PROLONGED GRIEF DISORDER IN THE DSM-V - trauma-ptsd
... the orderly investigation of the relationship between PGD and other related phenomena. Our overall understanding of PGD has been hampered due to the lack of agreed-upon terminology; thus, inclusion of PGD will encourage convergence on a common set of terms and criteria to better organize and advance ...
... the orderly investigation of the relationship between PGD and other related phenomena. Our overall understanding of PGD has been hampered due to the lack of agreed-upon terminology; thus, inclusion of PGD will encourage convergence on a common set of terms and criteria to better organize and advance ...
Workplace Mental Health Indicators: An EAP`s Perspective
... difficulty concentrating, and recurrent suicidal thoughts and attempts. It is sometimes accompanied by psychotic features (i.e., similar to schizophrenia). Dysthymic Disorder, a less intense but more chronic mood disorder, must be present for two or more years. Adjustment Disorder with Depressed Moo ...
... difficulty concentrating, and recurrent suicidal thoughts and attempts. It is sometimes accompanied by psychotic features (i.e., similar to schizophrenia). Dysthymic Disorder, a less intense but more chronic mood disorder, must be present for two or more years. Adjustment Disorder with Depressed Moo ...
Definition from DSM-5 ®—Understanding Mental Disorders What is
... this form of hoarding. The accumulation of objects can also be the result of persistently avoiding onerous rituals (e.g., not discarding objects in order to avoid endless washing or checking rituals) (Mataix-Cols et al. 2010; Pertusa et al. 2010). In OCD, the behavior is generally unwanted and highl ...
... this form of hoarding. The accumulation of objects can also be the result of persistently avoiding onerous rituals (e.g., not discarding objects in order to avoid endless washing or checking rituals) (Mataix-Cols et al. 2010; Pertusa et al. 2010). In OCD, the behavior is generally unwanted and highl ...
Chapter 12: Psychological Disorders
... characterized by hallucinations and delusions, social withdrawal, and a move away from reality • Organic Mental Disorder: Mental or emotional problem caused by brain pathology (i.e., brain injuries or diseases) • Mood Disorder: Disturbances in affect (emotions), like depression or mania • Anxiety Di ...
... characterized by hallucinations and delusions, social withdrawal, and a move away from reality • Organic Mental Disorder: Mental or emotional problem caused by brain pathology (i.e., brain injuries or diseases) • Mood Disorder: Disturbances in affect (emotions), like depression or mania • Anxiety Di ...
Surveying the Effectiveness of Dialectical Behavioral Therapy on
... Clinical symptoms questionnaire: This researcher-made questionnaire has 16 questions that assesses mental disorders with comorbidity with obesity, like major depression, suicidal tendency, the symptoms of psychosis, dysmorphic disorder. Each component has 4 questions. Scoring conditions are: “never” ...
... Clinical symptoms questionnaire: This researcher-made questionnaire has 16 questions that assesses mental disorders with comorbidity with obesity, like major depression, suicidal tendency, the symptoms of psychosis, dysmorphic disorder. Each component has 4 questions. Scoring conditions are: “never” ...
chapter 4 notes-ppt
... An eating disorder in which a person doesn’t eat enough food to maintain a healthy body weight. An eating disorder in which a person has uncontrolled eating binges followed by purging. An eating disorder in which a person regularly has an uncontrollable urge to eat large amounts of food, but without ...
... An eating disorder in which a person doesn’t eat enough food to maintain a healthy body weight. An eating disorder in which a person has uncontrolled eating binges followed by purging. An eating disorder in which a person regularly has an uncontrollable urge to eat large amounts of food, but without ...
Lesson 9 Powerpoint
... • try to protect others from people’s problems the harmful consequences • try to control other people of their behavior • feel responsible for what • do not meet their other people say or do own needs • seek the approval • avoid living their own of others lives by concentrating on • have difficulty ...
... • try to protect others from people’s problems the harmful consequences • try to control other people of their behavior • feel responsible for what • do not meet their other people say or do own needs • seek the approval • avoid living their own of others lives by concentrating on • have difficulty ...
Cari’s presentation - Richard Adler, M.D
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) ...
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) ...
Read PDF
... psychiatric problems in our culture as it accounts for 12.4% admissions in psychiatric in-patients of Pakistan.13 One of important reasons of this gradual increase in the incidence rate of conversion disorder is our cultural practice of accepting physical symptoms instead of psychological problems.2 ...
... psychiatric problems in our culture as it accounts for 12.4% admissions in psychiatric in-patients of Pakistan.13 One of important reasons of this gradual increase in the incidence rate of conversion disorder is our cultural practice of accepting physical symptoms instead of psychological problems.2 ...
Viktor`s Notes * Schizophrenia
... 4. Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior 5. Negative symptoms (Note: only one of these is required if delusions are bizarre or if hallucinations consist of voice keeping up running commentary on person's behavior or thoughts, or if there are two or more voices conversing with each other) B. Mar ...
... 4. Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior 5. Negative symptoms (Note: only one of these is required if delusions are bizarre or if hallucinations consist of voice keeping up running commentary on person's behavior or thoughts, or if there are two or more voices conversing with each other) B. Mar ...
Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures-neuropsychology as part of the
... DSM V One or more symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function. Clinical findings provide evidence of incompatibility between the symptom and recognized neurological or medical conditions. The symptom or deficit is not better explained by another medical or mental disorder. The symptom or ...
... DSM V One or more symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function. Clinical findings provide evidence of incompatibility between the symptom and recognized neurological or medical conditions. The symptom or deficit is not better explained by another medical or mental disorder. The symptom or ...
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) in DSM-5
... (Anastopoulus et al, 1992), and treatment can create even more stress. Sensitivity to the optimism, self-care, and endurance of the adults is the hallmark of a good therapist of ODD. 4. ODD-JI may be further aggravated by information processing problems, Attention Deficit Disorder, or mismatches in ...
... (Anastopoulus et al, 1992), and treatment can create even more stress. Sensitivity to the optimism, self-care, and endurance of the adults is the hallmark of a good therapist of ODD. 4. ODD-JI may be further aggravated by information processing problems, Attention Deficit Disorder, or mismatches in ...
Obsessive-Compulsive Spectrum Disorder in Darren Aronofsky`s
... and unitary nature of OCD is being re-evaluated. A number of investigators and clinicians have suggested that OCD is a continuum of conditions including compulsive weight control, hypochondriasis, tic disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and trichotillomania and self-harm, as well as "grooming disor ...
... and unitary nature of OCD is being re-evaluated. A number of investigators and clinicians have suggested that OCD is a continuum of conditions including compulsive weight control, hypochondriasis, tic disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and trichotillomania and self-harm, as well as "grooming disor ...
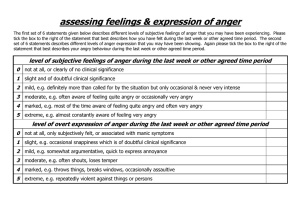
Anger Assessment Questionnaire
... BACKGROUND: This study sought to evaluate the degree of anger and aggression experienced by psychiatric outpatients and to determine whether anger is as prominent an emotional state in these patients as are depression and anxiety. We also sought to determine which Axis I and Axis II disorders were a ...
... BACKGROUND: This study sought to evaluate the degree of anger and aggression experienced by psychiatric outpatients and to determine whether anger is as prominent an emotional state in these patients as are depression and anxiety. We also sought to determine which Axis I and Axis II disorders were a ...
The Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT
... response and outcome in mood disorders? Many studies have found that compared with depressed patients without Axis II comorbidity, patients with PDs have a less complete or delayed response to pharmacotherapy alone42-45 or to pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy together.46 (Not all studies have suppor ...
... response and outcome in mood disorders? Many studies have found that compared with depressed patients without Axis II comorbidity, patients with PDs have a less complete or delayed response to pharmacotherapy alone42-45 or to pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy together.46 (Not all studies have suppor ...
journal - Breining Institute
... systems in the brain, with the neurotransmitter systems most profoundly affected by dependence on the CNS depressants. Anxiety disorder is a far more common problem than was once thought. It can affect people in their teenage years through middle age and later. Anxiety disorder appears to affect twi ...
... systems in the brain, with the neurotransmitter systems most profoundly affected by dependence on the CNS depressants. Anxiety disorder is a far more common problem than was once thought. It can affect people in their teenage years through middle age and later. Anxiety disorder appears to affect twi ...
The Swedish Version of the Ritvo Autism and
... the assumption that autism lies at the upper end of a spectrum of traits which are normally distributed in the population (Baron-Cohen et al. 2001). The AQ comprises 50 items, divided into five domains: (a) social skill, (b) communication, (c) attention switching, (d) attention to detail, and (e) im ...
... the assumption that autism lies at the upper end of a spectrum of traits which are normally distributed in the population (Baron-Cohen et al. 2001). The AQ comprises 50 items, divided into five domains: (a) social skill, (b) communication, (c) attention switching, (d) attention to detail, and (e) im ...
Association between diabetes and mental disorders
... confounding variables like sex, age, socioeconomic status, and marital status has not been considered. Additionally, most of these studies focus on depression rather than anxiety and other mental disorders. However, we believe it is essential to include these other mental disorders into the investig ...
... confounding variables like sex, age, socioeconomic status, and marital status has not been considered. Additionally, most of these studies focus on depression rather than anxiety and other mental disorders. However, we believe it is essential to include these other mental disorders into the investig ...
mash chapter 5
... May be co-morbid with learning disorders, slow processing speed, difficulties with information retrieval, anxiety, and mood disorders d. Some debate as to whether this should be thought of as a separate disorder altogether ...
... May be co-morbid with learning disorders, slow processing speed, difficulties with information retrieval, anxiety, and mood disorders d. Some debate as to whether this should be thought of as a separate disorder altogether ...
Autism Spectrum Disorder in Fragile X Syndrome
... • Reduced interest in and motivation for social interaction or a failure to attend to social information that might promote appropriate social behavior. Consequently, from educational and vocational viewpoints, individuals with FXS who meet criteria for ASD face similar but more severe challenges th ...
... • Reduced interest in and motivation for social interaction or a failure to attend to social information that might promote appropriate social behavior. Consequently, from educational and vocational viewpoints, individuals with FXS who meet criteria for ASD face similar but more severe challenges th ...
sample - Casa Fluminense
... you cannot scan it for bipolar or borderline personality disorders. And even if you could, would you be able to “see” these conditions with any clarity? Symptoms crisscross and overlap. Boundaries blur. Depression and anxiety often coexist with each other and with other conditions, including addicti ...
... you cannot scan it for bipolar or borderline personality disorders. And even if you could, would you be able to “see” these conditions with any clarity? Symptoms crisscross and overlap. Boundaries blur. Depression and anxiety often coexist with each other and with other conditions, including addicti ...
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum disorder is a mental disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be ""not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups"". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively ""severe"" mental disorders through to relatively ""mild and nonclinical deficits"".In some cases, a spectrum approach joins together conditions that were previously considered separately. A notable example of this trend is the autism spectrum, where conditions on this spectrum may now all be referred to as autism spectrum disorders. In other cases, what was treated as a single disorder comes to be seen (or seen once again) as comprising a range of types, a notable example being the bipolar spectrum. A spectrum approach may also expand the type or the severity of issues which are included, which may lessen the gap with other diagnoses or with what is considered ""normal"". Proponents of this approach argue that it is in line with evidence of gradations in the type or severity of symptoms in the general population, and helps reduce the stigma associated with a diagnosis. Critics, however, argue that it can take attention and resources away from the most serious conditions associated with the most disability, or on the other hand could unduly medicalize problems which are simply challenges people face in life.