neurological syndromes which can be mistaken for
... upsets, drugs, and infections, for example, are particularly associated with ‘‘delirium’’ or confusional states, with prominent impairment of attention, while slowly progressive pathologies are more often responsible for ‘‘chronic brain syndromes’’, such as dementia (table 1). c Site—Several more or ...
... upsets, drugs, and infections, for example, are particularly associated with ‘‘delirium’’ or confusional states, with prominent impairment of attention, while slowly progressive pathologies are more often responsible for ‘‘chronic brain syndromes’’, such as dementia (table 1). c Site—Several more or ...
Assessment and Diagnosis of DSM-5 Substance
... desire to continue use of substance to reduce unpleasant symptoms has physiological/cognitive consequences significant distress in social and occupational functioning symptoms are not attributed to another medical or mental disorder ...
... desire to continue use of substance to reduce unpleasant symptoms has physiological/cognitive consequences significant distress in social and occupational functioning symptoms are not attributed to another medical or mental disorder ...
Personality Disorders
... – We all may get depressed in our daily lives, but people who suffer from mood disorders tend to experience more intense—and particularly more intense negative—moods. – The most common symptom of mood disorders is negative mood. ...
... – We all may get depressed in our daily lives, but people who suffer from mood disorders tend to experience more intense—and particularly more intense negative—moods. – The most common symptom of mood disorders is negative mood. ...
Psych_Disorders_12
... Medical Perspective Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. George Wesley Bellows, Dancer in a Madhouse, 1907. © 1997 The Art Institute of Chicago ...
... Medical Perspective Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. George Wesley Bellows, Dancer in a Madhouse, 1907. © 1997 The Art Institute of Chicago ...
MENTAL HEALTH
... Often people with personality disorders don’t recognize that there is a problem until it involves others. Treatment is difficult. Group or family therapy: This approach is helpful in drawing attention to behaviors by one that are causing distress in others. Genetics has shown to be linked in peo ...
... Often people with personality disorders don’t recognize that there is a problem until it involves others. Treatment is difficult. Group or family therapy: This approach is helpful in drawing attention to behaviors by one that are causing distress in others. Genetics has shown to be linked in peo ...
Dissociative amnesia, Dissociative Fugue, DID
... of abuse, a medication) or a general medical condition (e.g. temporal lobe epilepsy). The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupation, or other important areas of functioning. ...
... of abuse, a medication) or a general medical condition (e.g. temporal lobe epilepsy). The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupation, or other important areas of functioning. ...
Bipolar Disorder
... Bipolar disorder was formerly known as manic depressive disorder. The words “depression” and “mania” have their origins in Ancient Greek. Hippocrates (460-337 B.C.) was the first to systematically describe mania and depression. In prehippocratic Greece the theory of the four bodily fluids essentiall ...
... Bipolar disorder was formerly known as manic depressive disorder. The words “depression” and “mania” have their origins in Ancient Greek. Hippocrates (460-337 B.C.) was the first to systematically describe mania and depression. In prehippocratic Greece the theory of the four bodily fluids essentiall ...
A Look into the Treatment, 1 Running head: A LOOK INTO THE
... The psychotherapist has to distinguish between the primary and secondary disorders. Which disorder do they treat first? According to Mulsow (2007) a disorder can be “chronologically secondary, regardless of the nature of the relationships between the primary and secondary disorders” (pg 128). A psyc ...
... The psychotherapist has to distinguish between the primary and secondary disorders. Which disorder do they treat first? According to Mulsow (2007) a disorder can be “chronologically secondary, regardless of the nature of the relationships between the primary and secondary disorders” (pg 128). A psyc ...
Pervasive Developmental Disorders
... developmental delays – Evaluation and follow-up of “at risk” children – Multidisciplinary coordinated interagency model – IFSP: family is central focus of service – Services to be provided in “natural environment” ...
... developmental delays – Evaluation and follow-up of “at risk” children – Multidisciplinary coordinated interagency model – IFSP: family is central focus of service – Services to be provided in “natural environment” ...
Other Specified and Unspecified Disorders
... before admission. Notification of unscheduled treatment (including Emergency admissions) should occur as soon as is reasonably possible. In the event that the Mental Health/Substance Use Disorder Designee is not notified of home-based outpatient treatment, benefits may be reduced. Check the member’s ...
... before admission. Notification of unscheduled treatment (including Emergency admissions) should occur as soon as is reasonably possible. In the event that the Mental Health/Substance Use Disorder Designee is not notified of home-based outpatient treatment, benefits may be reduced. Check the member’s ...
Mental health and nursing home residents
... three, four or five stages. But in fact the course of the illness is more like a downward slope. • Many dementia patients are more confused in the evening (sundowner syndrome) but, overall, a resident with dementia’s level of functioning will not change too much minute by minute, or hour by hour. ...
... three, four or five stages. But in fact the course of the illness is more like a downward slope. • Many dementia patients are more confused in the evening (sundowner syndrome) but, overall, a resident with dementia’s level of functioning will not change too much minute by minute, or hour by hour. ...
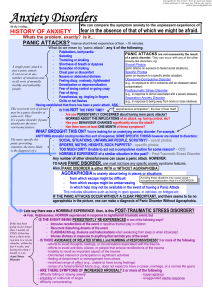
Anxiety Disorders - Deranged Physiology
... Avoiding these situations may cause social + - from which escape might be difficult occupational dysfunction; thus it’s a DISORDER - from which escape might be embarrassing - in which help may not be available in the event of having a Panic Attack This includes situations such as being in open space ...
... Avoiding these situations may cause social + - from which escape might be difficult occupational dysfunction; thus it’s a DISORDER - from which escape might be embarrassing - in which help may not be available in the event of having a Panic Attack This includes situations such as being in open space ...
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Curr Opin Psychiatry
... of later personality disorder. It is not uncommon that clinicians use the term emerging personality disorder (most often of the borderline type) to describe some adolescents with severe irritability. The relationship between irritability, variation in personality, and what is described as personalit ...
... of later personality disorder. It is not uncommon that clinicians use the term emerging personality disorder (most often of the borderline type) to describe some adolescents with severe irritability. The relationship between irritability, variation in personality, and what is described as personalit ...
DBSA Uni_Bipolar.v2:DBSA FindADocFinal
... mood stabilizers prevent, or delay, future episodes of depression, hypomania or mania. Often, other medications like traditional antidepressants are also necessary. But for some people with bipolar disorder, taking a traditional antidepressant alone, or along with a mood stabilizer, can make the ill ...
... mood stabilizers prevent, or delay, future episodes of depression, hypomania or mania. Often, other medications like traditional antidepressants are also necessary. But for some people with bipolar disorder, taking a traditional antidepressant alone, or along with a mood stabilizer, can make the ill ...
psychosis in childhood and its management
... may be considered to have ‘‘borderline syndrome of childhood’’ (40), and then later ‘‘schizotypal disorder of childhood’’ was considered (38). In 1986, Cohen et al. suggested the term multiplex developmental disorder and proposed that this condition was best understood as a developmental deviation w ...
... may be considered to have ‘‘borderline syndrome of childhood’’ (40), and then later ‘‘schizotypal disorder of childhood’’ was considered (38). In 1986, Cohen et al. suggested the term multiplex developmental disorder and proposed that this condition was best understood as a developmental deviation w ...
Treating Depression and Anxiety in the Geriatric Patient
... cognitive decline, medical illness, medications, substance use including caffeine and ETOH Be sure to screen for suicidal ideation: comorbid depression/anxiety increase suicide risk ...
... cognitive decline, medical illness, medications, substance use including caffeine and ETOH Be sure to screen for suicidal ideation: comorbid depression/anxiety increase suicide risk ...
SFR20_01 Gordon and Redish
... symptoms in 30–70% of patients with schizophrenia (Miyamoto et al. 2002; Lieberman et al. 2005); antidepressants induce remission in 35–40% of patients with major depressive disorder and significant improvement in 50–60% (Rush et al. 2006a). Furthermore, since there is a good inter-rater reliability ...
... symptoms in 30–70% of patients with schizophrenia (Miyamoto et al. 2002; Lieberman et al. 2005); antidepressants induce remission in 35–40% of patients with major depressive disorder and significant improvement in 50–60% (Rush et al. 2006a). Furthermore, since there is a good inter-rater reliability ...
RTI/MTSS Universal Screening - Psych-PLC
... academic or occupational performance, or with activities of daily living, as confirmed by individually administered standardized achievement measures and comprehensive clinical assessment. For individuals age 17 years and older, a documented history of impairing learning difficulties may be substitu ...
... academic or occupational performance, or with activities of daily living, as confirmed by individually administered standardized achievement measures and comprehensive clinical assessment. For individuals age 17 years and older, a documented history of impairing learning difficulties may be substitu ...
Anxiety Disorders - NAMI
... Everyone knows what it's like to feel anxious-the "butterflies" in your stomach before that first date, the "jitters" before giving a speech, the sweaty palms or racing heartbeat that often accompany challenging or dangerous situations. These feelings are normal. But what if you were to find yoursel ...
... Everyone knows what it's like to feel anxious-the "butterflies" in your stomach before that first date, the "jitters" before giving a speech, the sweaty palms or racing heartbeat that often accompany challenging or dangerous situations. These feelings are normal. But what if you were to find yoursel ...
Assessment and Diagnosis of Dissociative Identity Disorder
... past events and thoughts, and/or present and anticipated ones as well. It has a sense of its own identity and ideation, and a capacity for initiating thought processes and action. ...
... past events and thoughts, and/or present and anticipated ones as well. It has a sense of its own identity and ideation, and a capacity for initiating thought processes and action. ...
ASD and pscyhosis the overlap - Royal College of Psychiatrists
... early childhood and anxiety in early adolescence with new school, but settled and did well. • After school at 18 moves on to college in town centre. Here anxious, hallucinates briefly and admitted to hospital where quickly recovers with antipsychotics. Clearly shaken by experience but keen to achiev ...
... early childhood and anxiety in early adolescence with new school, but settled and did well. • After school at 18 moves on to college in town centre. Here anxious, hallucinates briefly and admitted to hospital where quickly recovers with antipsychotics. Clearly shaken by experience but keen to achiev ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... lower socioeconomic groups. – Depression prevalence varies across cultures ...
... lower socioeconomic groups. – Depression prevalence varies across cultures ...
jAnxiety Disorders - Dr. Ameneh Mirzael 2009
... • life time prevalence: 12.5% • most common mental d/o in women & 2nd most common d/o in men (after substancerelated d/o) • F:M = 2:1 • start at a young age (5-12 years) ...
... • life time prevalence: 12.5% • most common mental d/o in women & 2nd most common d/o in men (after substancerelated d/o) • F:M = 2:1 • start at a young age (5-12 years) ...
Psychiatric Terminology
... ii. Characterized by at least 2 years of hypomania and numerous depressive episodes that do not meet the criteria that defines a major depressive episode d. Depressive disorders: marked by occurrence of one or more major depressive episodes without a history of mania or hypomania e. Major depression ...
... ii. Characterized by at least 2 years of hypomania and numerous depressive episodes that do not meet the criteria that defines a major depressive episode d. Depressive disorders: marked by occurrence of one or more major depressive episodes without a history of mania or hypomania e. Major depression ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.