The Reproductive Health Implications of Depression. (2011)
... Therapy seems to provide protection against relapse or recurrence 90% who have had 3 episodes will have recurrence w/o lifelong pharmacotherapy ...
... Therapy seems to provide protection against relapse or recurrence 90% who have had 3 episodes will have recurrence w/o lifelong pharmacotherapy ...
Chapter 6.Teacher 1. Depression is
... c) Psychomotor retardation d) All of the above (A) 75. Hopelessness is an expectation that: a) Positive outcomes will not occur b) Negative outcomes will occur c) The individual has no responses available that will change this state of affairs d) All of the above (A) 76. Studies that have examined H ...
... c) Psychomotor retardation d) All of the above (A) 75. Hopelessness is an expectation that: a) Positive outcomes will not occur b) Negative outcomes will occur c) The individual has no responses available that will change this state of affairs d) All of the above (A) 76. Studies that have examined H ...
Depression
... Learning Objectives 1. Understand the various anxiety disorders , Depression and how each disorder presents 2. Understand the treatment strategies for each disorder 3. Understand the signs and symptoms of each disorder 4. Understand the consequences to the health care system of anxiety and depressi ...
... Learning Objectives 1. Understand the various anxiety disorders , Depression and how each disorder presents 2. Understand the treatment strategies for each disorder 3. Understand the signs and symptoms of each disorder 4. Understand the consequences to the health care system of anxiety and depressi ...
Axis I comorbidity in bipolar disorder with psychotic features.
... psychotic symptoms either were secondary to acute intoxication or withdrawal from alcohol or other substances or were presenting with concomitant severe medical conditions defined according to Black et a1 (1998) as any serious or acute life-threatening illness such as cancer, myocardial infarction, ...
... psychotic symptoms either were secondary to acute intoxication or withdrawal from alcohol or other substances or were presenting with concomitant severe medical conditions defined according to Black et a1 (1998) as any serious or acute life-threatening illness such as cancer, myocardial infarction, ...
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY (PAPER II) B Sc COUNSELING PSYCHOLOGY VI SEMESTER
... Strong correlation between closeness of blood relationship ...
... Strong correlation between closeness of blood relationship ...
Childhood Bipolar Disorder
... What happens to these children over time? What is the treatment for children with BP? ...
... What happens to these children over time? What is the treatment for children with BP? ...
Criteria for ADD/ADHD
... prior documentation may have been useful in determining appropriate services in the past, current documentation must validate the need for services based on the individual’s present level of functioning I the educational setting. A school plan such ass an Individualized Education Program (IEP) or a ...
... prior documentation may have been useful in determining appropriate services in the past, current documentation must validate the need for services based on the individual’s present level of functioning I the educational setting. A school plan such ass an Individualized Education Program (IEP) or a ...
Randomised controlled trial of early detection and cognitive therapy
... There is a consensus among clinicians that psychotic disorders can be conceptualised using stress vulnerability models, which suggest that inherited vulnerabilities interact with environmental factors to produce psychosis (Zubin & Spring, 1977; Neuchterlein & Dawson, 1984). These models are consiste ...
... There is a consensus among clinicians that psychotic disorders can be conceptualised using stress vulnerability models, which suggest that inherited vulnerabilities interact with environmental factors to produce psychosis (Zubin & Spring, 1977; Neuchterlein & Dawson, 1984). These models are consiste ...
Newsletter of
... workers in the U.S. to diagnose mental illness, the DSM is an important factor in our mental health system. The manual often influences what type of care people get (or should get), how practitioners are reimbursed, and how people diagnosed with mental illness view themselves and their recoveries. W ...
... workers in the U.S. to diagnose mental illness, the DSM is an important factor in our mental health system. The manual often influences what type of care people get (or should get), how practitioners are reimbursed, and how people diagnosed with mental illness view themselves and their recoveries. W ...
Disruptive Disorders Help! - School Based Behavioral Health
... Oppositional Defiant Disorder • Average age of onset is 6 years old, symptoms can be seen in children as early as 3 years old3 • Symptoms usually manifests by 8 years old, with most children diagnosed during preadolesence1 • Children with ODD have a significantly higher rate of having more that one ...
... Oppositional Defiant Disorder • Average age of onset is 6 years old, symptoms can be seen in children as early as 3 years old3 • Symptoms usually manifests by 8 years old, with most children diagnosed during preadolesence1 • Children with ODD have a significantly higher rate of having more that one ...
A Brief Overview of the New DSM 5 With Ethical Citations
... symptomology. The new format provides more precision so that the reader has a clear and comprehensive picture of the client. Diagnostic criteria are almost less important than factors that led to the issue in the first place. Because the DSM now defines mental disorder as “A syndrome characterized b ...
... symptomology. The new format provides more precision so that the reader has a clear and comprehensive picture of the client. Diagnostic criteria are almost less important than factors that led to the issue in the first place. Because the DSM now defines mental disorder as “A syndrome characterized b ...
t\bnormal Practice Test
... and worrying about whether his business would still be open next week despite the fact that his business was evidencing its highest profit ever. Jim's condition would most likely be diagnosed as a. major depression b. a phobic disorder c. generalized anxiety disorder d. a minor psychotic break 33. C ...
... and worrying about whether his business would still be open next week despite the fact that his business was evidencing its highest profit ever. Jim's condition would most likely be diagnosed as a. major depression b. a phobic disorder c. generalized anxiety disorder d. a minor psychotic break 33. C ...
Steinberg – Medication Management of Behaviors in RCFEs
... Off-label use does not mean inappropriate use. Some offlabel use is absolutely appropriate. Treat people like you would want your own family members to be treated—but be mindful that not everyone will agree on specific treatment plans, etc. ...
... Off-label use does not mean inappropriate use. Some offlabel use is absolutely appropriate. Treat people like you would want your own family members to be treated—but be mindful that not everyone will agree on specific treatment plans, etc. ...
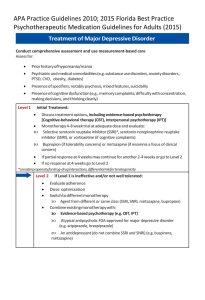
Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder with Psychosis
... Minimal evidence for treating major depressive disorder (MDD) with mixed features Discuss treatment options, including evidence-based psychotherapy [Cognitivebehavioral therapy (CBT), Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT)] Consider second generation antipsychotic (SGA) or mood stabilizer (e.g. lithium) ...
... Minimal evidence for treating major depressive disorder (MDD) with mixed features Discuss treatment options, including evidence-based psychotherapy [Cognitivebehavioral therapy (CBT), Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT)] Consider second generation antipsychotic (SGA) or mood stabilizer (e.g. lithium) ...
to - Owokoniran Memorial Hospital Limited
... of a life-threatening emergency. Always involve law enforcement personnel when you are called to assist a patient with a severe behavior or psychiatric crisis. • If a patient poses an immediate threat, leave the area until law enforcement personnel secure the scene. • Underlying causes of behavioral ...
... of a life-threatening emergency. Always involve law enforcement personnel when you are called to assist a patient with a severe behavior or psychiatric crisis. • If a patient poses an immediate threat, leave the area until law enforcement personnel secure the scene. • Underlying causes of behavioral ...
Mood (affective) disorders (F30-F39)
... significant mood disturbance, and has not done so for several months. Periods of remission during prophylactic treatment should be coded here. F32 Depressive episode In typical mild, moderate, or severe depressive episodes, the patient suffers from lowering of mood, reduction of energy, and decrease ...
... significant mood disturbance, and has not done so for several months. Periods of remission during prophylactic treatment should be coded here. F32 Depressive episode In typical mild, moderate, or severe depressive episodes, the patient suffers from lowering of mood, reduction of energy, and decrease ...
DSM-Ill Diagnoses and Offenses in Committed Female Juvenile
... had a remission of conduct disorder symptoms following antidepressant response to a tricyclic. Second. the accompanying psychiatric disorders may not be etiologic but instead contributory to the exacerbation of preexisting antisocial behavior. Third. even if there is no etiologic relationship betwee ...
... had a remission of conduct disorder symptoms following antidepressant response to a tricyclic. Second. the accompanying psychiatric disorders may not be etiologic but instead contributory to the exacerbation of preexisting antisocial behavior. Third. even if there is no etiologic relationship betwee ...
Statement of Principles concerning ACUTE STRESS DISORDER No
... days to one month after trauma exposure. Symptoms typically begin immediately after the trauma, but persistence for at least three days and up to one month is needed to meet disorder criteria; and The disturbance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other ...
... days to one month after trauma exposure. Symptoms typically begin immediately after the trauma, but persistence for at least three days and up to one month is needed to meet disorder criteria; and The disturbance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other ...
ADHD information
... Whilst the fundamental diagnostic criteria for ADHD have not changed in the DSM5TM compared with the previous version, the DSM-5TM has been updated to more accurately characterize the experience of adolescents and adults with ADHD. This has been achieved with the inclusion of additional examples to ...
... Whilst the fundamental diagnostic criteria for ADHD have not changed in the DSM5TM compared with the previous version, the DSM-5TM has been updated to more accurately characterize the experience of adolescents and adults with ADHD. This has been achieved with the inclusion of additional examples to ...
volition1
... horizons here. That the performance of x might be perceived by the subject to lead to a diminution of the desired state not currently realized whilst in immediate and longer-term horizons might actually contribute to an elevated sense of the psychic discomfit of that current state not being able to ...
... horizons here. That the performance of x might be perceived by the subject to lead to a diminution of the desired state not currently realized whilst in immediate and longer-term horizons might actually contribute to an elevated sense of the psychic discomfit of that current state not being able to ...
Anxiety Disorders - Texas Christian University
... Specific Phobia-marked and persistent fear that is excessive or unreasonable cued by the presence or anticipation of a specific object or situation. Social Phobia-identical to specific phobia, except must be afraid of social categories. Fear of being humiliated lies at the heart of the disorder. ...
... Specific Phobia-marked and persistent fear that is excessive or unreasonable cued by the presence or anticipation of a specific object or situation. Social Phobia-identical to specific phobia, except must be afraid of social categories. Fear of being humiliated lies at the heart of the disorder. ...
Memory - mphspsych
... depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. Signs include: 1. Lethargy and fatigue 2. Feelings of worthlessness 3. Loss of interest in family & friends 4. Loss of interest in activities ...
... depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. Signs include: 1. Lethargy and fatigue 2. Feelings of worthlessness 3. Loss of interest in family & friends 4. Loss of interest in activities ...
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5
... testing, however, may help prevent situations that often occur now, in which even minimal screening for cognitive deficits is not performed. Research suggests that primary care physicians fail to diagnose minor to moderate dementia at least 50% of the time (McPherson & Schoephoerster, 2012). One rea ...
... testing, however, may help prevent situations that often occur now, in which even minimal screening for cognitive deficits is not performed. Research suggests that primary care physicians fail to diagnose minor to moderate dementia at least 50% of the time (McPherson & Schoephoerster, 2012). One rea ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.