Suicide Among Veterans with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
... confronted with an event that involved actual or threatened death or serious injury, or a threat to self or others’ physical well-being › Second category: Continuously reliving the traumatic event by dreams, recurrent recollections of the event, flashback episodes, intense psychological distress t ...
... confronted with an event that involved actual or threatened death or serious injury, or a threat to self or others’ physical well-being › Second category: Continuously reliving the traumatic event by dreams, recurrent recollections of the event, flashback episodes, intense psychological distress t ...
Memory - Union County College
... I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be ...
... I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be ...
Somatoform and Dissociative
... Typically occurs following traumatic events. May involve motivated forgetting of events, poor storage of information during events due to overarousal, or avoidance of emotions experience during an event ...
... Typically occurs following traumatic events. May involve motivated forgetting of events, poor storage of information during events due to overarousal, or avoidance of emotions experience during an event ...
Psychological Disorders
... who has no memory of the experience until two days later is experiencing localized amnesia. • Selective amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place in a defined period of time. For example, an abuse victim may recall only some parts of the series of events aro ...
... who has no memory of the experience until two days later is experiencing localized amnesia. • Selective amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place in a defined period of time. For example, an abuse victim may recall only some parts of the series of events aro ...
Chapter 7 Mood Disorders
... –Nearly always accompanied by markedly diminished interest or ability to experience pleasure (anhedonia) from life ...
... –Nearly always accompanied by markedly diminished interest or ability to experience pleasure (anhedonia) from life ...
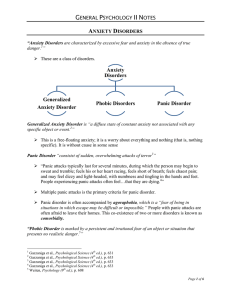
Is it an Anxiety Disorder?
... medical condition or high risk for developing a general medical condition is present, the illness concerns are clearly excessive or disproportionate. The individual's concern is focused not on any physical distress per se, but rather on a suspected, underlying medical diagnosis. C. High level of anx ...
... medical condition or high risk for developing a general medical condition is present, the illness concerns are clearly excessive or disproportionate. The individual's concern is focused not on any physical distress per se, but rather on a suspected, underlying medical diagnosis. C. High level of anx ...
is her diagnosis major depression or sexual repression?
... diagnosis. On the other hand, when the treatment is ineffective than the diagnosis is assumed to be incorrect. In what follows, I present a comprehensive single clinical case study of diagnosis of major depressive disorder in a female patient, thus showing the appropriate diagnosis based on self-rep ...
... diagnosis. On the other hand, when the treatment is ineffective than the diagnosis is assumed to be incorrect. In what follows, I present a comprehensive single clinical case study of diagnosis of major depressive disorder in a female patient, thus showing the appropriate diagnosis based on self-rep ...
DSM 5: TOP 10 Changes Justin K. Hughes, MA, LPC, NCC
... early childhood • Attempts to encourage earlier recognition (within 1-2 years if possible) • If ASD is not realized until beyond childhood, it can still be diagnosed, but only if there is prior criteria ...
... early childhood • Attempts to encourage earlier recognition (within 1-2 years if possible) • If ASD is not realized until beyond childhood, it can still be diagnosed, but only if there is prior criteria ...
Substance
... individual needs and capacity to change Focusing on and treatment of co-morbid mood and anxiety disorders (30-40%) Family-level intervention Counseling and community-level intervention: - motivation to maintain abstinence and prevent relapse – showing the consequences - cope with everyday stress - s ...
... individual needs and capacity to change Focusing on and treatment of co-morbid mood and anxiety disorders (30-40%) Family-level intervention Counseling and community-level intervention: - motivation to maintain abstinence and prevent relapse – showing the consequences - cope with everyday stress - s ...
Etiology of drug use ENG - United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
... – Reduce exposure to the potentially long-term adverse effects of the above etiological conditions, including the early use of drugs itself. ...
... – Reduce exposure to the potentially long-term adverse effects of the above etiological conditions, including the early use of drugs itself. ...
Athletic Goals - Alzheimer's Association
... Language disturbance Difficulty performing motor activities (w/ intact motor ability) ...
... Language disturbance Difficulty performing motor activities (w/ intact motor ability) ...
Achieving Permanency For Children Diagnosed With Reactive
... lying, stealing, fire setting, failure to conform to social norms, irritability, aggressively and impulsivity. These people have little regard for the truth, and lack empathy and remorse. Many of these adults were themselves abused or neglected in early childhood. ...
... lying, stealing, fire setting, failure to conform to social norms, irritability, aggressively and impulsivity. These people have little regard for the truth, and lack empathy and remorse. Many of these adults were themselves abused or neglected in early childhood. ...
The prevalence of the psychiatric disorders in the Endocrinological
... Asberg Depression Rating Scale) and HAMA (Hamilton for Anxiety Rating Scale). The diagnosis of psychiatric disorders was established according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) and DSM-IV-TR (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders). In typical depressive episodes, a ...
... Asberg Depression Rating Scale) and HAMA (Hamilton for Anxiety Rating Scale). The diagnosis of psychiatric disorders was established according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) and DSM-IV-TR (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders). In typical depressive episodes, a ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... most trauma victims • B) most DID patients do not report early abuse • C) trauma victims usually repress memories but do not develop DID • D) none of the above are true ...
... most trauma victims • B) most DID patients do not report early abuse • C) trauma victims usually repress memories but do not develop DID • D) none of the above are true ...
Depressive Disorders - New York Medical College
... fast...like shooting stars you follow until brighter ones appear...all shyness disappears, the right words and gestures are suddenly there...uninteresting people, things, become intensely interesting. Sensuality is pervasive, the desire to seduce and be seduced is irresistible. Your marrow is infuse ...
... fast...like shooting stars you follow until brighter ones appear...all shyness disappears, the right words and gestures are suddenly there...uninteresting people, things, become intensely interesting. Sensuality is pervasive, the desire to seduce and be seduced is irresistible. Your marrow is infuse ...
Mood Disorders - School District of Cambridge
... Global – My explanation applies to many areas of my life ...
... Global – My explanation applies to many areas of my life ...
PSY 220-Abnormal Psychology-Uzma Mazhar
... 2. Identify & apply the current multi‐axial diagnostic & classification system for psychological disorders as listed in the DSM IV‐TR 3. To understand the signs, symptoms, incidence, prevalence, risk factors, etiology, treatment & prognosis of various disorders, providing an integrativ ...
... 2. Identify & apply the current multi‐axial diagnostic & classification system for psychological disorders as listed in the DSM IV‐TR 3. To understand the signs, symptoms, incidence, prevalence, risk factors, etiology, treatment & prognosis of various disorders, providing an integrativ ...
Psyche means mind/soul, "osis“ means abnormal condition or
... A cluster of symptoms which results in “one’s mind playing tricks on that person” constitutes psychosis It is a mental condition where a person’s contact with reality is distorted or lost So a person with psychosis will have 1. Altered thinking and 2.Altered emotions This can lead to Impaired functi ...
... A cluster of symptoms which results in “one’s mind playing tricks on that person” constitutes psychosis It is a mental condition where a person’s contact with reality is distorted or lost So a person with psychosis will have 1. Altered thinking and 2.Altered emotions This can lead to Impaired functi ...
Griggs Chapter 10: Abnormal Psychology
... equally vulnerable Higher incidence in lower socioeconomic groups and for people who are single, separated or divorced rather than married ...
... equally vulnerable Higher incidence in lower socioeconomic groups and for people who are single, separated or divorced rather than married ...
Asperger syndrome

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome, Asperger disorder (AD) or simply Asperger's, is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development. Although not required for diagnosis, physical clumsiness and atypical (peculiar or odd) use of language are frequently reported. The diagnosis of Asperger's was eliminated in the 2013 fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and replaced by a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder on a severity scale.The syndrome is named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger who, in 1944, studied and described children in his practice who lacked nonverbal communication skills, demonstrated limited empathy with their peers, and were physically clumsy. The modern conception of Asperger syndrome came into existence in 1981 and went through a period of popularization, becoming standardized as a diagnosis in the early 1990s. Many questions and controversies remain about aspects of the disorder. There is doubt about whether it is distinct from high-functioning autism (HFA); partly because of this, its prevalence is not firmly established.The exact cause of Asperger's is unknown. Although research suggests the likelihood of a genetic basis, there is no known genetic cause, and brain imaging techniques have not identified a clear common pathology. There is no single treatment, and the effectiveness of particular interventions is supported by only limited data. Intervention is aimed at improving symptoms and function. The mainstay of management is behavioral therapy, focusing on specific deficits to address poor communication skills, obsessive or repetitive routines, and physical clumsiness. Most children improve as they mature to adulthood, but social and communication difficulties may persist. Some researchers and people with Asperger's have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that it is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured. Globally Asperger's is estimated to affect 31 million people as of 2013.