READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494
... READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
... READING GUIDE: 17.3 – The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
Cedrus libani (Cedar of Lebanon ) Size/Shape
... Cedrus libani (Cedar of Lebanon ) Cedrus libanii is a native evergreen slow growing tree. It can reach up to 40 m. Its leaves are needle like in a cluster of 15-20. Female and male flower separate but on the same tree. It has 10-15 cm brownish, reddish cone.When the tree is younger it has more pyram ...
... Cedrus libani (Cedar of Lebanon ) Cedrus libanii is a native evergreen slow growing tree. It can reach up to 40 m. Its leaves are needle like in a cluster of 15-20. Female and male flower separate but on the same tree. It has 10-15 cm brownish, reddish cone.When the tree is younger it has more pyram ...
PlantDefenses
... Plant defenses against herbivores • Plants can’t run away from herbivores • Plants can’t hide – leaves must be exposed too catch light for photosynthesis. • Plants are usually too abundant to be cryptically colored! • Therefore, plant defenses operate in situ, either directly or indirectly ...
... Plant defenses against herbivores • Plants can’t run away from herbivores • Plants can’t hide – leaves must be exposed too catch light for photosynthesis. • Plants are usually too abundant to be cryptically colored! • Therefore, plant defenses operate in situ, either directly or indirectly ...
Life Cycles of Plants and Animals
... The Life Cycle of a Butterfly The life of a butterfly begins as an egg… then it grows into a caterpillar… the caterpillar makes a cocoon… then after time, a butterfly emerges! ...
... The Life Cycle of a Butterfly The life of a butterfly begins as an egg… then it grows into a caterpillar… the caterpillar makes a cocoon… then after time, a butterfly emerges! ...
document
... and is carried by air to the female part of the plant, where it enters the ovary and fertilizes the ovule. This develops into the seed. In angiosperms, the seed is surrounded by the developed ovary, which becomes the fruit. • .How does this represent an advantage over the Bryophytes and Seedless Vas ...
... and is carried by air to the female part of the plant, where it enters the ovary and fertilizes the ovule. This develops into the seed. In angiosperms, the seed is surrounded by the developed ovary, which becomes the fruit. • .How does this represent an advantage over the Bryophytes and Seedless Vas ...
Lecture 20 The word gymnosperm means “naked seed” the seeds
... What is a seed? It is a plant embryo, with some stored food, enclosed in a seed coat. The stored food in gymnosperms is primarily female gametophyte tissue. In angiosperms it is endosperm. In some angiosperms the endosperm is abundant (as in maize) in others the endosperm is almost completely used u ...
... What is a seed? It is a plant embryo, with some stored food, enclosed in a seed coat. The stored food in gymnosperms is primarily female gametophyte tissue. In angiosperms it is endosperm. In some angiosperms the endosperm is abundant (as in maize) in others the endosperm is almost completely used u ...
58 Round-leaved Greenbrier
... LEAVES: Shiny, smooth, and arranged alternately along the length of the vine. They are round to heart-shaped, with a pointed end (up to 13 cm long and smooth leaf edges). STEM: Highly branched, climbing vine with many bent thorny prickles and curling strands. FLOWERS: Clusters of greenishbrown flowe ...
... LEAVES: Shiny, smooth, and arranged alternately along the length of the vine. They are round to heart-shaped, with a pointed end (up to 13 cm long and smooth leaf edges). STEM: Highly branched, climbing vine with many bent thorny prickles and curling strands. FLOWERS: Clusters of greenishbrown flowe ...
Leaves 23-4 - SCHOOLinSITES
... What is the main function of a plant’s leaf? The leaves of a plant are its main organs of photosynthesis. How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis? The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. How does gas exchange take place ...
... What is the main function of a plant’s leaf? The leaves of a plant are its main organs of photosynthesis. How does the structure of a leaf enable it to carry out photosynthesis? The structure of a leaf is optimized for absorbing light and carrying out photosynthesis. How does gas exchange take place ...
Juncus acutiflorus
... Identification features: Upright leafy rush to 1 m tall. Often found in loose clumps and sometimes extending from rhizome lines. Leaves: tubular with internal cross walls (feels like clicks if you hold base of leaf between finger and thumb and slide up) with a small ear-like membrane (auricle) where ...
... Identification features: Upright leafy rush to 1 m tall. Often found in loose clumps and sometimes extending from rhizome lines. Leaves: tubular with internal cross walls (feels like clicks if you hold base of leaf between finger and thumb and slide up) with a small ear-like membrane (auricle) where ...
FInal Exam Master Concept and Vocab sheet
... Pedigrees (make sure that you are comfortable interpreting these) ...
... Pedigrees (make sure that you are comfortable interpreting these) ...
5 VEGETATIVE PLANT MORPHOLOGY
... to produce simple sugars (glucose) and release oxygen to the air. Actually this is a very complex set of processes, which we don't have time to delve into. What's important is that this allows the plant to make organic substances (components of living cells) from simple, common substances such as ca ...
... to produce simple sugars (glucose) and release oxygen to the air. Actually this is a very complex set of processes, which we don't have time to delve into. What's important is that this allows the plant to make organic substances (components of living cells) from simple, common substances such as ca ...
Life Cycle of a Plant
... a seed. •Inside the seed is a tiny new plant. •The outside of the seed has a special covering called a seed coat. •The seed leaf has a bit of food or energy to help the seed to germinate. ...
... a seed. •Inside the seed is a tiny new plant. •The outside of the seed has a special covering called a seed coat. •The seed leaf has a bit of food or energy to help the seed to germinate. ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 18
... at very low levels. There are five main groups of plant hormones: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethylene. Tropism is the directional response by a plant to a stimulus. It may be positive or negative (i.e. towards or away from the source of stimulus). There are a number of ‘trop ...
... at very low levels. There are five main groups of plant hormones: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethylene. Tropism is the directional response by a plant to a stimulus. It may be positive or negative (i.e. towards or away from the source of stimulus). There are a number of ‘trop ...
Green Briar Vine Plant Feature Description
... 3. The table lists some features of the green briar vine. Green Briar Vine Plant Feature ...
... 3. The table lists some features of the green briar vine. Green Briar Vine Plant Feature ...
Geraniums - Town and Country Gardens
... throughout the season. They are compatible with almost any plant so they do well in both the garden and containers. Common or Zonal Geraniums named for its “zoned’ leaf markings, this is the most popular geranium. It is propagated by two methods: Cuttings- are noted for early season, tall plants wit ...
... throughout the season. They are compatible with almost any plant so they do well in both the garden and containers. Common or Zonal Geraniums named for its “zoned’ leaf markings, this is the most popular geranium. It is propagated by two methods: Cuttings- are noted for early season, tall plants wit ...
STUDY GUIDE:
... Epiphytes are plants that grow on trees but do not leech food from the tree or harm the tree in any way. For example, in some tropical forests, ferns may grow on the sides of taller trees. Fruit is the name given to the ripened ovary that surrounds and protects the seeds. Germination refers to the b ...
... Epiphytes are plants that grow on trees but do not leech food from the tree or harm the tree in any way. For example, in some tropical forests, ferns may grow on the sides of taller trees. Fruit is the name given to the ripened ovary that surrounds and protects the seeds. Germination refers to the b ...
Flower ID # 4
... • Yellow / Orange flowers • Big, But shallow root systems * Can live up to 130 years ...
... • Yellow / Orange flowers • Big, But shallow root systems * Can live up to 130 years ...
2013floralexam
... 1) Water clings to the walls of the xylem tubes in stems. This force is called: A) Adhesion B) Choloplastism C) Cohesion D) respiration 2) True or False – Plants with a tap root system are easier to transplant than plants with fibrous root systems. A) True B) False 3) Which part of the plant flower ...
... 1) Water clings to the walls of the xylem tubes in stems. This force is called: A) Adhesion B) Choloplastism C) Cohesion D) respiration 2) True or False – Plants with a tap root system are easier to transplant than plants with fibrous root systems. A) True B) False 3) Which part of the plant flower ...
Plant Classification pdf
... Genera (plural of genus) are groupings whose members have more characteristics in common with each other than they do with other genera within the same family. Similarity of flowers and fruits is the most widely used feature, although roots, stems, buds, and leaves are also used. Common names of pla ...
... Genera (plural of genus) are groupings whose members have more characteristics in common with each other than they do with other genera within the same family. Similarity of flowers and fruits is the most widely used feature, although roots, stems, buds, and leaves are also used. Common names of pla ...
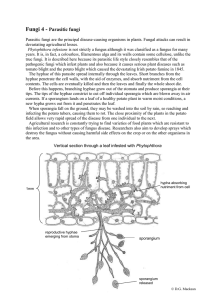
Parasitic fungi - Biology Resources
... Parasitic fungi are the principal disease-causing organisms in plants. Fungal attacks can result in devastating agricultural losses. Phytophthora infestans is not strictly a fungus although it was classified as a fungus for many years. It is, in fact, a colourless, filamentous alga and its walls con ...
... Parasitic fungi are the principal disease-causing organisms in plants. Fungal attacks can result in devastating agricultural losses. Phytophthora infestans is not strictly a fungus although it was classified as a fungus for many years. It is, in fact, a colourless, filamentous alga and its walls con ...
Careers in Floral Design - Montgomery County Public Schools
... flowers, and other floriculture crops May be independent or in a retail outlet ...
... flowers, and other floriculture crops May be independent or in a retail outlet ...
Ch - ReadingtonScience
... 4. a layer of cells that divides to produce new phloem and xylem 5. root 6. contains a young plant inside a protective covering 7. xylem 8. phloem 9. protects the growing tip of the root from injury 10. stomata 11. Accept one of the following: carries substances between the roots and leaves, provide ...
... 4. a layer of cells that divides to produce new phloem and xylem 5. root 6. contains a young plant inside a protective covering 7. xylem 8. phloem 9. protects the growing tip of the root from injury 10. stomata 11. Accept one of the following: carries substances between the roots and leaves, provide ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.