A Structure for Psychiatry at Century's Turn - The View from Johns Hopkins | by Paul McHugh | Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine | 1992
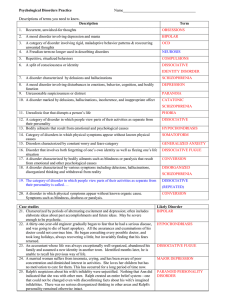
... psychiatric disorders are clearly seen and others are obscured. In combination, they provide a basic structure for psychiatric explanations and illuminate what is pathologic in psychopathology (Table 1). Each perspective is rule governed. Each is unique in its initiating premises, operational guidel ...
... psychiatric disorders are clearly seen and others are obscured. In combination, they provide a basic structure for psychiatric explanations and illuminate what is pathologic in psychopathology (Table 1). Each perspective is rule governed. Each is unique in its initiating premises, operational guidel ...
Current Topics in Complex Post
... could address the array of symptoms frequently observed in people who had endured prolonged, chronic trauma in childhood. The symptoms which were identified as being correlated with such trauma, whether physical abuse, sexual abuse, neglect, war trauma, or any other sustained and totalitarian violat ...
... could address the array of symptoms frequently observed in people who had endured prolonged, chronic trauma in childhood. The symptoms which were identified as being correlated with such trauma, whether physical abuse, sexual abuse, neglect, war trauma, or any other sustained and totalitarian violat ...
Personality
... disorders marked by extreme, longstanding, inflexible personality traits that cause subjective distress or impaired social and occupational functioning. They are not so much severe mental disorders as dysfunctional styles of living. ...
... disorders marked by extreme, longstanding, inflexible personality traits that cause subjective distress or impaired social and occupational functioning. They are not so much severe mental disorders as dysfunctional styles of living. ...
Hypochondria: hypochondriasis
... E. The duration of the disturbance is at least 6 months. F. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by Generalized Anxiety Disorder, ObsessiveCompulsive Disorder, Panic Disorder, a Major Depressive Episode, Separation Anxiety, or another Somatoform Disorder.” ...
... E. The duration of the disturbance is at least 6 months. F. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by Generalized Anxiety Disorder, ObsessiveCompulsive Disorder, Panic Disorder, a Major Depressive Episode, Separation Anxiety, or another Somatoform Disorder.” ...
Workbook Assignment 4 Chapters 12 and 13 to correspond with
... Why did Dr Anderson talk to the wall? (this is part of a lecture and can only be answered after Dr Anderson has given this lecture). ...
... Why did Dr Anderson talk to the wall? (this is part of a lecture and can only be answered after Dr Anderson has given this lecture). ...
AEMT Transition - Unit 22
... • Discuss assessment and strategies for managing a patient with a psychiatric disorder. ...
... • Discuss assessment and strategies for managing a patient with a psychiatric disorder. ...
Issues in child psychopathology
... Determining what is normal and abnormal is an arbitrary process Traditionally defined as a pattern of behavioral, cognitive, or physical symptoms, that is associated with one or more of: ...
... Determining what is normal and abnormal is an arbitrary process Traditionally defined as a pattern of behavioral, cognitive, or physical symptoms, that is associated with one or more of: ...
Slide 1
... and situational types of specific phobias are women – 55 to 70% of individuals with fear of heights and bloodinjection-injury phobias are women (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition) ...
... and situational types of specific phobias are women – 55 to 70% of individuals with fear of heights and bloodinjection-injury phobias are women (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition) ...
Abnormal Psych Syllabus
... Final Exam: (25%) The final exam will be held during finals week. The exact date will be announced later in the semester. The final exam will be in a format similar to the midterm and worth 25 points toward your grade. It will focus on material from the second half of the semester (however, there ma ...
... Final Exam: (25%) The final exam will be held during finals week. The exact date will be announced later in the semester. The final exam will be in a format similar to the midterm and worth 25 points toward your grade. It will focus on material from the second half of the semester (however, there ma ...
Personality Disorders in Adults and Abnormal Behavior in Children
... disorders is characterized by socially disruptive behaviors. Disorders seen under this category include Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), conduct disorder, and oppositional defiant disorder. 6. Anxiety Disorders in childhood—like adults, children can also experience the many different ...
... disorders is characterized by socially disruptive behaviors. Disorders seen under this category include Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), conduct disorder, and oppositional defiant disorder. 6. Anxiety Disorders in childhood—like adults, children can also experience the many different ...
Psychology and You
... DSM-IV, the following descriptions are included: – Essential features—characteristics that define disorder. – Associated features—additional features that are usually present. – Information on differential diagnosis—how to distinguish one disorder from another disorders. – Diagnostic criteria—a list ...
... DSM-IV, the following descriptions are included: – Essential features—characteristics that define disorder. – Associated features—additional features that are usually present. – Information on differential diagnosis—how to distinguish one disorder from another disorders. – Diagnostic criteria—a list ...
8th Edition
... Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
... Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...