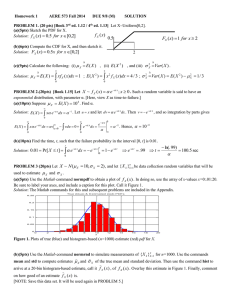
Scaling UP - Chart Industries
... advantageous. For two-phase streams where the UA increase associated with the mixing percentage with no device or perforated plate is detrimental, or for manifolded assemblies of exchangers (where two-phase flow separation can occur not only within the individual core header, but also within the man ...
... advantageous. For two-phase streams where the UA increase associated with the mixing percentage with no device or perforated plate is detrimental, or for manifolded assemblies of exchangers (where two-phase flow separation can occur not only within the individual core header, but also within the man ...
Algebra I - Hickman County Schools
... and solve literal equations. 3102.3.6 Understand and use relations and functions in various representations to solve contextual problems. 3102.3.7 Construct and solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two variables by various methods. ...
... and solve literal equations. 3102.3.6 Understand and use relations and functions in various representations to solve contextual problems. 3102.3.7 Construct and solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two variables by various methods. ...
Static and free vibration analysis of thin plates of the curved edges
... algorithms in relation to engineering problems. General application of BEM in a variety of fields of engineering analysis, together with the appropriate solutions and a discussion of the basic types of boundary elements was described by Burczyński [1], Wrobel and Aliabadi [2] and Katsikadelis [3]. M ...
... algorithms in relation to engineering problems. General application of BEM in a variety of fields of engineering analysis, together with the appropriate solutions and a discussion of the basic types of boundary elements was described by Burczyński [1], Wrobel and Aliabadi [2] and Katsikadelis [3]. M ...
Here are the steps required for Solving Rational Equations
... fractions. Option 1; multiply the entire problem by the least common denominator or LCD. Option 2; you can cross multiply. Option 1 will work for any problem, but you can only cross multiply if you have one fraction equal to one fraction, that is, if the fractions are proportional. Click on the link ...
... fractions. Option 1; multiply the entire problem by the least common denominator or LCD. Option 2; you can cross multiply. Option 1 will work for any problem, but you can only cross multiply if you have one fraction equal to one fraction, that is, if the fractions are proportional. Click on the link ...
2OA1-Mrs.-Smiths-Class-Problem-2
... 16 = 1 sharpened + 15 unsharpened 16 = 2 sharpened + 14 unsharpened 16 = 3 sharpened + 13 unsharpened 16 = 4 sharpened + 12 unsharpened 16 = 5 sharpened + 11 unsharpened 16 = 6 sharpened + 10 unsharpened 16 = 7 sharpened + 9 unsharpened 16 = 8 sharpened + 8 unsharpened 16 = 9 sharpened + 7 unsharpen ...
... 16 = 1 sharpened + 15 unsharpened 16 = 2 sharpened + 14 unsharpened 16 = 3 sharpened + 13 unsharpened 16 = 4 sharpened + 12 unsharpened 16 = 5 sharpened + 11 unsharpened 16 = 6 sharpened + 10 unsharpened 16 = 7 sharpened + 9 unsharpened 16 = 8 sharpened + 8 unsharpened 16 = 9 sharpened + 7 unsharpen ...
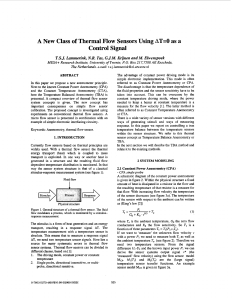
A new class of thermal flow sensors using /spl Delta/T=0 as a control
... T.S.J. Lammerink, N.R. Tas, G.J.M. Krijnen and M. Elwenspoek MESA+ Research Institute, University of Twente, P.O. Box 21 7,7500AE Enschede, The Netherlands. e-mail: [email protected] The advantage of constant power driving mode is its simple electronic implementation. This mode is often ...
... T.S.J. Lammerink, N.R. Tas, G.J.M. Krijnen and M. Elwenspoek MESA+ Research Institute, University of Twente, P.O. Box 21 7,7500AE Enschede, The Netherlands. e-mail: [email protected] The advantage of constant power driving mode is its simple electronic implementation. This mode is often ...
Spreading speed and traveling waves for the diffusive logistic
... where v(t, x) and w(t, x) are spatial densities of migrating and sedentary subpopulations, respectively, D is diffusion coefficient of migrating subpopulation, γ1 and γ2 are transition rates between two states. In model (1.1), the migrants have a positive mortality µ while the sedentary subpopulatio ...
... where v(t, x) and w(t, x) are spatial densities of migrating and sedentary subpopulations, respectively, D is diffusion coefficient of migrating subpopulation, γ1 and γ2 are transition rates between two states. In model (1.1), the migrants have a positive mortality µ while the sedentary subpopulatio ...
Optimal consumption and portfolio choice with borrowing constraints
... problem a nonlinear partial differential equation, namely the Bellman equation. We show that if the utility function satisfies some general regularity conditions, the Bellman equation has a unique solution which is twice continuously differentiable. Using a verification theorem, this solution turns ...
... problem a nonlinear partial differential equation, namely the Bellman equation. We show that if the utility function satisfies some general regularity conditions, the Bellman equation has a unique solution which is twice continuously differentiable. Using a verification theorem, this solution turns ...
Introduction to Differential Equations
... The second condition, slope 2 at x = 1, is a condition on y0 . We want y0 (1) = 2. We calculate y0 : y0 = 2C1x + C2 + 6x2, and then set x = 1 and y0 = 2. This yields the equation 2C1 + C2 + 6 = 2 which implies 2C1 + C2 = −4. Now we solve the two equations simultaneously: ...
... The second condition, slope 2 at x = 1, is a condition on y0 . We want y0 (1) = 2. We calculate y0 : y0 = 2C1x + C2 + 6x2, and then set x = 1 and y0 = 2. This yields the equation 2C1 + C2 + 6 = 2 which implies 2C1 + C2 = −4. Now we solve the two equations simultaneously: ...
The U-Tube Manometer
... laboratory experiments. However, certain design aspects of the manometer may be applied to Experiment 2. Instead of using just one pressure transducer located at the base of the water tank, the protocol may be improved by using two pressure transducers. The placement of the pressure transducers will ...
... laboratory experiments. However, certain design aspects of the manometer may be applied to Experiment 2. Instead of using just one pressure transducer located at the base of the water tank, the protocol may be improved by using two pressure transducers. The placement of the pressure transducers will ...
555
... Proportional Band: 0.1 to 999% of input range Integral: 1 to 9999 seconds/repeat Manual Reset/Load Line: 0 to 100% output Cycle Time: 0.3 to 120 seconds Control Deadband: in engineering units Dosage: 0 to 400%, Integral only: 0-250% Two sets of PI values may be stored in memory and selected automati ...
... Proportional Band: 0.1 to 999% of input range Integral: 1 to 9999 seconds/repeat Manual Reset/Load Line: 0 to 100% output Cycle Time: 0.3 to 120 seconds Control Deadband: in engineering units Dosage: 0 to 400%, Integral only: 0-250% Two sets of PI values may be stored in memory and selected automati ...
Methods S1.
... A JAVA-based mathematical model heart was developed in which a modeled subject’s end-of-life CM age distributions, defined by the modeled subject’s lifespan and CM turnover dynamics could be computed. These age distributions were produced by initializing the model with a starting number of CMs and t ...
... A JAVA-based mathematical model heart was developed in which a modeled subject’s end-of-life CM age distributions, defined by the modeled subject’s lifespan and CM turnover dynamics could be computed. These age distributions were produced by initializing the model with a starting number of CMs and t ...
expansion planning in electricity markets. two different
... due to the so-called complementary slackness condition. However, unlike the Cournot-based model, now x only represents the operation decision variables and h and g only limit such operation variables. In general, MPEC models are non-convex and difficult to solve. As a result of this non-convexity, i ...
... due to the so-called complementary slackness condition. However, unlike the Cournot-based model, now x only represents the operation decision variables and h and g only limit such operation variables. In general, MPEC models are non-convex and difficult to solve. As a result of this non-convexity, i ...
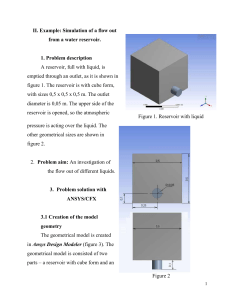
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.