MSIV personality disorders v 2012_Dr D Mercer
... happens in their environment – treatment has to help them find ways to : 1.Solve problems causing painful emotions 2.Feel better 3.Tolerate both the situation and how they feel about it without making the situation worse ...
... happens in their environment – treatment has to help them find ways to : 1.Solve problems causing painful emotions 2.Feel better 3.Tolerate both the situation and how they feel about it without making the situation worse ...
Psychobabble 101: Mental Health Professions, Diagnoses, Terminology, and Methods April 17, 2007
... Pervasive Developmental Disorders Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders ...
... Pervasive Developmental Disorders Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders ...
Neuroscience Jeopardy
... Hypersensitivity of senses (light, touch) Large variability in symptoms Not a mental illness ...
... Hypersensitivity of senses (light, touch) Large variability in symptoms Not a mental illness ...
w-36 mental illness - CHILD SUPPORT DIRECTORS ASSOCIATION
... Depression and Professional Competency Some people will experience depression once in awhile and will still be able to do their jobs. For some people, depression can affect various aspects of their lives and have a serious impact on professional competency. Work problems related to depression may i ...
... Depression and Professional Competency Some people will experience depression once in awhile and will still be able to do their jobs. For some people, depression can affect various aspects of their lives and have a serious impact on professional competency. Work problems related to depression may i ...
The DSM-5
... Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders Bipolar and Related Disorders Depressive Disorders Anxiety Disorders Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders Dissociative Disorders Somatic Symptom Disorders Feeding and Eating Disorders Elimination Disord ...
... Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders Bipolar and Related Disorders Depressive Disorders Anxiety Disorders Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders Dissociative Disorders Somatic Symptom Disorders Feeding and Eating Disorders Elimination Disord ...
Chapter Summary/Lecture Organizer I. STUDYING
... C. Classifying Abnormal Behavior - The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) categorizes disorders and provides detailed descriptions useful for communication among professionals. The current DSM-IV-TR is organized according to five major dimensions, called axes, which ar ...
... C. Classifying Abnormal Behavior - The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) categorizes disorders and provides detailed descriptions useful for communication among professionals. The current DSM-IV-TR is organized according to five major dimensions, called axes, which ar ...
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY OF CHILDREN AND FAMILY
... Adjustment Disorders • Is a maladaptive reaction to an identified stressor that develops within a few months of the onset of the stressor • Adjustment disorder is characterized by significant impairment in social, occupational, or academic functioning ...
... Adjustment Disorders • Is a maladaptive reaction to an identified stressor that develops within a few months of the onset of the stressor • Adjustment disorder is characterized by significant impairment in social, occupational, or academic functioning ...
SPED and Psychology Terms
... Autism is one type of Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD). Estimates indicate that it affects 210 of every 10,000 people. Although the causes of autism aren’t yet known, indications are that it is caused by abnormal brain development in early fetal development. It is NOT caused by poor parenting ...
... Autism is one type of Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD). Estimates indicate that it affects 210 of every 10,000 people. Although the causes of autism aren’t yet known, indications are that it is caused by abnormal brain development in early fetal development. It is NOT caused by poor parenting ...
SECTION 7: MENTAL HEALTH Summary: This table is based on the
... was observed in those aged 35 to 44 years (0.7% and 1.1% respectively). The age standardised prevalence of psychotic disorder was significantly higher among black men (3.1%) than men from other ethnic groups (0.2%of white men, no cases observed among men in the South Asian or 'other' ethnic group). ...
... was observed in those aged 35 to 44 years (0.7% and 1.1% respectively). The age standardised prevalence of psychotic disorder was significantly higher among black men (3.1%) than men from other ethnic groups (0.2%of white men, no cases observed among men in the South Asian or 'other' ethnic group). ...
Quick Guide
... Dissociative Disorders Overview of Dissociative Disorders Dissociative Amnesia. The client cannot remember important information that is usually of a personal nature. This is usually stress-related. Dissociative Fugue. The client suddenly travels away from home and cannot remember important details ...
... Dissociative Disorders Overview of Dissociative Disorders Dissociative Amnesia. The client cannot remember important information that is usually of a personal nature. This is usually stress-related. Dissociative Fugue. The client suddenly travels away from home and cannot remember important details ...
Risk Factors in the Individual
... • Relationship to other conditions – is an “at-risk” condition in and of itself – contributes to intensity of other “at-risk” conditions ...
... • Relationship to other conditions – is an “at-risk” condition in and of itself – contributes to intensity of other “at-risk” conditions ...
Dissociative Disorders - Weber State University
... These complaints are not explained by physical illness or injury. Must include four levels of symptoms Four pain symptoms (different areas of body) Two gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, bloating) One sexual symptom (sexual dysfunction / irregularity) One pseudoneurological symptom (sensory lo ...
... These complaints are not explained by physical illness or injury. Must include four levels of symptoms Four pain symptoms (different areas of body) Two gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, bloating) One sexual symptom (sexual dysfunction / irregularity) One pseudoneurological symptom (sensory lo ...
Pediatric and Clinical Child Psychology
... pediatric psychology (child health psychology) A branch of psychology that deals with treating children and adolescents prior to or early in the development of psychopathology. Pediatric psychology referrals often come from pediatricians, and the work is frequently performed in medical settings. Co ...
... pediatric psychology (child health psychology) A branch of psychology that deals with treating children and adolescents prior to or early in the development of psychopathology. Pediatric psychology referrals often come from pediatricians, and the work is frequently performed in medical settings. Co ...
September 12, Schizophrenia
... • “NEITHER DEVIANT BEHAVIOR (E.G. POLITICAL, RELIGIOUS, OR SEXUAL) NOR CONFLICTS BETWEEN THE INDIVIDUAL AND SOCIETY ARE MENTAL DISORDERS UNLESS THE DEVIANCE OR CONFLICT IS A SYMPTOM OF A DYSFUNCTION IN THE INDIVIDUAL.” ...
... • “NEITHER DEVIANT BEHAVIOR (E.G. POLITICAL, RELIGIOUS, OR SEXUAL) NOR CONFLICTS BETWEEN THE INDIVIDUAL AND SOCIETY ARE MENTAL DISORDERS UNLESS THE DEVIANCE OR CONFLICT IS A SYMPTOM OF A DYSFUNCTION IN THE INDIVIDUAL.” ...
Downloadable PowerPoint Presentation
... For nearly half of the children who do receive services, the school was the only provider. Suicide is the 3rd leading cause of death among children ages 10 – 19 Acute psychiatric illness is the single most common and dangerous trigger for suicide. 90% of youth who died by suicide were suffering from ...
... For nearly half of the children who do receive services, the school was the only provider. Suicide is the 3rd leading cause of death among children ages 10 – 19 Acute psychiatric illness is the single most common and dangerous trigger for suicide. 90% of youth who died by suicide were suffering from ...
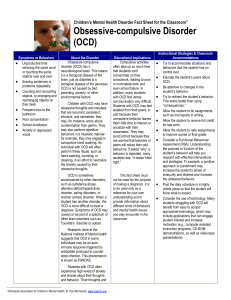
Children`s Mental Health Disorder Fact Sheet for the Classroom
... coexist or be part of a spectrum of other brain disorders such as Tourette’s disorder or autism. Research done at the National Institute of Mental health suggests that OCD in some individuals may be an autoimmune response triggered by antibodies produced to counter strep infection. This phenomenon i ...
... coexist or be part of a spectrum of other brain disorders such as Tourette’s disorder or autism. Research done at the National Institute of Mental health suggests that OCD in some individuals may be an autoimmune response triggered by antibodies produced to counter strep infection. This phenomenon i ...
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
... support the suspicion that a particular client has a mental illness. Response to substance use treatment – Clients with both psychiatric and substance use disorders often have significant difficulty complying with traditional substance use treatment programs and relapse during or shortly after treat ...
... support the suspicion that a particular client has a mental illness. Response to substance use treatment – Clients with both psychiatric and substance use disorders often have significant difficulty complying with traditional substance use treatment programs and relapse during or shortly after treat ...
Ch 12
... Unpredictability: behave erratically and inconsistently at different times or from one situation to another Unconventionality and undesirable behavior: behave in ways that are statistically rare and violate social norms of what is legally or morally acceptable or desirable ...
... Unpredictability: behave erratically and inconsistently at different times or from one situation to another Unconventionality and undesirable behavior: behave in ways that are statistically rare and violate social norms of what is legally or morally acceptable or desirable ...
Asperger syndrome

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome, Asperger disorder (AD) or simply Asperger's, is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development. Although not required for diagnosis, physical clumsiness and atypical (peculiar or odd) use of language are frequently reported. The diagnosis of Asperger's was eliminated in the 2013 fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and replaced by a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder on a severity scale.The syndrome is named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger who, in 1944, studied and described children in his practice who lacked nonverbal communication skills, demonstrated limited empathy with their peers, and were physically clumsy. The modern conception of Asperger syndrome came into existence in 1981 and went through a period of popularization, becoming standardized as a diagnosis in the early 1990s. Many questions and controversies remain about aspects of the disorder. There is doubt about whether it is distinct from high-functioning autism (HFA); partly because of this, its prevalence is not firmly established.The exact cause of Asperger's is unknown. Although research suggests the likelihood of a genetic basis, there is no known genetic cause, and brain imaging techniques have not identified a clear common pathology. There is no single treatment, and the effectiveness of particular interventions is supported by only limited data. Intervention is aimed at improving symptoms and function. The mainstay of management is behavioral therapy, focusing on specific deficits to address poor communication skills, obsessive or repetitive routines, and physical clumsiness. Most children improve as they mature to adulthood, but social and communication difficulties may persist. Some researchers and people with Asperger's have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that it is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured. Globally Asperger's is estimated to affect 31 million people as of 2013.