Why is Maxwell`s Theory so hard to understand?
... field-strength is the square-root of a joule per cubic meter. A joule is a unit of energy and a meter is a unit of length, but a square-root of a joule is not a unit of anything tangible. There is no way we can imagine measuring directly the square-root of a joule. The unit of electric field-strengt ...
... field-strength is the square-root of a joule per cubic meter. A joule is a unit of energy and a meter is a unit of length, but a square-root of a joule is not a unit of anything tangible. There is no way we can imagine measuring directly the square-root of a joule. The unit of electric field-strengt ...
Quantum Physics 2005 Notes-8 Three-dimensional Schrodinger Equation Notes 8
... In chemistry, we designate the l=0 case as s, l=1 as p, l=2 as d, and l=3 as f. Note the ml does not affect the energy of a state because it does not appear in the radial equation. ...
... In chemistry, we designate the l=0 case as s, l=1 as p, l=2 as d, and l=3 as f. Note the ml does not affect the energy of a state because it does not appear in the radial equation. ...
Band-trap capture and emission in the generalized kinetic theory of
... which do not preserve necessarily momentum and kinetic energy [8], [9], [10]. For generality, particles or quasi–particles are allowed to obey general statistics, in order to possibly include non–standard or non–extensive effects [11]. We shall follow the lines of a recent paper [12], in which a gen ...
... which do not preserve necessarily momentum and kinetic energy [8], [9], [10]. For generality, particles or quasi–particles are allowed to obey general statistics, in order to possibly include non–standard or non–extensive effects [11]. We shall follow the lines of a recent paper [12], in which a gen ...
Why an Antenna Radiates
... We see in Fig 4 a snapshot of the coulomb field near the antenna. This picture shows an instant in time when the right-hand half of the antenna is positively charged and the left-hand half is negatively charged, as a result of a process that we'll examine in a moment. A half-cycle later, the polari ...
... We see in Fig 4 a snapshot of the coulomb field near the antenna. This picture shows an instant in time when the right-hand half of the antenna is positively charged and the left-hand half is negatively charged, as a result of a process that we'll examine in a moment. A half-cycle later, the polari ...
Higher-order energy level spacing distributions in the transition
... accepted that the Brody distribution is a good approximation for high-energy spectra of mixed systems. In Prosen (1995) and Prosen and Robnik (1994) it is argued that the Brody distribution only describes the so-called ‘near-semiclassical regime’, whereas the so-called ‘far-semiclassical regime’ of ...
... accepted that the Brody distribution is a good approximation for high-energy spectra of mixed systems. In Prosen (1995) and Prosen and Robnik (1994) it is argued that the Brody distribution only describes the so-called ‘near-semiclassical regime’, whereas the so-called ‘far-semiclassical regime’ of ...
H - Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group
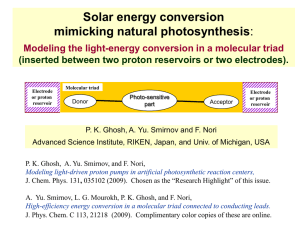
... Modeling light-driven proton pumps in artificial photosynthetic reaction centers, J. Chem. Phys. 131, 035102 (2009). Chosen as the “Research Highlight” of this issue. A. Yu. Smirnov, L. G. Mourokh, P. K. Ghosh, and F. Nori, High-efficiency energy conversion in a molecular triad connected to conducti ...
... Modeling light-driven proton pumps in artificial photosynthetic reaction centers, J. Chem. Phys. 131, 035102 (2009). Chosen as the “Research Highlight” of this issue. A. Yu. Smirnov, L. G. Mourokh, P. K. Ghosh, and F. Nori, High-efficiency energy conversion in a molecular triad connected to conducti ...
Multiparty Quantum Coin Flipping
... In this paper, we focus on quantum coin flipping for more than two players. However, for our multiparty quantum protocols we will first need a new two-party quantum protocol for coin flipping with penalty for cheating. In this problem, players can be heavily penalized for cheating, which will allow ...
... In this paper, we focus on quantum coin flipping for more than two players. However, for our multiparty quantum protocols we will first need a new two-party quantum protocol for coin flipping with penalty for cheating. In this problem, players can be heavily penalized for cheating, which will allow ...
PDF
... problem. According to the model of measurement provided by the quantum formalism, if we let our initial quantum system interact with a macroscopic measurement device we obtain what is known as macroscopic superposition infection: the composite (system + device) goes into a superposition. Formally, t ...
... problem. According to the model of measurement provided by the quantum formalism, if we let our initial quantum system interact with a macroscopic measurement device we obtain what is known as macroscopic superposition infection: the composite (system + device) goes into a superposition. Formally, t ...
Quantum Mechanical Modelling and Optical Spectroscopy of
... events including position, momentum and energy. Therefore we speak instead of expectation values. The uncertainty ingrained in quantum theory describes the probabilistic nature of events involving these particles. The magnitude of this uncertainty is given by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle δxδ ...
... events including position, momentum and energy. Therefore we speak instead of expectation values. The uncertainty ingrained in quantum theory describes the probabilistic nature of events involving these particles. The magnitude of this uncertainty is given by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle δxδ ...
13. atoms - Sakshi Education
... The theory could not account the spectra of atoms more complex than hydrogen. ...
... The theory could not account the spectra of atoms more complex than hydrogen. ...
Atomic Orbitals - Stephen Berry
... of an electron and not by a moving point-charge, simply because the classical electron would go through many orbits during the event. Phenomena requiring less than lo-" see, say, are not well described by average distributions of charge in atoms. By the same token phenomena involving energies much g ...
... of an electron and not by a moving point-charge, simply because the classical electron would go through many orbits during the event. Phenomena requiring less than lo-" see, say, are not well described by average distributions of charge in atoms. By the same token phenomena involving energies much g ...
Is the Zero-Point Energy Real? - General Guide To Personal and
... modes of the field up to the cut-off Λ. If this is set at the Planck mass, Λ ∼ mP lanck ∼ 1019 GeV , then given the current upper bound on the cosmological constant λ < 10−29 g/cm3 ∼ (10−11 GeV )4 , the observed value is more than 120 orders of magnitude smaller than we expect. If the contribution f ...
... modes of the field up to the cut-off Λ. If this is set at the Planck mass, Λ ∼ mP lanck ∼ 1019 GeV , then given the current upper bound on the cosmological constant λ < 10−29 g/cm3 ∼ (10−11 GeV )4 , the observed value is more than 120 orders of magnitude smaller than we expect. If the contribution f ...
Quantum entanglement, topological order, and tensor category theory
... |ΦSF � = all conf. � = direct-product state → unentangled state (classical) - Superfluid, as an exemplary quantum state of matter, is actually very classical and unquantum from entanglement point of view. ...
... |ΦSF � = all conf. � = direct-product state → unentangled state (classical) - Superfluid, as an exemplary quantum state of matter, is actually very classical and unquantum from entanglement point of view. ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.