Lecture 12 Atomic structure
... In addition to nuclear binding potential, there is a further Coulomb interaction between electrons. As we have seen with helium, this contribution can have important consequences on spectra and spin structure of wavefunction. However, electron-electron interaction makes problem “many-body” in charac ...
... In addition to nuclear binding potential, there is a further Coulomb interaction between electrons. As we have seen with helium, this contribution can have important consequences on spectra and spin structure of wavefunction. However, electron-electron interaction makes problem “many-body” in charac ...
Document
... any measurement of an object without disturbing it. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. • The only quantity that can be known is the probability for an electron to occupy a ...
... any measurement of an object without disturbing it. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. • The only quantity that can be known is the probability for an electron to occupy a ...
Quantum Theory
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
Lecture 17
... Cautionary Note In our derivation of the first-order formula for the shift in energy induced by a perturbation, we assumed that there were no degeneracies in the energy eigenvalue spectrum and noted that the method could break down in the presence of degeneracies. • In general, when considering the ...
... Cautionary Note In our derivation of the first-order formula for the shift in energy induced by a perturbation, we assumed that there were no degeneracies in the energy eigenvalue spectrum and noted that the method could break down in the presence of degeneracies. • In general, when considering the ...
Lecture 4
... crystal lattice. In these collisions energy between the particles and the lattice is exchanged. This is modeled by the creation and destruction of pseudo particles (phonons). In crystals this is by far the most important collision mechanism (more frequent than particle - particle collisions). The en ...
... crystal lattice. In these collisions energy between the particles and the lattice is exchanged. This is modeled by the creation and destruction of pseudo particles (phonons). In crystals this is by far the most important collision mechanism (more frequent than particle - particle collisions). The en ...
PowerPoint - Subir Sachdev
... The superfluid density evolves smoothly from large values at small U/t, to small values at large U/t, and there is no quantum phase transition at any intermediate value of U/t. (In systems with Galilean invariance and at zero temperature, superfluid density=density of bosons always, independent of t ...
... The superfluid density evolves smoothly from large values at small U/t, to small values at large U/t, and there is no quantum phase transition at any intermediate value of U/t. (In systems with Galilean invariance and at zero temperature, superfluid density=density of bosons always, independent of t ...
primer notes
... tunes down the intensity of light in a double-slit experiment, one does not get a ‘dimmer’ interference pattern, but discrete strikes on the photographic plate and illumination at specific points. That means light is composed of ‘particles’ whose energy and momentum are concentrated in one point whi ...
... tunes down the intensity of light in a double-slit experiment, one does not get a ‘dimmer’ interference pattern, but discrete strikes on the photographic plate and illumination at specific points. That means light is composed of ‘particles’ whose energy and momentum are concentrated in one point whi ...
Entanglement, which-way measurements, and a quantum erasure Christian Ferrari Bernd Braunecker
... focus on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer with only two detectors at the exit instead of the screen used in Young’s twoslit experiment, which corresponds to a continuum of detectors. The Mach–Zehnder interferometer allows us to model the step by step evolution of the state of a quantum particle in the ...
... focus on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer with only two detectors at the exit instead of the screen used in Young’s twoslit experiment, which corresponds to a continuum of detectors. The Mach–Zehnder interferometer allows us to model the step by step evolution of the state of a quantum particle in the ...
Q.M3 Home work 1 Due date 8.11.15 1
... 2)Find a state |Bi that is orthogonal to |Ai. Make sure |Bi is normalized. 3) Express |hi and |si in the {|Ai, |Bi} basis. 4) What are possible outcomes of a hardness measurement on the state |Ai, and with what probability will each occur? 5) Express the hardness operator in the {|Ai, |Bi} basis. ...
... 2)Find a state |Bi that is orthogonal to |Ai. Make sure |Bi is normalized. 3) Express |hi and |si in the {|Ai, |Bi} basis. 4) What are possible outcomes of a hardness measurement on the state |Ai, and with what probability will each occur? 5) Express the hardness operator in the {|Ai, |Bi} basis. ...
Teaching Modern Physics - IMSA Digital Commons
... Add sensors to see which slit the particle passed through – show how interference disappears ...
... Add sensors to see which slit the particle passed through – show how interference disappears ...
Decoherence of matter waves by thermal emission of radiation
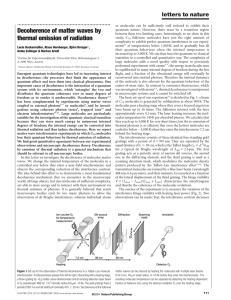
... between these two limiting cases. Interestingly, as we show in this study, C70 fullerene molecules have just the right amount of complexity to exhibit perfect quantum interference in our experiments13 at temperatures below 1,000 K, and to gradually lose all their quantum behaviour when the internal ...
... between these two limiting cases. Interestingly, as we show in this study, C70 fullerene molecules have just the right amount of complexity to exhibit perfect quantum interference in our experiments13 at temperatures below 1,000 K, and to gradually lose all their quantum behaviour when the internal ...
pdf
... this difference can be largely attributed to the instructors’ treatments of topic category B: the photoelectric effect and photons. While both PHYS3 courses had the greatest point totals in this topic area, PHYS3A clearly devoted a greater proportion of lecture time here to addressing themes of inde ...
... this difference can be largely attributed to the instructors’ treatments of topic category B: the photoelectric effect and photons. While both PHYS3 courses had the greatest point totals in this topic area, PHYS3A clearly devoted a greater proportion of lecture time here to addressing themes of inde ...
- IMSA Digital Commons
... Add sensors to see which slit the particle passed through – show how interference disappears ...
... Add sensors to see which slit the particle passed through – show how interference disappears ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.