) – The plant begins producing chloroplasts in response to sunlight. C. Hormones are released to target tissues to relay information. (Remember, only need small amounts cell ...
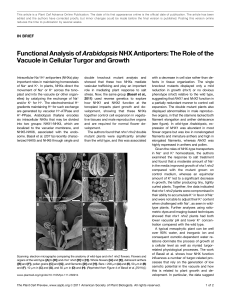
Functional Analysis ofArabidopsisNHX Antiporters
... NHX5-NHX6, associated with the endosome. Bassil et al. (2011a) recently characterized NHX5 and NHX6 through single and ...
... NHX5-NHX6, associated with the endosome. Bassil et al. (2011a) recently characterized NHX5 and NHX6 through single and ...
Kingdom Plantae
... derived from it (by mitosis) are also haploid. In due course, this multicellular structure produces gametes — by mitosis — and sexual reproduction then produces the diploid sporophyte generation. ...
... derived from it (by mitosis) are also haploid. In due course, this multicellular structure produces gametes — by mitosis — and sexual reproduction then produces the diploid sporophyte generation. ...
Hepatica. Liverwort Liver
... The leaf-stems and flower-stems rise from the ground to the height of 4 or 6 inches The leaf is heart-shaped, and 3-lobed, of a tough, strong fibre that often survives the winter. Its color is dark green above and dull violet beneath. The beautiful flower is composed of 6 to 9 petal-like calyx-parts ...
... The leaf-stems and flower-stems rise from the ground to the height of 4 or 6 inches The leaf is heart-shaped, and 3-lobed, of a tough, strong fibre that often survives the winter. Its color is dark green above and dull violet beneath. The beautiful flower is composed of 6 to 9 petal-like calyx-parts ...
garden disease problems
... Leaves turn yellow, wilt, and die. Brown spots on petals or red-pink spots on lighter colored flower buds. Brown dieback of cut canes, brown fuzzy mold on debris around the plant. In severe cases, the entire flower bud rots. Botrytis. This disease is caused by a fungus that is commonly found on dead ...
... Leaves turn yellow, wilt, and die. Brown spots on petals or red-pink spots on lighter colored flower buds. Brown dieback of cut canes, brown fuzzy mold on debris around the plant. In severe cases, the entire flower bud rots. Botrytis. This disease is caused by a fungus that is commonly found on dead ...
Study Guide – Unit 6: Plants
... 19. The vascular tissue through which food moves is called the ______________. 20. The vascular tissue through which water moves is called the ______________. 21. Food made in the plant’s ____________ travels to the roots and stems. 22. Water and nutrients absorbed by the plant’s ________________ tr ...
... 19. The vascular tissue through which food moves is called the ______________. 20. The vascular tissue through which water moves is called the ______________. 21. Food made in the plant’s ____________ travels to the roots and stems. 22. Water and nutrients absorbed by the plant’s ________________ tr ...
Plants Study Guide (Answer Key)
... Describe dormancy. Which plants experience this and what time of year does it happen? a period of lower activity or suspended life processes brought on by changes in the environment; usually in winter or times of drought; begins in fall when leaves on broad-leafed change colors. Fill in the blanks ...
... Describe dormancy. Which plants experience this and what time of year does it happen? a period of lower activity or suspended life processes brought on by changes in the environment; usually in winter or times of drought; begins in fall when leaves on broad-leafed change colors. Fill in the blanks ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.