umax
... 2. Water flows through a horizontal, 180o pipe bend as illustrated in Figure. The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value of 0.1 ft2 through the bend. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are 30 psia and ...
... 2. Water flows through a horizontal, 180o pipe bend as illustrated in Figure. The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value of 0.1 ft2 through the bend. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are 30 psia and ...
Exam2 - Purdue Engineering
... 4) The NACA 3412 airfoil has a maximum distance between the chord line and the camber line of a. 12% of chord b. 3 % of chord c. 4% of chord d. 1% of chord e. 2% of chord 5) An airplane flies through sea level air. Its pitot tube reads a gage pressure of 0.2 atm. The air speed (in m/s) is closest t ...
... 4) The NACA 3412 airfoil has a maximum distance between the chord line and the camber line of a. 12% of chord b. 3 % of chord c. 4% of chord d. 1% of chord e. 2% of chord 5) An airplane flies through sea level air. Its pitot tube reads a gage pressure of 0.2 atm. The air speed (in m/s) is closest t ...
Sediment transport via dam-break flows over sloping
... the simple exact solution of the shallow-water equations for both a dry bed [5] and a bed with ‘tail water’. Recent studies by the current authors [9, 10] have shown that under the assumption of dilute suspensions employed in [2] the suspended particles will play a relatively minor role in modifying ...
... the simple exact solution of the shallow-water equations for both a dry bed [5] and a bed with ‘tail water’. Recent studies by the current authors [9, 10] have shown that under the assumption of dilute suspensions employed in [2] the suspended particles will play a relatively minor role in modifying ...
Min-218 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
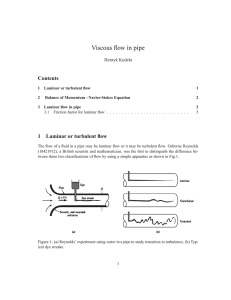
... the pipe wall is virtually stationary, while the layers further out move at increasingly higher velocities until a maximum velocity is attained at the center (Figure 3-1). In addition, a fluid is always a continuous medium without voids. However, the properties of a fluid, e.g., density, may vary fr ...
... the pipe wall is virtually stationary, while the layers further out move at increasingly higher velocities until a maximum velocity is attained at the center (Figure 3-1). In addition, a fluid is always a continuous medium without voids. However, the properties of a fluid, e.g., density, may vary fr ...
Substitution method
... Use the Master method to find T(n) = Θ(?) in each of the following cases: a. T(n) = 7T(n/2) + n2 b. T(n) = 4T(n/2) + n2 c. T(n) = 2T(n/3) + n3 ...
... Use the Master method to find T(n) = Θ(?) in each of the following cases: a. T(n) = 7T(n/2) + n2 b. T(n) = 4T(n/2) + n2 c. T(n) = 2T(n/3) + n3 ...
VARIOUS ESTIMATIONS OF π AS
... The Monte Carlo method uses pseudo-random numbers (numbers which are generated by a formula using the selection of one random “seed” number) as values for certain variables in algorithms to generate random variates of chosen probability functions to be used in simulations of statistical models or to ...
... The Monte Carlo method uses pseudo-random numbers (numbers which are generated by a formula using the selection of one random “seed” number) as values for certain variables in algorithms to generate random variates of chosen probability functions to be used in simulations of statistical models or to ...
Section 7 * 1 Solving Systems of Equations by Graphing
... Section 7 – 1 Solving Systems of Equations by Graphing Objectives: To solve systems by graphing To analyze special types of systems ...
... Section 7 – 1 Solving Systems of Equations by Graphing Objectives: To solve systems by graphing To analyze special types of systems ...
chpt10examp
... Example 10.1 We will discretize the domain in Figure 10.1 using a uniform mesh of 40 by 40 square bilinear elements. The parameters are chosen as Ra = 105, Pr = 1.0 and the time step t = 10-3. Starting from uniform initial conditions T(x,y,0) = u(x,y,0) = v(x,y,0) = 0.0, the steadystate solution is ...
... Example 10.1 We will discretize the domain in Figure 10.1 using a uniform mesh of 40 by 40 square bilinear elements. The parameters are chosen as Ra = 105, Pr = 1.0 and the time step t = 10-3. Starting from uniform initial conditions T(x,y,0) = u(x,y,0) = v(x,y,0) = 0.0, the steadystate solution is ...
An s we rs
... The day after a hurricane, the barometric pressure in a coastal town has risen to 29.7 inches of mercury, which is 2.9 inches of mercury higher than the pressure when the eye of the hurricane passed over. ...
... The day after a hurricane, the barometric pressure in a coastal town has risen to 29.7 inches of mercury, which is 2.9 inches of mercury higher than the pressure when the eye of the hurricane passed over. ...
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.