1 against all odds episode 22 – “sampling distributions”
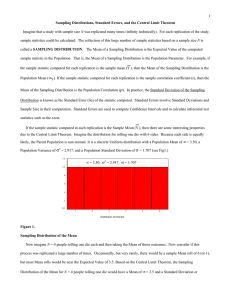
... how, with the right statistical tools, we can use samples from a population to make inferences about the population as a whole. Remember, we get statistics from sample data, while parameters are generally unknown because they describe an entire population. Here’s our population, the nine-year olds a ...
... how, with the right statistical tools, we can use samples from a population to make inferences about the population as a whole. Remember, we get statistics from sample data, while parameters are generally unknown because they describe an entire population. Here’s our population, the nine-year olds a ...
Hypothesis Testing Demonstration 2
... say different from 100, because if the score fell in the upper rejection region it would probably have been produced by sampling from a population with a mean greater than 100. Okay, so we've rejected the H0. Are we correct? We'll never know. However, we can rest assured about some things. For insta ...
... say different from 100, because if the score fell in the upper rejection region it would probably have been produced by sampling from a population with a mean greater than 100. Okay, so we've rejected the H0. Are we correct? We'll never know. However, we can rest assured about some things. For insta ...
Homework 5
... get results to fill in the following tables, you will choose 10,000 samples (this will get samples 10,000 times. Each time, sample of size N is taken and the statistics for the sample computed) so that it will simulate the sampling distribution well. ...
... get results to fill in the following tables, you will choose 10,000 samples (this will get samples 10,000 times. Each time, sample of size N is taken and the statistics for the sample computed) so that it will simulate the sampling distribution well. ...
Probability and Statistical Distributions
... Sampling Distributions (§4.11 - 4.12) • Typically we select sample data from a population in order to compute some statistic of interest. • If we were to take two random samples from the same population, it would be very unlikely that we would find that we have computed the exact same value of the s ...
... Sampling Distributions (§4.11 - 4.12) • Typically we select sample data from a population in order to compute some statistic of interest. • If we were to take two random samples from the same population, it would be very unlikely that we would find that we have computed the exact same value of the s ...