Gardenia jasminoides`Prostrata` Dwarf Gardenia1 - EDIS
... This dwarf cultivar of Gardenia jasminoides is much different from the species (Fig. 1). Trailing gardenia reaches a height of 2 to 3 feet and can spread 4 to 6 feet. This plant has an open, horizontal branching habit that makes it an attractive ground cover. It will not grow into a shrub as does th ...
... This dwarf cultivar of Gardenia jasminoides is much different from the species (Fig. 1). Trailing gardenia reaches a height of 2 to 3 feet and can spread 4 to 6 feet. This plant has an open, horizontal branching habit that makes it an attractive ground cover. It will not grow into a shrub as does th ...
Nipponanthemum nipponicum (Montauk Daisy)
... so tough that the plant is able to survive and even thrive in harsh seaside conditions. This robust grower needs a place in the back of your flower beds because of its larger growth habit and size. It is often good to plant shorter perennials around its base, because the plant may lose some of its l ...
... so tough that the plant is able to survive and even thrive in harsh seaside conditions. This robust grower needs a place in the back of your flower beds because of its larger growth habit and size. It is often good to plant shorter perennials around its base, because the plant may lose some of its l ...
Chapter 35
... • The shoot system of a plant consists of the stems and the leaves, as well as flowers. • Leaves are the main sites of photosynthesis. • Stems hold and display the leaves to the sun and provide connections for the transport of materials between roots and leaves. • A node is the point where a leaf at ...
... • The shoot system of a plant consists of the stems and the leaves, as well as flowers. • Leaves are the main sites of photosynthesis. • Stems hold and display the leaves to the sun and provide connections for the transport of materials between roots and leaves. • A node is the point where a leaf at ...
Backyard Nursery Production Presentation
... • In the propagation area think about: – What are the propagation requirements of the plants you want to grow – What size you want to sell or grow or use – Design & installation of irrigation & or mist systems ...
... • In the propagation area think about: – What are the propagation requirements of the plants you want to grow – What size you want to sell or grow or use – Design & installation of irrigation & or mist systems ...
Bio10
... 1. Gofio food used in the Canary Islands. Its use begun preHispanic. What does it mean? It was used before the Hispanic arrived to the Canary Islands. It was originally prepared by the Guanche culture. 2. Who were the Guanches? Guanches were the Berberrelated aboriginal inhabitants of the Canary Isl ...
... 1. Gofio food used in the Canary Islands. Its use begun preHispanic. What does it mean? It was used before the Hispanic arrived to the Canary Islands. It was originally prepared by the Guanche culture. 2. Who were the Guanches? Guanches were the Berberrelated aboriginal inhabitants of the Canary Isl ...
please plant the daisies - Charlotte County Extension Service
... both the Gerbera Daisy and the African Bush Daisy look daisy-like and offer perennial spender in the garden. The Gerbera daisy is also called the Transvaal daisy as this plant originated in Transvaal, South Africa. These perennials have been cultivated to the degree that there are many hybrids in br ...
... both the Gerbera Daisy and the African Bush Daisy look daisy-like and offer perennial spender in the garden. The Gerbera daisy is also called the Transvaal daisy as this plant originated in Transvaal, South Africa. These perennials have been cultivated to the degree that there are many hybrids in br ...
PowerPoint
... Types of layering Simple layering - branches are bent to the ground and portions of branches are covered with soil. The terminal ends are left exposed. The covered portion must have a bud or buds and must be injured - roots should form in this area. ...
... Types of layering Simple layering - branches are bent to the ground and portions of branches are covered with soil. The terminal ends are left exposed. The covered portion must have a bud or buds and must be injured - roots should form in this area. ...
ch_5 - WordPress.com
... Morphology:The study of various external features of the organism is knownas morphology. The angiosperms are characterized by presence of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. ...
... Morphology:The study of various external features of the organism is knownas morphology. The angiosperms are characterized by presence of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. ...
16. transmission of stimulus - theories of flowering.
... treatment is essential for vernalization. Depending upon the degree of temperature and in different species this period may vary, but usually the duration of the chilling treatment is about one and half months or more. ...
... treatment is essential for vernalization. Depending upon the degree of temperature and in different species this period may vary, but usually the duration of the chilling treatment is about one and half months or more. ...
12th Botany Taxonomy of Angiosperms Class Notes D
... 1753, Carolus Linnaeus of Sweden in his book “ Species Plantarum” he described 7,300 species. His division 24 classes based on number, union, length of stamens. Also known as sexual system of classification. The importance of floral characters was felt by Linnaeus and so his classification was more ...
... 1753, Carolus Linnaeus of Sweden in his book “ Species Plantarum” he described 7,300 species. His division 24 classes based on number, union, length of stamens. Also known as sexual system of classification. The importance of floral characters was felt by Linnaeus and so his classification was more ...
29 Origin of Plants
... Pteridophytes evolved over 400 MYA Seedless, Vascular plants (having Xylem & Phloem). Today represented by two divisions: Pterophyta: Ferns, Horsetails (Equisetum) Lycophyta: Club moss Cooksonia, an extinct plant over 400 million years old, is the earliest known vascular plant. The branched sporoph ...
... Pteridophytes evolved over 400 MYA Seedless, Vascular plants (having Xylem & Phloem). Today represented by two divisions: Pterophyta: Ferns, Horsetails (Equisetum) Lycophyta: Club moss Cooksonia, an extinct plant over 400 million years old, is the earliest known vascular plant. The branched sporoph ...
Horticulture
... • “test tube plants” • Must have extremely sanitary laboratory conditions for tissue culture. ...
... • “test tube plants” • Must have extremely sanitary laboratory conditions for tissue culture. ...
Marine Plants
... Lenticels - specialized cells in the prop root that open up during low tide and allows air to diffuse into the plant. During high tide, the lenticel closes have a chemical defense mechanism against insects and other animals Black Mangroves -Pneumatophores - are roots of this tree that are aerial ...
... Lenticels - specialized cells in the prop root that open up during low tide and allows air to diffuse into the plant. During high tide, the lenticel closes have a chemical defense mechanism against insects and other animals Black Mangroves -Pneumatophores - are roots of this tree that are aerial ...
Angiosperm Plant Reproduction (Chap. 28)
... – two other cells in the pollen grain called sperm cells finally penetrate the ovule (various maternal cells) in the ovary in a process called double fertilization • one sperm fertilizes the egg cells that eventually becomes the zygote • other sperm fertilizes the central cell that produce the endo ...
... – two other cells in the pollen grain called sperm cells finally penetrate the ovule (various maternal cells) in the ovary in a process called double fertilization • one sperm fertilizes the egg cells that eventually becomes the zygote • other sperm fertilizes the central cell that produce the endo ...
September Lesson Plan Grades 2
... covering a seed or seeds. Horticulturally speaking, the tomato is a vegetable plant. The plant is an annual and non-woody. Roots: Why do plants have roots? Roots function like feet. They help plants stay firmly in the soil. How do you suppose roots also are like our mouths? They take up water for th ...
... covering a seed or seeds. Horticulturally speaking, the tomato is a vegetable plant. The plant is an annual and non-woody. Roots: Why do plants have roots? Roots function like feet. They help plants stay firmly in the soil. How do you suppose roots also are like our mouths? They take up water for th ...
Plant kingdom
... Angiosperms add the final improvement to plant reproduction: they grow their seeds inside an ovary (Greek: angeion = vessel) which is, itself, embedded in a flower. After it is fertilized, the flower falls away and the ovary swells to become a fruit. Angiosperms in the class Dicotyledoneae grow two ...
... Angiosperms add the final improvement to plant reproduction: they grow their seeds inside an ovary (Greek: angeion = vessel) which is, itself, embedded in a flower. After it is fertilized, the flower falls away and the ovary swells to become a fruit. Angiosperms in the class Dicotyledoneae grow two ...
SPIDER PLANTS.pub
... Description A tufted perennial herb growing up to 60 cm tall 19. It prefers light to medium, well-drained, moist soils in protected, shaded areas. It is drought and frost tender 1. Stems/Leaves Erect, slender, wiry stems arching over when the small plantlets develop 1. Linear, basal leaves usually s ...
... Description A tufted perennial herb growing up to 60 cm tall 19. It prefers light to medium, well-drained, moist soils in protected, shaded areas. It is drought and frost tender 1. Stems/Leaves Erect, slender, wiry stems arching over when the small plantlets develop 1. Linear, basal leaves usually s ...
Native Plant Flashcards - Oregon State University Extension Service
... corresponding flashcard to determine if it is your mystery plant. Once you have found your plant, make a record of what the plant is! Common Name (first name listed on page): _________________________________ Botanical Name (Name in italicized font): ___________________________________ Fun fact! Did ...
... corresponding flashcard to determine if it is your mystery plant. Once you have found your plant, make a record of what the plant is! Common Name (first name listed on page): _________________________________ Botanical Name (Name in italicized font): ___________________________________ Fun fact! Did ...
Massachusetts Framework: Life Science Concepts
... Functions:food production, support, water transport, reproduction, growth, protection Plant/Animal life cycles includes: birth, growth, development, reproduction, death. Animals sometimes go through metamorphosis (butterfly, frog) Distinguished between observed characteristics that are inherited and ...
... Functions:food production, support, water transport, reproduction, growth, protection Plant/Animal life cycles includes: birth, growth, development, reproduction, death. Animals sometimes go through metamorphosis (butterfly, frog) Distinguished between observed characteristics that are inherited and ...
Balloon vine - Cape Town Invasives
... What if I can’t remove it myself? Join the Spotter Network and the Cape Town Early Detection and ...
... What if I can’t remove it myself? Join the Spotter Network and the Cape Town Early Detection and ...
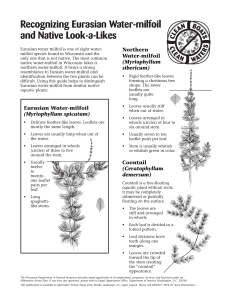
Milfoil Look-a-Likes fact sheet – pdf
... Eurasian water milfoil is one of eight watermilfoil species found in Wisconsin and the only one that is not native. The most common native water-milfoil in Wisconsin lakes is northern water-milfoil. It bears a strong resemblance to Eurasin water-milfoil and identification between the two plants can ...
... Eurasian water milfoil is one of eight watermilfoil species found in Wisconsin and the only one that is not native. The most common native water-milfoil in Wisconsin lakes is northern water-milfoil. It bears a strong resemblance to Eurasin water-milfoil and identification between the two plants can ...
PLANTS - Weebly
... Most are autotrophs Some are parasites or saprobes that live on decaying material ...
... Most are autotrophs Some are parasites or saprobes that live on decaying material ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.