SNAP-IV Teacher and Parent Rating Scale
... Conners Questionnaire (Loney and Milich, 1985). The IOWA was developed using divergent validity to separate items which measure inattention/overactivity (I/ O — items #4, #8, #11, #31, #32) from those items which measure aggression/defiance (A/D — items #21, #23, #29, #34, #35). The Conners Index (i ...
... Conners Questionnaire (Loney and Milich, 1985). The IOWA was developed using divergent validity to separate items which measure inattention/overactivity (I/ O — items #4, #8, #11, #31, #32) from those items which measure aggression/defiance (A/D — items #21, #23, #29, #34, #35). The Conners Index (i ...
A Review of Postpartum Psychosis Review
... women with childbearing-related onset of psychosis frequently experienced cognitive disorganization and unusual psychotic symptoms. These were often mood-incongruent delusions of reference, persecution, jealousy, and grandiosity,4,6,11 along with visual, tactile, or olfactory hallucinations that sug ...
... women with childbearing-related onset of psychosis frequently experienced cognitive disorganization and unusual psychotic symptoms. These were often mood-incongruent delusions of reference, persecution, jealousy, and grandiosity,4,6,11 along with visual, tactile, or olfactory hallucinations that sug ...
Slide 1
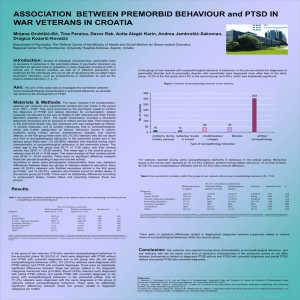
... Materials & Methods: The study included 415 compensationseeking war veterans who experienced combat and war stress in the period from 1991 – 1995. They were examined by the psychiatric expert to confirm the diagnosis of PTSD and related disorders for compensation- related purposes, as required by th ...
... Materials & Methods: The study included 415 compensationseeking war veterans who experienced combat and war stress in the period from 1991 – 1995. They were examined by the psychiatric expert to confirm the diagnosis of PTSD and related disorders for compensation- related purposes, as required by th ...
Conversion Disorder in the Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology 2
... a few of these patients are referred for additional psychiatric evaluation, it remains unknown how many of these patients meet the diagnostic criteria for conversion disorder. Prevalence rates are higher in rural and lower socio-economic groups, and conversion disorder is more common in females than ...
... a few of these patients are referred for additional psychiatric evaluation, it remains unknown how many of these patients meet the diagnostic criteria for conversion disorder. Prevalence rates are higher in rural and lower socio-economic groups, and conversion disorder is more common in females than ...
Eliminating the Stigma of Mental Illness in the Schools
... A serious mental illness that interferes with a person's ability to think clearly, distinguish reality from fantasy, manage emotions, make decisions and relate to others. ...
... A serious mental illness that interferes with a person's ability to think clearly, distinguish reality from fantasy, manage emotions, make decisions and relate to others. ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Barriers to obtaining an accurate diagnosis Common Psychiatric Diagnosis in Autism Role of Functional Behavior Assessments in differentiating diagnoses Treating the Underlying Syndrome: The Process Monitoring / Tracking response to medications Ways to present mental health information to the treatin ...
... Barriers to obtaining an accurate diagnosis Common Psychiatric Diagnosis in Autism Role of Functional Behavior Assessments in differentiating diagnoses Treating the Underlying Syndrome: The Process Monitoring / Tracking response to medications Ways to present mental health information to the treatin ...
Prevalence, Pathogenesis, and Diagnosis of Depressive Disorders
... • Depression co-occurring with medical illness may increase psychosocial impairment and impair adherence to medical treatment and rehabilitation • Suicide rates higher among the physically ill than general population (e.g., end-stage renal disease, cancer, AIDS) • Depression in the physically ill ca ...
... • Depression co-occurring with medical illness may increase psychosocial impairment and impair adherence to medical treatment and rehabilitation • Suicide rates higher among the physically ill than general population (e.g., end-stage renal disease, cancer, AIDS) • Depression in the physically ill ca ...
Mood Disorders
... • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close relationships often precede depression • With each new generation, depression is striking earlier and affecting more people ...
... • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close relationships often precede depression • With each new generation, depression is striking earlier and affecting more people ...
Functions - E
... 1.Explain the Factors affecting mental health Studies of the significant causes and processes involved in the development of mental illness have found that there are physical, social, environmental and psychological causes for mental illness. Physical causes are those which are biological in nature. ...
... 1.Explain the Factors affecting mental health Studies of the significant causes and processes involved in the development of mental illness have found that there are physical, social, environmental and psychological causes for mental illness. Physical causes are those which are biological in nature. ...
Advances in Diagnosis, Neurobiology, and Treatment of Mood
... distinguishing grief from a major depressive episode (MDE), it is useful to consider that in grief the predominant affect is feelings of emptiness and loss, while in MDE it is persistent depressed mood and the inability to anticipate happiness or pleasure. The dysphoria in grief is likely to decreas ...
... distinguishing grief from a major depressive episode (MDE), it is useful to consider that in grief the predominant affect is feelings of emptiness and loss, while in MDE it is persistent depressed mood and the inability to anticipate happiness or pleasure. The dysphoria in grief is likely to decreas ...
Understanding the DSM-5
... practitioners and researchers: Better understand the diagnostic language they are using Identify future directions for an improved nosology Better understand the DSM’s strengths and limitations For example, many of the diagnostic criteria are not based on empirical research but on expert con ...
... practitioners and researchers: Better understand the diagnostic language they are using Identify future directions for an improved nosology Better understand the DSM’s strengths and limitations For example, many of the diagnostic criteria are not based on empirical research but on expert con ...
Document
... A. Performance in daily activities that require motor coordination is substantially below that expected given the person's chronological age and measured intelligence. This may be manifested by marked delays in achieving motor milestones (e.g., walking, crawling, sitting), dropping things, "clumsine ...
... A. Performance in daily activities that require motor coordination is substantially below that expected given the person's chronological age and measured intelligence. This may be manifested by marked delays in achieving motor milestones (e.g., walking, crawling, sitting), dropping things, "clumsine ...
Coexisting Disorders in Children
... destructive behaviour, deceitfulness, and rule violation. Co-occurrence of ADHD and CD in adolescents is often a precursor of antisocial behaviours, nicotine use, substance use or abuse, anxiety or depression, and development of antisocial personality disorder as adults. These coexisting conditi ...
... destructive behaviour, deceitfulness, and rule violation. Co-occurrence of ADHD and CD in adolescents is often a precursor of antisocial behaviours, nicotine use, substance use or abuse, anxiety or depression, and development of antisocial personality disorder as adults. These coexisting conditi ...
Bipolar Disorder
... depression throughout the course of their lives although they may have periods when they are free of symptoms. About 33% of people have residual symptoms even between manic and depressive episodes, and some people have persistent symptoms that don’t respond well to medications. The course of the dis ...
... depression throughout the course of their lives although they may have periods when they are free of symptoms. About 33% of people have residual symptoms even between manic and depressive episodes, and some people have persistent symptoms that don’t respond well to medications. The course of the dis ...
How are medications used to treat mental disorders?
... Below is a summary of information about the medications most commonly used to treat major mental illness. This information is excerpted from the website of the National Institute of Mental Health. You can find more detailed information at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/mental-health-med ...
... Below is a summary of information about the medications most commonly used to treat major mental illness. This information is excerpted from the website of the National Institute of Mental Health. You can find more detailed information at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/mental-health-med ...
GLOssARY
... Dependence is a substance use disorder and was measured in relation to alcohol and four separate categories of drugs (cannabis, stimulants, sedatives and opioids). It is characterised by tolerance to the effects of the substance, withdrawal symptoms if use of the substance is stopped or cut back and ...
... Dependence is a substance use disorder and was measured in relation to alcohol and four separate categories of drugs (cannabis, stimulants, sedatives and opioids). It is characterised by tolerance to the effects of the substance, withdrawal symptoms if use of the substance is stopped or cut back and ...
Other Conditions That May Be a Focus of Clinical Attention
... DSM-5 is striving to be more etiological-however disorders are caused by a complex interaction of multiple factors and various etiological factors can present with the same symptom pattern The diagnostic groups have been reshuffled There is a dimensional component to the categories to be further res ...
... DSM-5 is striving to be more etiological-however disorders are caused by a complex interaction of multiple factors and various etiological factors can present with the same symptom pattern The diagnostic groups have been reshuffled There is a dimensional component to the categories to be further res ...
What are Mental Disorders?
... • Heredity A person may inherit a tendency toward a mental disorder. • Early Experiences Extremely negative experiences that occur early in life can lead to mental illness. • Recent Experiences Some mental health experts think that recent experiences are more likely than early experiences to trigger ...
... • Heredity A person may inherit a tendency toward a mental disorder. • Early Experiences Extremely negative experiences that occur early in life can lead to mental illness. • Recent Experiences Some mental health experts think that recent experiences are more likely than early experiences to trigger ...
Chapter 8
... – “Fear of fear” is often viewed as the key feature of panic disorder • Behavioral inhibition and shy temperament – An enduring tendency to respond to unfamiliar events with anxiety – Relative stability of socially inhibited behavior from the first years of life until adulthood is consistent with th ...
... – “Fear of fear” is often viewed as the key feature of panic disorder • Behavioral inhibition and shy temperament – An enduring tendency to respond to unfamiliar events with anxiety – Relative stability of socially inhibited behavior from the first years of life until adulthood is consistent with th ...
Folie a Deux Versus Genetically Driven Delusional Disorder: Case
... unknown. This might be due to the fact that the phenomenon “delusion” is not uniform and monocausal, but rather a symptom of varying pathophysiologic mechanisms. Folie a deux (FD), or shared psychotic disorder, is a rare psychiatric condition in which an “inducer” (primary patient), who is the “orig ...
... unknown. This might be due to the fact that the phenomenon “delusion” is not uniform and monocausal, but rather a symptom of varying pathophysiologic mechanisms. Folie a deux (FD), or shared psychotic disorder, is a rare psychiatric condition in which an “inducer” (primary patient), who is the “orig ...
Randye Huron Keeping Current Autism 2015
... to specific sounds or textures, excessive smelling or touching of objects, visual fascination with lights or movement) ...
... to specific sounds or textures, excessive smelling or touching of objects, visual fascination with lights or movement) ...
Psychological Disorders
... Examples of positive symptoms are hallucinations, delusions, thought disorders, and bizarre behaviors. Negative symptoms include cognitive, emotional, and behavioral deficits. Examples of negative symptoms are apathy, flattened affect, social withdrawal, inattention, and slowed speech or no speech. ...
... Examples of positive symptoms are hallucinations, delusions, thought disorders, and bizarre behaviors. Negative symptoms include cognitive, emotional, and behavioral deficits. Examples of negative symptoms are apathy, flattened affect, social withdrawal, inattention, and slowed speech or no speech. ...
Session 2: MH Classifications - Listen, Acknowledge, Respond
... • anxiety and depression are commonly associated with the above symptoms and signs, • and suicidal ideation is not infrequent. • The onset follows the trauma with a latency period that may range from a few weeks to ...
... • anxiety and depression are commonly associated with the above symptoms and signs, • and suicidal ideation is not infrequent. • The onset follows the trauma with a latency period that may range from a few weeks to ...
Abnormal Quiz Overivew
... B) replace controversial, theoretical concepts with behavioral terms. C) explain theoretical concepts in more detail. D) replace the term neurosis with the classification anxiety disorders. ...
... B) replace controversial, theoretical concepts with behavioral terms. C) explain theoretical concepts in more detail. D) replace the term neurosis with the classification anxiety disorders. ...
Memory
... – There is usually a main personality present, with a variety of “subpersonalities” – Some personalities may be aware of one another, while others may not – Approximately 99% of those suffering with D.I.D. have experienced physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, as well as neglect during early childh ...
... – There is usually a main personality present, with a variety of “subpersonalities” – Some personalities may be aware of one another, while others may not – Approximately 99% of those suffering with D.I.D. have experienced physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, as well as neglect during early childh ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.