Plant structure and function
... xylem − long thin hollow cells with woody thickened walls used for transporting water and mineral ions in solution and helping to support the plant. ...
... xylem − long thin hollow cells with woody thickened walls used for transporting water and mineral ions in solution and helping to support the plant. ...
Organization of Flowering Plants
... • In primary growth the apical meristem within a terminal bud is active. • In secondary growth: the vascular cambium is active. • Vascular cambium: is meristem tissue, which produces new xylem and phloem called secondary xylem and phloem each year. • Wood: is the buildup of secondary xylem year afte ...
... • In primary growth the apical meristem within a terminal bud is active. • In secondary growth: the vascular cambium is active. • Vascular cambium: is meristem tissue, which produces new xylem and phloem called secondary xylem and phloem each year. • Wood: is the buildup of secondary xylem year afte ...
Common Jacob`s Ladder
... above the foliage from mid spring to mid summer, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. It's ferny pinnately compound leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
... above the foliage from mid spring to mid summer, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. It's ferny pinnately compound leaves remain green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues
... • Dermal tissue covers the outside of a plant. – protects the plant stem – secretes cuticle of leaves – forms outer bark of trees • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. – provides support – stores materials in roots and stems – Photosynthesis (in the shoot) ...
... • Dermal tissue covers the outside of a plant. – protects the plant stem – secretes cuticle of leaves – forms outer bark of trees • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. – provides support – stores materials in roots and stems – Photosynthesis (in the shoot) ...
hibiscus - Platt Hill Nursery
... The most common cause of leaf drop is a lack of water in the summer. INDOOR CARE: Preparing to bring the hibiscus indoors for the winter, realize the differences in light levels from outside on the patio to the inside of a house are vast. The plant’s natural reaction is to drop all of its leaves. Th ...
... The most common cause of leaf drop is a lack of water in the summer. INDOOR CARE: Preparing to bring the hibiscus indoors for the winter, realize the differences in light levels from outside on the patio to the inside of a house are vast. The plant’s natural reaction is to drop all of its leaves. Th ...
K_U1_L2 Plant Parts
... play with the mystery bags of plant parts. 10. Divide class into small groups with one bag per group. Put part name signs around the room in different areas. 11. Pass the bags around. Tell students to reach in without looking and see if they can guess what things are. Tell them to use their senses, ...
... play with the mystery bags of plant parts. 10. Divide class into small groups with one bag per group. Put part name signs around the room in different areas. 11. Pass the bags around. Tell students to reach in without looking and see if they can guess what things are. Tell them to use their senses, ...
Top 10 Families - Field Studies Council
... About 60-70% of flowering plants in Britain are in about 15 families. (there are over 140 families in the British flora 600+ worldwide!!) So learning families can be short cut to using any key ...
... About 60-70% of flowering plants in Britain are in about 15 families. (there are over 140 families in the British flora 600+ worldwide!!) So learning families can be short cut to using any key ...
Five-leaf Akebia (Akebia quinata) - Friends of Hopewell Valley Open
... in May. Flowers emerge from leaf axils in racemes. Individual flowers are one inch across and may smell of sweet chocolate. Fruit: Large, soft, sausage-shaped pods 2.25 to 4 inches in length. Pulp is whitish with many tiny black seeds. Ripening in September. Look-alikes: None. Habitat: Forest, fores ...
... in May. Flowers emerge from leaf axils in racemes. Individual flowers are one inch across and may smell of sweet chocolate. Fruit: Large, soft, sausage-shaped pods 2.25 to 4 inches in length. Pulp is whitish with many tiny black seeds. Ripening in September. Look-alikes: None. Habitat: Forest, fores ...
Hibbertia dentata
... often retaining reddish or bronze tinges throughout their life. The bright yellow flowers are about 30mm across, with a central cluster of stamens. Each flower lasts only about a day, but the flowers appear continually over a long period. The genus is named after George Hibbert, an 18th and 19th cen ...
... often retaining reddish or bronze tinges throughout their life. The bright yellow flowers are about 30mm across, with a central cluster of stamens. Each flower lasts only about a day, but the flowers appear continually over a long period. The genus is named after George Hibbert, an 18th and 19th cen ...
CHAPTER 2 GENERAL VARIETY OF ORGANISMS
... a. The animals in Animal Kingdom can be divided into 2 large groups : Invertebrates: animals without backbones. Vertebrates: animals with backbones. b. The plants in Plant Kingdom can be divided into 2 large groups : Non-flowering plants : plants without flowers. Flowering plants : plants with flowe ...
... a. The animals in Animal Kingdom can be divided into 2 large groups : Invertebrates: animals without backbones. Vertebrates: animals with backbones. b. The plants in Plant Kingdom can be divided into 2 large groups : Non-flowering plants : plants without flowers. Flowering plants : plants with flowe ...
lavender growing tips
... • Pruning. Pruning is absolutely required for good flower development and to prevent woody stalks. In our climate we choose to prune in late fall before the plant goes dormant for the winter. Cut the flowers down to within two leaf nodes above the grey/brown woody part of the stem (leaving approxima ...
... • Pruning. Pruning is absolutely required for good flower development and to prevent woody stalks. In our climate we choose to prune in late fall before the plant goes dormant for the winter. Cut the flowers down to within two leaf nodes above the grey/brown woody part of the stem (leaving approxima ...
Classifying Plants
... Plants dominate the land and many bodies of water. Plants exhibit tremendous diversity. Some plants are less than .04 inches in width, and some plants grow to more than 328 ft in height. All organisms in this kingdom are multicellular and most are photosynthetic and live on land. ...
... Plants dominate the land and many bodies of water. Plants exhibit tremendous diversity. Some plants are less than .04 inches in width, and some plants grow to more than 328 ft in height. All organisms in this kingdom are multicellular and most are photosynthetic and live on land. ...
Growing Carnations from Seed
... After a good percentage of the seedlings have emerged, I remove the container from the bag and set it out into direct sun. It is early enough in the season so sunburn should not be a problem, but don't forget to water as necessary to prevent the soil from drying. When 2-3 true leaves have developed ...
... After a good percentage of the seedlings have emerged, I remove the container from the bag and set it out into direct sun. It is early enough in the season so sunburn should not be a problem, but don't forget to water as necessary to prevent the soil from drying. When 2-3 true leaves have developed ...
Plant Regulation
... The technique of tissue culture (or cloning) may be used to obtain large numbers of plants in a relatively short time. Cloned plants are genetically identical to the plant from which the original cells were taken. When small groups of unspecialised cells are used, they are sterilised and grown on ag ...
... The technique of tissue culture (or cloning) may be used to obtain large numbers of plants in a relatively short time. Cloned plants are genetically identical to the plant from which the original cells were taken. When small groups of unspecialised cells are used, they are sterilised and grown on ag ...
Homeostasis in Plants
... The technique of tissue culture (or cloning) may be used to obtain large numbers of plants in a relatively short time. Cloned plants are genetically identical to the plant from which the original cells were taken. When small groups of unspecialised cells are used, they are sterilised and grown on ag ...
... The technique of tissue culture (or cloning) may be used to obtain large numbers of plants in a relatively short time. Cloned plants are genetically identical to the plant from which the original cells were taken. When small groups of unspecialised cells are used, they are sterilised and grown on ag ...
Curriculum Overview for Year 3 Spring Term
... safe self-rescue in different water-based situations. AD 42 and the power of its army successful invasion by Gymnastics - develop flexibility, strength, technique, control and Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall British balance [for example, through athletics and gymnastics] resistan ...
... safe self-rescue in different water-based situations. AD 42 and the power of its army successful invasion by Gymnastics - develop flexibility, strength, technique, control and Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall British balance [for example, through athletics and gymnastics] resistan ...
Chapters 29
... organisms living on land until about 430 mya) • Problems with living on land- must evolve protective features to live on land preventing water loss reproducing by seeds and spores transporting materials throughout body ...
... organisms living on land until about 430 mya) • Problems with living on land- must evolve protective features to live on land preventing water loss reproducing by seeds and spores transporting materials throughout body ...
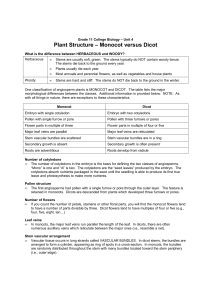
Unit 4 - Lesson 6 - Monocot and Dicot
... • In most dicots, the root develops from the lower end of the embryo from a region called the RADICLE. The radicle gives rise to the APICAL MERISTEM which produces new root tissue throughout the plant’s life. In monocots, the radicle stops growing and new roots grow ADVENTIOUSLY from nodes in the st ...
... • In most dicots, the root develops from the lower end of the embryo from a region called the RADICLE. The radicle gives rise to the APICAL MERISTEM which produces new root tissue throughout the plant’s life. In monocots, the radicle stops growing and new roots grow ADVENTIOUSLY from nodes in the st ...
Blue Butterfly Plant
... Blue Butterfly Plant is bathed in stunning panicles of blue orchid-like flowers with white overtones at the ends of the branches from early spring to mid fall. It has green foliage. The glossy oval leaves remain green through the winter. It produces black berries in early summer. The bark is not par ...
... Blue Butterfly Plant is bathed in stunning panicles of blue orchid-like flowers with white overtones at the ends of the branches from early spring to mid fall. It has green foliage. The glossy oval leaves remain green through the winter. It produces black berries in early summer. The bark is not par ...
Chapter vocabulary graphic organizer
... Hold the plant in the ground Take in water and materials called minerals from the soil. Store food made by the plant Taproots are large roots such as carrots, dandelions and beets Water and minerals travel up the root through tubes to the stem and leaves Water enters the root through the root ...
... Hold the plant in the ground Take in water and materials called minerals from the soil. Store food made by the plant Taproots are large roots such as carrots, dandelions and beets Water and minerals travel up the root through tubes to the stem and leaves Water enters the root through the root ...
Unit 8
... Distinguish between macronutrient and micronutrient. Macronutrients are elements required by plants in large amounts. Micronutrients are elements required by plants in small amounts. List the nine macronutrients required by plants and describe their importance in normal plant structure and metabolis ...
... Distinguish between macronutrient and micronutrient. Macronutrients are elements required by plants in large amounts. Micronutrients are elements required by plants in small amounts. List the nine macronutrients required by plants and describe their importance in normal plant structure and metabolis ...
Created with Sketch. Plant parts
... discuss what is meant by ‘fruit’ and ‘vegetable’. To a botanist, a fruit is part of a flower that develops to protect seeds – that includes pumpkins, chillies and cucumbers, but you won’t find those in the fruit section of the supermarket. Botanists classify plant parts by their functions more than ...
... discuss what is meant by ‘fruit’ and ‘vegetable’. To a botanist, a fruit is part of a flower that develops to protect seeds – that includes pumpkins, chillies and cucumbers, but you won’t find those in the fruit section of the supermarket. Botanists classify plant parts by their functions more than ...
Master Gardener 2015 Basic Botany
... the four “parts” they possess Complete flower – has all four parts Incomplete flower – missing 1 or more parts Perfect flower – has at least the male and female parts Imperfect flower – has only one functional set of sexual parts (male or female) -male “staminate” flower (stamens, no pistils/carpels ...
... the four “parts” they possess Complete flower – has all four parts Incomplete flower – missing 1 or more parts Perfect flower – has at least the male and female parts Imperfect flower – has only one functional set of sexual parts (male or female) -male “staminate” flower (stamens, no pistils/carpels ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.