Anxiety Disorders - Partners for Youth with Disabilities
... Stay calm with your mentee and do not pressure them into taking part in activities that make them anxious. Remember that their feelings are real. Be aware that anxiety disorders can translate to physical problems. Create a safe, quiet space for your mentee to get away and calm down if they need to. ...
... Stay calm with your mentee and do not pressure them into taking part in activities that make them anxious. Remember that their feelings are real. Be aware that anxiety disorders can translate to physical problems. Create a safe, quiet space for your mentee to get away and calm down if they need to. ...
Anxiety Disorders FACT SHEET
... little or no actual danger for most people. This fear can be very disabling when it leads to avoidance of objects or situations that may cause extreme feelings of terror, ...
... little or no actual danger for most people. This fear can be very disabling when it leads to avoidance of objects or situations that may cause extreme feelings of terror, ...
Microsoft PowerPoint - DSM-5Dissociative Disorders \252\272\266E
... make the diagnosis: A. One or more neurologic symptoms such as altered voluntary motor, sensory function, cognition, or seizure-like episodes. B. The symptom, after appropriate medical assessment, is found not to be due to a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or a cultural ...
... make the diagnosis: A. One or more neurologic symptoms such as altered voluntary motor, sensory function, cognition, or seizure-like episodes. B. The symptom, after appropriate medical assessment, is found not to be due to a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or a cultural ...
Mania in late life
... seen in 9% of patients with traumatic brain injury, with a preponderance of basal temporal lesions noted in these patients. A positive family history of affective disorder and subcortical atrophy before injury are added risk factors (Shulman 2008). A number of further studies have supported the con ...
... seen in 9% of patients with traumatic brain injury, with a preponderance of basal temporal lesions noted in these patients. A positive family history of affective disorder and subcortical atrophy before injury are added risk factors (Shulman 2008). A number of further studies have supported the con ...
ANALYSIS OF MULTI-INSTRUMENTAL ASSESSMENT OF EATING
... Introduction: The origin and course of eating disorders constitute a multifactorial etiopathology. This is why it is important to consider the psychological, developmental, biological and socio - cultural evaluation of each patient.The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual DSM IV - TR (APA, 1994) distin ...
... Introduction: The origin and course of eating disorders constitute a multifactorial etiopathology. This is why it is important to consider the psychological, developmental, biological and socio - cultural evaluation of each patient.The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual DSM IV - TR (APA, 1994) distin ...
Child and Adolescent Anxiety Disorders
... repeatedly for no apparent reason, often accompanied by intense physical symptoms such as dizziness, abdominal distress, chest pain, pounding heart, and shortness of breath.This is differentiated from a generalized anxiety attack because there’s no apparent reason, and no identifiable worry that bro ...
... repeatedly for no apparent reason, often accompanied by intense physical symptoms such as dizziness, abdominal distress, chest pain, pounding heart, and shortness of breath.This is differentiated from a generalized anxiety attack because there’s no apparent reason, and no identifiable worry that bro ...
Slide 1
... Community orders require people to receive treatment for a mental illness whilst living in the community. People are required to accept treatment including medication and other therapy. Most often these apply to people who have a history of refusing treatment and becoming seriously unwell repeatedly ...
... Community orders require people to receive treatment for a mental illness whilst living in the community. People are required to accept treatment including medication and other therapy. Most often these apply to people who have a history of refusing treatment and becoming seriously unwell repeatedly ...
Understanding Psychiatric Emergencies
... • Avoidant: pattern of social inhibition, feelings of inadequacy, and hypersensitivity to negative evaluation. • Dependent: pattern of submissive and clinging behavior related to an excessive need to be taken care of. • Obsessive-Compulsive: pattern of preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, ...
... • Avoidant: pattern of social inhibition, feelings of inadequacy, and hypersensitivity to negative evaluation. • Dependent: pattern of submissive and clinging behavior related to an excessive need to be taken care of. • Obsessive-Compulsive: pattern of preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, ...
Somatoform Disorders
... According to the fourth edition of Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV), the somatoform disorders are distinguished by physical symptoms suggesting a medical condition, yet the symptoms are not fully explained by the medical condition, by substance use, or by another mental ...
... According to the fourth edition of Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV), the somatoform disorders are distinguished by physical symptoms suggesting a medical condition, yet the symptoms are not fully explained by the medical condition, by substance use, or by another mental ...
Abnormal Psych
... Cluster C: The Anxious-Fearful Personality Disorders Avoidant personality disorder Pervasive anxiety, a sense of inadequacy, and a fear of being criticized, which leads to the avoidance of social interactions and nervousness. Dependent personality disorder: Pervasive selflessness, need to be cared ...
... Cluster C: The Anxious-Fearful Personality Disorders Avoidant personality disorder Pervasive anxiety, a sense of inadequacy, and a fear of being criticized, which leads to the avoidance of social interactions and nervousness. Dependent personality disorder: Pervasive selflessness, need to be cared ...
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
... of the following symptoms must be present for at least six months, and to a degree that is maladaptive: ...
... of the following symptoms must be present for at least six months, and to a degree that is maladaptive: ...
How To Pay for Mental Health Services
... young people are very self-conscious, feel tense, and have a strong need for reassurance. They may complain about stomachaches or other discomforts that do not appear to have any physical cause. ¾ Separation Anxiety Disorder: Children with separation anxiety disorder often have difficulty leaving th ...
... young people are very self-conscious, feel tense, and have a strong need for reassurance. They may complain about stomachaches or other discomforts that do not appear to have any physical cause. ¾ Separation Anxiety Disorder: Children with separation anxiety disorder often have difficulty leaving th ...
The Garety et al. Model of CBT for Psychosis
... • Balance between a non‐colluding yet non‐confrontative style • Viewing the person as a reasonable and rational person attempting to cope with difficult, confusing and distressing experiences “a survivor in the face of adversity” • Interventions are characterised by collaborative empiricism and g ...
... • Balance between a non‐colluding yet non‐confrontative style • Viewing the person as a reasonable and rational person attempting to cope with difficult, confusing and distressing experiences “a survivor in the face of adversity” • Interventions are characterised by collaborative empiricism and g ...
Anxiety Disorders
... G. The fear or avoidance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or a general medical condition and is not better accounted fro by other mental disorder (e.g., Panic Disorder With or Without Agoraphobia, Separation Anxiety Disorder, Body Dy ...
... G. The fear or avoidance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or a general medical condition and is not better accounted fro by other mental disorder (e.g., Panic Disorder With or Without Agoraphobia, Separation Anxiety Disorder, Body Dy ...
Highlights of Changes from DSM-IV-TR to DSM-5
... and family histories of major depressive episodes. It is genetically influenced and is associated with similar personality characteristics, patterns of comorbidity, and risks of chronicity and/or recurrence as non–bereavement-related major depressive episodes. Finally, the depressive symptoms associ ...
... and family histories of major depressive episodes. It is genetically influenced and is associated with similar personality characteristics, patterns of comorbidity, and risks of chronicity and/or recurrence as non–bereavement-related major depressive episodes. Finally, the depressive symptoms associ ...
Abnormal Psychology - Complementary course of BA Sociology/ BA Philosophy - III semester - CUCBCSS 2014 Admn onwards
... remembering commitments as a result of lack of concentration/preoccupation with worry. Appearance looks strained, with increased sweating from the hands, feet, and axillae, and they may be tearful, which can suggest depression. Before a diagnosis of anxiety disorder is made, physicians must rule out ...
... remembering commitments as a result of lack of concentration/preoccupation with worry. Appearance looks strained, with increased sweating from the hands, feet, and axillae, and they may be tearful, which can suggest depression. Before a diagnosis of anxiety disorder is made, physicians must rule out ...
Are Symptom Clusters Explanatory? A Study in Mental Disorders
... (Covell, 2013, emphasis added). In the wake of a mass shooting, it is common for people to cite the shooter’s mental illness in explaining the atrocity (Craghill & Clement, 2015). Consider the most basic form of such explanatory claims: those that appeal to a diagnostic category to explain the prese ...
... (Covell, 2013, emphasis added). In the wake of a mass shooting, it is common for people to cite the shooter’s mental illness in explaining the atrocity (Craghill & Clement, 2015). Consider the most basic form of such explanatory claims: those that appeal to a diagnostic category to explain the prese ...
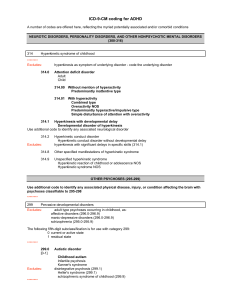
ICD-9-CM coding for ADHD
... Use additional code(s) to identify any associated injuries 995.59 Other child abuse and neglect Multiple forms of abuse Use additional code to identify intent of neglect (E904.0,E968.4) ...
... Use additional code(s) to identify any associated injuries 995.59 Other child abuse and neglect Multiple forms of abuse Use additional code to identify intent of neglect (E904.0,E968.4) ...
Visionary Spiritual Experiences - Spiritual Competency Resource
... Criteria for making the differential diagnosis between VSEs and mental disorders have also been proposed by Agosin,49 Grof and Grof,7 and Lukoff.8 There is considerable overlap among all the proposed criteria. The following four criteria are based on published research on prognostic factors that pre ...
... Criteria for making the differential diagnosis between VSEs and mental disorders have also been proposed by Agosin,49 Grof and Grof,7 and Lukoff.8 There is considerable overlap among all the proposed criteria. The following four criteria are based on published research on prognostic factors that pre ...
Assessment of Substance Use Disorders
... - symptoms have never met criteria for Dependence for this class of substance Failure to fulfill role obligations at school, work, or home (e.g., many absences or poor work performance; neglect of kids) ...
... - symptoms have never met criteria for Dependence for this class of substance Failure to fulfill role obligations at school, work, or home (e.g., many absences or poor work performance; neglect of kids) ...
Lithium genetics
... for a large proportion of bipolar sufferers. Not all patients are so-called ‘lithium responders’ and it has become a task of great importance to be able to establish whether or not a given patient will benefit from lithium treatment. Unfortunately, the fragmentary state of our current understanding ...
... for a large proportion of bipolar sufferers. Not all patients are so-called ‘lithium responders’ and it has become a task of great importance to be able to establish whether or not a given patient will benefit from lithium treatment. Unfortunately, the fragmentary state of our current understanding ...
What is a Personality Disorder?
... People with borderline personality disorder are unstable in several areas, including interpersonal relationships, behavior, mood, and self-image. Abrupt and extreme mood changes, stormy interpersonal relationships, and unstable and fluctuating self-image, unpredictable and self-destructive actions c ...
... People with borderline personality disorder are unstable in several areas, including interpersonal relationships, behavior, mood, and self-image. Abrupt and extreme mood changes, stormy interpersonal relationships, and unstable and fluctuating self-image, unpredictable and self-destructive actions c ...
.5 USING PSYCHIATRIST DSM-I11
... muhiplc, interacting etiological factors: biological, psychological, genetic, environmental, and/or social. In fact, it is widely acknowledged in psychiatry that there is not yet much known about the actual causes of most disorders. Further, though there are some drugs that do act specifically on pa ...
... muhiplc, interacting etiological factors: biological, psychological, genetic, environmental, and/or social. In fact, it is widely acknowledged in psychiatry that there is not yet much known about the actual causes of most disorders. Further, though there are some drugs that do act specifically on pa ...
Chapter 16
... Disorders: Depression and Anxiety Children can be diagnosed with “adult” anxiety disorders (e.g., MDD, OCD, GAD) Specific symptoms may differ from adults Some symptoms may be absent due to children’s developmental differences Difficulty in obtaining reliable information due to problems with ...
... Disorders: Depression and Anxiety Children can be diagnosed with “adult” anxiety disorders (e.g., MDD, OCD, GAD) Specific symptoms may differ from adults Some symptoms may be absent due to children’s developmental differences Difficulty in obtaining reliable information due to problems with ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.